Intro
Learn how to boost sugar levels naturally with effective tips and remedies, managing hypoglycemia symptoms, and balancing blood glucose levels for overall health and wellness.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being. When sugar levels drop, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to serious health issues. Understanding how to boost sugar levels safely and effectively is essential for individuals who experience hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. This article will delve into the importance of managing blood sugar, the causes of low blood sugar, and most importantly, the ways to increase sugar levels when they drop.
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when the glucose levels in the blood fall below a certain threshold, typically below 70 mg/dL. It can be caused by various factors, including skipping meals, taking too much diabetes medication, or engaging in strenuous physical activity without adequate food intake. Recognizing the signs of low blood sugar, such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or even loss of consciousness in severe cases, is vital for prompt intervention.
The management of blood sugar levels is not just about treating low blood sugar when it happens; it's also about adopting lifestyle habits that prevent these episodes. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to medication regimens (for those with diabetes) are foundational. However, when low blood sugar strikes, acting quickly to raise blood glucose levels is critical to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. This can be achieved through the consumption of glucose-rich foods or drinks, which are absorbed quickly into the bloodstream.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
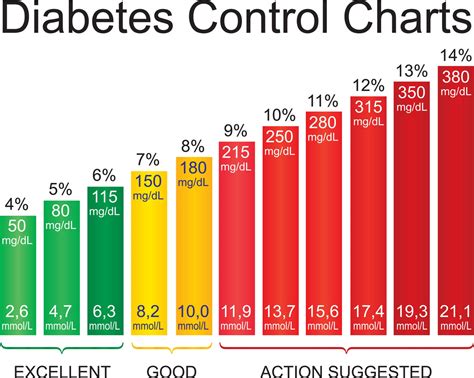
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: - **Diet:** The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed play a significant role. - **Physical Activity:** Regular exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. - **Medications:** Certain medications, especially those for diabetes, can affect how the body regulates blood sugar. - **Stress and Sleep:** Stress and lack of quality sleep can raise blood sugar levels.Ways to Boost Sugar Levels
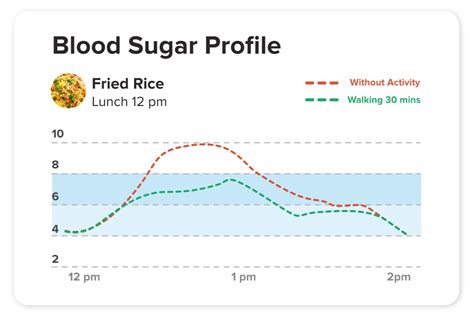
Preventing Low Blood Sugar Episodes
Prevention is always better than cure. To minimize the risk of low blood sugar episodes: - **Eat Regular Meals:** Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar. - **Choose Complex Carbohydrates:** Foods high in fiber and protein can help stabilize blood sugar levels. - **Monitor Blood Sugar:** Regular monitoring, especially for those with diabetes, can help identify trends and patterns. - **Stay Hydrated:** Drinking enough water is essential for overall health and can help manage blood sugar levels.Lifestyle Changes for Better Blood Sugar Management

Importance of Monitoring
For individuals with diabetes or those prone to low blood sugar, monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is vital. It helps in: - **Identifying Patterns:** Understanding how different foods, activities, and medications affect blood sugar. - **Adjusting Treatment Plans:** Based on the data collected, adjustments can be made to diet, exercise, or medication to better manage blood sugar levels. - **Preventing Complications:** Early detection of high or low blood sugar levels can prevent serious health complications.Nutritional Advice for Managing Blood Sugar

Meal Planning for Better Blood Sugar Control
Meal planning can help ensure that blood sugar levels remain stable throughout the day. Consider: - **Eating Small, Frequent Meals:** This can help maintain a steady level of glucose in the blood. - **Including a Balance of Carbohydrates, Protein, and Fat:** This balance can help regulate how quickly glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream. - **Avoiding Skipping Meals:** Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar, especially in individuals with diabetes.Exercises for Blood Sugar Management

Types of Exercises Beneficial for Blood Sugar Control
- **Aerobic Exercises:** Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent for improving cardiovascular health and lowering blood sugar. - **Strength Training:** Building muscle through strength training can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar levels. - **High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):** This form of exercise has been shown to be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar levels.Stress Management Techniques

The Impact of Stress on Blood Sugar
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Managing stress through lifestyle changes and relaxation techniques is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

If you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your feedback and comments are also welcome, as they help us improve and provide more relevant content in the future. Remember, managing blood sugar is a journey, and with the right strategies and support, it's possible to maintain healthy levels and reduce the risk of related complications.
What are the symptoms of low blood sugar?
+Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or even loss of consciousness in severe cases.
How can I quickly raise my blood sugar levels if they drop?
+To quickly raise blood sugar levels, consume glucose-rich foods or drinks like glucose tablets, fruit juice, regular soda, candy, or honey. It's essential to act quickly to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
What lifestyle changes can help manage blood sugar levels?
+Lifestyle changes such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga, and ensuring adequate sleep can significantly improve blood sugar management.
