Intro
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a significant health concern worldwide, affecting millions of people and causing a range of gastrointestinal disorders. The bacteria are known to colonize the stomach lining, leading to chronic inflammation, ulcers, and even stomach cancer. Understanding the causes of H. pylori infection is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
H. pylori infection is typically acquired in childhood, and the risk of infection is higher in developing countries where sanitation and hygiene practices are poor. The bacteria can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, and close contact with an infected person. In developed countries, the risk of infection is lower, but it can still occur, particularly in areas with high population density and poor living conditions.
The exact mechanisms of H. pylori transmission are not fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to the spread of the bacteria. These include poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands regularly, especially after using the bathroom or before handling food. Contaminated food and water are also significant sources of H. pylori transmission, as the bacteria can survive in these environments for extended periods.
H. Pylori Infection Risk Factors
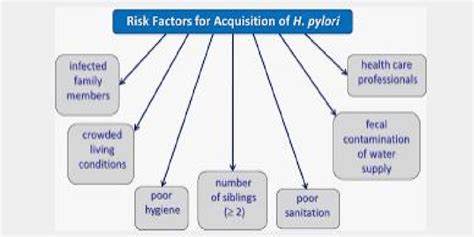
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of acquiring H. pylori infection. These include socioeconomic status, with people from lower-income backgrounds being more likely to be infected. Crowding and poor living conditions also contribute to the spread of the bacteria, as they facilitate close contact between individuals and increase the risk of transmission.
Transmission through Contaminated Food and Water
H. pylori bacteria can contaminate food and water, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. The bacteria can survive in these environments for extended periods, increasing the risk of transmission. Contaminated food and water can be a significant source of H. pylori infection, particularly in developing countries where access to clean water and sanitation facilities is limited.H. Pylori Infection Symptoms
The symptoms of H. pylori infection can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may develop chronic inflammation, ulcers, or stomach cancer. Common symptoms of H. pylori infection include abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea, as well as vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue.
Diagnosis and Treatment of H. Pylori Infection
Diagnosing H. pylori infection typically involves a combination of tests, including endoscopy, blood tests, and stool tests. Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria, as well as medications to reduce stomach acid and alleviate symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat complications such as ulcers or stomach cancer.H. Pylori Infection Prevention Strategies
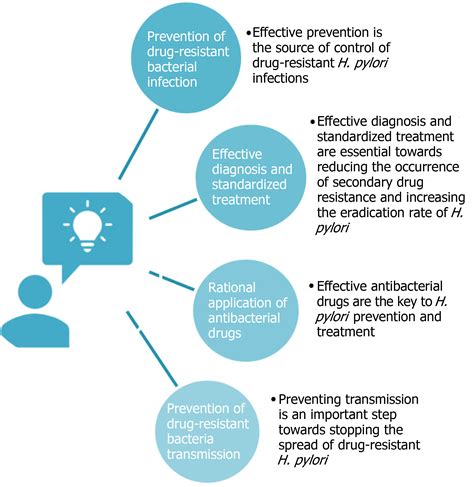
Preventing H. pylori infection requires a combination of good hygiene practices, safe food handling, and access to clean water and sanitation facilities. Regular hand washing, particularly after using the bathroom or before handling food, can help reduce the risk of transmission. Avoiding close contact with people who are infected and avoiding contaminated food and water can also help prevent H. pylori infection.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of H. pylori infection are crucial for preventing long-term complications such as ulcers and stomach cancer. Regular screening and testing can help identify people who are infected, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of transmission.H. Pylori Infection Complications
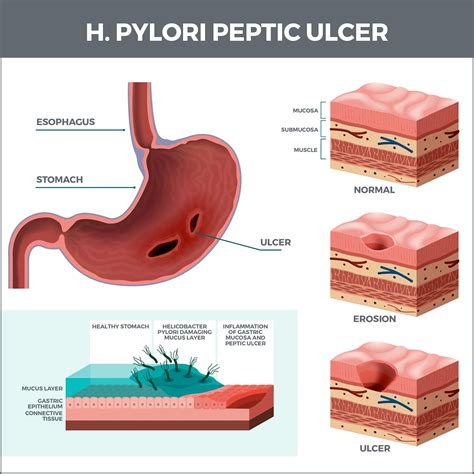
H. pylori infection can lead to a range of complications, including chronic inflammation, ulcers, and stomach cancer. These complications can have significant impacts on quality of life, increasing the risk of disability and death. Early detection and treatment of H. pylori infection are essential for preventing these complications and reducing the burden of the disease.
Current Research and Developments
Current research is focused on developing more effective prevention and treatment strategies for H. pylori infection. This includes the development of new antibiotics and vaccines, as well as improved diagnostic tests and screening programs. Understanding the causes and risk factors of H. pylori infection is crucial for developing targeted interventions and reducing the burden of the disease.H. Pylori Infection Management

Managing H. pylori infection requires a comprehensive approach that includes good hygiene practices, safe food handling, and access to clean water and sanitation facilities. Regular screening and testing can help identify people who are infected, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of transmission.
Public Health Implications
The public health implications of H. pylori infection are significant, with the disease affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes and risk factors of H. pylori infection is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, reducing the burden of the disease, and improving public health outcomes.H. Pylori Infection Future Directions
Future directions for H. pylori infection research and management include the development of more effective prevention and treatment strategies, improved diagnostic tests and screening programs, and increased awareness and education about the disease. Understanding the causes and risk factors of H. pylori infection is crucial for developing targeted interventions and reducing the burden of the disease.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, H. pylori infection is a significant health concern worldwide, affecting millions of people and causing a range of gastrointestinal disorders. Understanding the causes and risk factors of H. pylori infection is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, reducing the burden of the disease, and improving public health outcomes. Recommendations for future research and management include the development of more effective prevention and treatment strategies, improved diagnostic tests and screening programs, and increased awareness and education about the disease.What is H. pylori infection?
+H. pylori infection is a bacterial infection that affects the stomach lining, causing chronic inflammation, ulcers, and stomach cancer.
How is H. pylori infection transmitted?
+H. pylori infection is typically transmitted through contaminated food, water, and close contact with an infected person.
What are the symptoms of H. pylori infection?
+The symptoms of H. pylori infection can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe, and may include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of H. pylori infection causes, symptoms, and management strategies. If you have any further questions or comments, please do not hesitate to share them with us. Your feedback is valuable to us, and we look forward to hearing from you. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards reducing the burden of H. pylori infection and improving public health outcomes.
