Intro
Discover 5 ways to diagnose diabetes, including symptoms, blood tests, and risk assessments, to identify type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, and learn about glucose monitoring and insulin resistance.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is essential to diagnose it early to prevent complications. The importance of diagnosing diabetes cannot be overstated, as it allows individuals to take control of their health and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage the condition. In this article, we will explore the different ways to diagnose diabetes, the benefits of early diagnosis, and the steps individuals can take to manage the condition.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects the way the body processes glucose, a type of sugar that is used as energy. When an individual has diabetes, their body either does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates glucose levels, or is unable to use insulin effectively. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a range of symptoms, including increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
The benefits of diagnosing diabetes early are numerous. Early diagnosis allows individuals to take control of their health and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage the condition. This can include changes to diet and exercise, as well as monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. Early diagnosis can also help prevent complications, such as heart disease and kidney damage, which can be costly and debilitating. Furthermore, early diagnosis can help individuals with diabetes to live a long and healthy life, free from the complications associated with the condition.
Understanding Diabetes Diagnosis
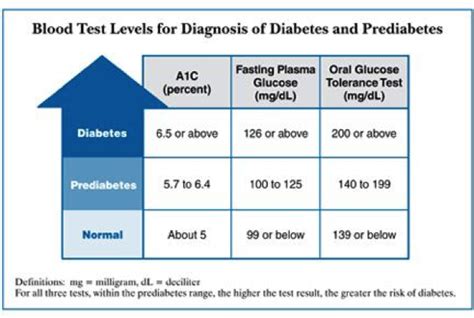
Diabetes diagnosis is a critical step in managing the condition. There are several ways to diagnose diabetes, including blood tests, physical examinations, and medical history. The most common method of diagnosis is through a blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. This test is usually performed after an overnight fast, and the results are used to determine whether an individual has diabetes. Other methods of diagnosis include physical examinations, which can help identify symptoms of diabetes, such as increased thirst and urination, and medical history, which can help identify risk factors for the condition.
5 Ways to Diagnose Diabetes

There are several ways to diagnose diabetes, including:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after consuming a sugary drink.
- Random Plasma Glucose Test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood at any time of day.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: This test measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2-3 months.
- Urine Test: This test measures the level of glucose in the urine.
Benefits of Each Diagnostic Method
Each diagnostic method has its benefits and drawbacks. The Fasting Plasma Glucose Test is a simple and inexpensive test that can be performed in a doctor's office. The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test is a more accurate test that can help diagnose diabetes in individuals who have borderline blood sugar levels. The Random Plasma Glucose Test is a quick and easy test that can be performed at any time of day. The Hemoglobin A1c Test is a useful test for monitoring blood sugar levels over time. The Urine Test is a non-invasive test that can be performed at home.Preparing for a Diabetes Diagnosis

Preparing for a diabetes diagnosis is essential. Individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes should speak with their doctor about their risk factors and schedule a blood test. It is also essential to keep a record of symptoms, such as increased thirst and urination, and to monitor blood sugar levels regularly. Additionally, individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes should make lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, to reduce their risk of developing the condition.
Lifestyle Changes for Diabetes Management
Making lifestyle changes is essential for managing diabetes. This can include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. A healthy diet for diabetes management should include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and should be low in added sugars, saturated fats, and salt. Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly can help individuals with diabetes to identify patterns and make adjustments to their treatment plan.Managing Diabetes

Managing diabetes is a lifelong process. Individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medications, such as insulin or oral medications. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure that the treatment plan is working effectively. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should attend regular check-ups with their healthcare team to monitor for complications and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes can lead to a range of complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Heart disease is a major complication of diabetes, and can be caused by high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Kidney damage is another common complication of diabetes, and can be caused by high blood sugar levels and high blood pressure. Nerve damage is a complication of diabetes that can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.Living with Diabetes

Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it is possible to manage the condition and live a long and healthy life. Individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes and medications. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure that the treatment plan is working effectively. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should attend regular check-ups with their healthcare team to monitor for complications and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Diabetes
Diabetes can have a significant emotional impact on individuals and their families. The diagnosis of diabetes can be overwhelming, and can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and frustration. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to seek support from their healthcare team, family, and friends. Joining a support group or speaking with a counselor can also be helpful in coping with the emotional impact of diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, diagnosing diabetes is a critical step in managing the condition. There are several ways to diagnose diabetes, including blood tests, physical examinations, and medical history. Making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, is essential for managing diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and attending regular check-ups with a healthcare team can help individuals with diabetes to live a long and healthy life, free from the complications associated with the condition. We invite readers to share their experiences with diabetes diagnosis and management, and to ask questions about the topic.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
+The symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
+Diabetes is diagnosed through a blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. Other methods of diagnosis include physical examinations and medical history.
What are the complications of diabetes?
+The complications of diabetes include heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. These complications can be caused by high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
How can diabetes be managed?
+Diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, and medications, such as insulin or oral medications. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and attending regular check-ups with a healthcare team can also help individuals with diabetes to live a long and healthy life.
What is the importance of early diagnosis of diabetes?
+Early diagnosis of diabetes is essential to prevent complications and to improve treatment outcomes. It allows individuals to take control of their health and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage the condition.
