Intro
Learn how to prevent impetigo, a highly contagious skin infection, by understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments, including home remedies and antibiotics, to reduce risk of contagion and promote healthy skin habits.
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that can spread quickly, especially among children. It is caused by bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. The infection is characterized by red sores on the skin that can burst and form crusts, and it can be itchy and painful. If left untreated, impetigo can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis or kidney damage.
Impetigo is often spread through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, and it can also be spread through contact with contaminated objects, such as towels, clothing, or toys. The bacteria that cause impetigo can survive on surfaces for long periods, making it easy for the infection to spread. In addition, impetigo can be spread through contact with infected nasal discharge or other bodily fluids. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, are more susceptible to contracting impetigo.
The symptoms of impetigo can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but they often include red, itchy, and painful sores on the skin. The sores can burst and form crusts, and they can be surrounded by a red, inflamed area. In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the face, arms, or legs. If left untreated, impetigo can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis, which is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues. Cellulitis can cause redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area, and it can be treated with antibiotics.
Causes and Risk Factors
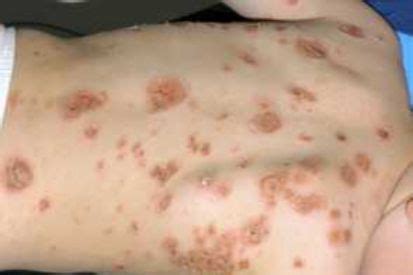
Impetigo is caused by bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. The bacteria can enter the body through a cut or scratch in the skin, and they can multiply quickly, causing an infection. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, are more susceptible to contracting impetigo. Additionally, people who play contact sports, such as football or wrestling, are at a higher risk of contracting impetigo due to the close contact with other players.
Types of Impetigo
There are two main types of impetigo: bullous impetigo and non-bullous impetigo. Bullous impetigo is characterized by large blisters that can burst and form crusts, while non-bullous impetigo is characterized by small, red, itchy sores. Both types of impetigo can be treated with antibiotics, and it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.Symptoms and Diagnosis
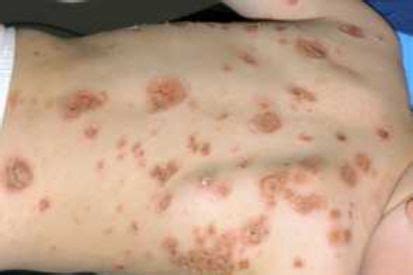
The symptoms of impetigo can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but they often include red, itchy, and painful sores on the skin. The sores can burst and form crusts, and they can be surrounded by a red, inflamed area. In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the face, arms, or legs. A diagnosis of impetigo is typically made based on a physical examination and a review of medical history. A healthcare provider may also take a sample of the infected skin to test for the presence of bacteria.
Treatment Options
Impetigo can be treated with antibiotics, which can help to clear up the infection quickly. In some cases, a topical antibiotic ointment may be prescribed to apply directly to the affected area. It is essential to follow the treatment plan carefully and to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure that the infection is fully cleared. Additionally, it is crucial to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others, to prevent the spread of the infection.Prevention and Complications

Preventing impetigo requires practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others. It is also essential to avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, and to keep wounds clean and covered. If symptoms of impetigo occur, it is crucial to seek medical attention quickly to prevent the spread of the infection. If left untreated, impetigo can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis or kidney damage.
Home Remedies
There are several home remedies that can help to alleviate the symptoms of impetigo, such as applying warm compresses to the affected area or using over-the-counter antibiotic ointments. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any home remedies to ensure that they are safe and effective.Living with Impetigo

Living with impetigo can be challenging, especially if the infection is severe or persistent. However, with proper treatment and self-care, it is possible to manage the symptoms and prevent the spread of the infection. It is essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others, and to follow the treatment plan carefully.
Coping with Impetigo
Coping with impetigo requires a combination of medical treatment and self-care. It is essential to seek medical attention quickly if symptoms occur and to follow the treatment plan carefully. Additionally, practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with others can help to prevent the spread of the infection.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that can spread quickly, especially among children. It is caused by bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. If left untreated, impetigo can lead to more serious complications, such as cellulitis or kidney damage. However, with proper treatment and self-care, it is possible to manage the symptoms and prevent the spread of the infection.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with impetigo in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may be interested in learning more about impetigo.
What is impetigo?
+Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that can spread quickly, especially among children. It is caused by bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces.
How is impetigo treated?
+Impetigo can be treated with antibiotics, which can help to clear up the infection quickly. In some cases, a topical antibiotic ointment may be prescribed to apply directly to the affected area.
Can impetigo be prevented?
+Yes, impetigo can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others. It is also essential to avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, and to keep wounds clean and covered.
