Intro
The importance of understanding creatinine cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in assessing kidney function and overall health. Creatinine is a waste product that is generated from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue, and it is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. When kidney function is impaired, creatinine levels in the blood can rise, serving as a key indicator of kidney health. In this article, we will delve into the world of creatinine, exploring its significance, how it is measured, and what factors can influence its levels.
As we navigate the complexities of creatinine, it becomes clear that its measurement is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of kidney disease. Healthcare professionals rely on creatinine tests to assess the severity of kidney impairment and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Moreover, understanding creatinine levels can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their kidney health, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions.
The relationship between creatinine and kidney function is intricate, and several factors can impact creatinine levels. For instance, muscle mass, age, and sex can all influence creatinine production, while certain medications and medical conditions can affect kidney function and, in turn, creatinine levels. As we explore the nuances of creatinine, it becomes apparent that a comprehensive understanding of this topic is essential for promoting kidney health and preventing kidney disease.
Understanding Creatinine

Factors Influencing Creatinine Levels
Several factors can influence creatinine levels, including: * Muscle mass: Individuals with greater muscle mass tend to produce more creatinine. * Age: Creatinine levels tend to increase with age, as kidney function declines. * Sex: Men generally have higher creatinine levels than women, due to greater muscle mass. * Diet: A high-protein diet can increase creatinine production, while a low-protein diet may decrease it. * Certain medications: Some medications, such as trimethoprim and cimetidine, can interfere with creatinine excretion. * Medical conditions: Kidney disease, heart failure, and liver disease can all impact creatinine levels.Measuring Creatinine
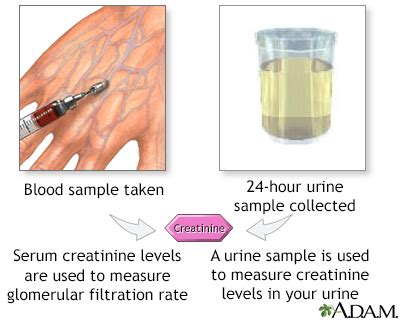
Interpreting Creatinine Test Results
When interpreting creatinine test results, it is essential to consider the individual's overall health and medical history. Elevated creatinine levels may indicate: * Kidney disease or kidney damage * Dehydration * Heart failure * Liver disease * Certain medications or toxinsMaintaining Healthy Creatinine Levels

Practical Tips for Healthy Kidneys
In addition to maintaining healthy creatinine levels, individuals can take practical steps to support kidney health: * Get regular check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help detect kidney disease early. * Monitor blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys, so it is essential to monitor and manage blood pressure. * Limit protein intake: A high-protein diet can put strain on the kidneys, so it is recommended to limit protein intake. * Avoid smoking: Smoking can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease.Creatinine and Kidney Disease
Stages of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is typically classified into five stages, based on creatinine levels and kidney function: * Stage 1: Normal kidney function, with elevated creatinine levels * Stage 2: Mild kidney impairment, with creatinine levels between 1.2 and 1.4 mg/dL * Stage 3: Moderate kidney impairment, with creatinine levels between 1.5 and 2.9 mg/dL * Stage 4: Severe kidney impairment, with creatinine levels between 3.0 and 4.9 mg/dL * Stage 5: Kidney failure, with creatinine levels above 5.0 mg/dLCreatinine and Other Medical Conditions

Managing Creatinine Levels in Medical Conditions
When managing creatinine levels in individuals with other medical conditions, it is essential to consider the underlying condition and develop a comprehensive treatment plan. This may involve: * Medication adjustments: Adjusting medications that may be impacting creatinine levels. * Lifestyle modifications: Encouraging lifestyle modifications, such as increased hydration and balanced diet. * Regular monitoring: Regularly monitoring creatinine levels to assess the effectiveness of treatment.What is the normal range for creatinine levels?
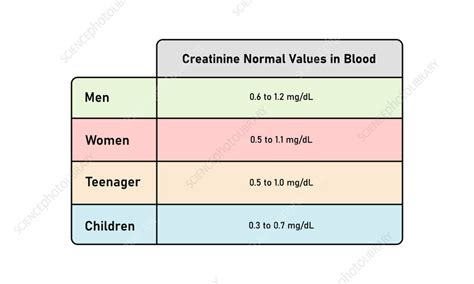
+The normal range for creatinine levels is typically between 0.6 and 1.2 mg/dL for adult men and between 0.5 and 1.1 mg/dL for adult women.
What can cause elevated creatinine levels?
+Elevated creatinine levels can be caused by kidney disease, dehydration, heart failure, liver disease, and certain medications.
How can I lower my creatinine levels?
+To lower creatinine levels, it is essential to address the underlying cause of elevated levels. This may involve managing underlying medical conditions, staying hydrated, and making lifestyle modifications, such as increasing physical activity and maintaining a balanced diet.
In conclusion, understanding creatinine is essential for maintaining kidney health and preventing kidney disease. By recognizing the factors that influence creatinine levels, individuals can take proactive steps to support kidney function and overall well-being. As we continue to explore the complexities of creatinine, it becomes clear that a comprehensive approach to kidney health is crucial for promoting healthy living and preventing disease. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about creatinine and kidney health, and to take action in protecting your kidney function for a healthier tomorrow.
