Intro
Learn how to prevent and treat kidney infections with expert tips. Discover symptoms, causes, and natural remedies to reduce risk of kidney disease and urinary tract infections.
Kidney infections, also known as pyelonephritis, are a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that can be painful and potentially serious if left untreated. Understanding how to get kidney infections is crucial in preventing and managing this condition. Kidney infections occur when bacteria, typically from the bladder or urethra, travel up the urinary tract and reach the kidneys.
The importance of understanding kidney infections cannot be overstated, as they can lead to severe complications, including permanent kidney damage, if not properly treated. Factors such as age, sex, and underlying medical conditions can increase the risk of developing a kidney infection. For instance, women are more likely to get kidney infections due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
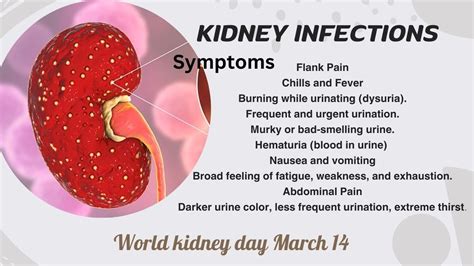
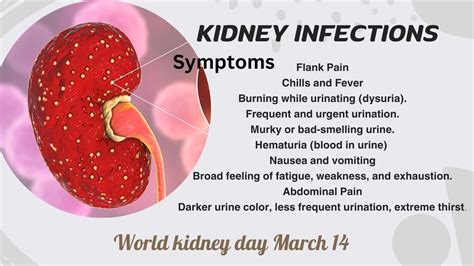
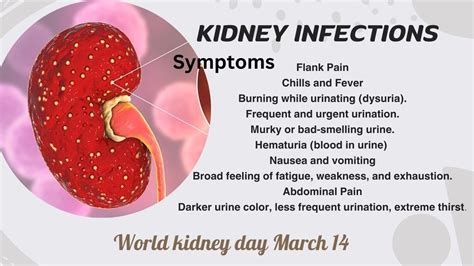
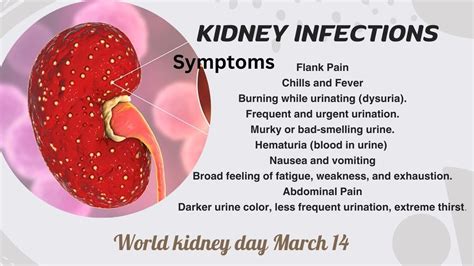
Moreover, individuals with conditions like diabetes, kidney stones, or an enlarged prostate are at a higher risk of developing kidney infections. The symptoms of kidney infections can vary but often include severe back pain, fever, chills, and painful urination. Recognizing these symptoms early on can help in seeking timely medical intervention, which is critical in managing the infection and preventing long-term damage to the kidneys.
Understanding Kidney Infections
For example, practices such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, urinating when the need arises, and staying hydrated can help prevent bacteria from entering and multiplying in the urinary tract. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or those who use catheters are more susceptible to kidney infections and should take extra precautions to maintain urinary tract health.
Risk Factors for Kidney Infections
Certain groups of people are more prone to developing kidney infections due to various risk factors. These include: - Women, due to their anatomy - Older adults, whose immune systems may be weaker - Individuals with diabetes, as high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of infection - People with kidney stones or other obstructions in the urinary tract - Those who use catheters for a prolonged period - Individuals with a weakened immune system due to illness or medicationPrevention Strategies

Treatment Options for Kidney Infections
Treatment for kidney infections usually involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure the patient receives the appropriate care and to monitor for any complications.Symptoms of Kidney Infections
Complications of Untreated Kidney Infections
Untreated kidney infections can lead to serious complications, including: - Permanent kidney damage - Sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream - Kidney failure, in severe cases - Increased risk of future kidney infectionsDiagnosis of Kidney Infections
Managing Kidney Infections at Home
While medical treatment is necessary for kidney infections, there are steps individuals can take at home to help manage their symptoms and support their recovery: - Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids - Using a heating pad to alleviate back pain - Practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection - Getting plenty of rest to help the body fight the infectionLong-term Effects of Kidney Infections
Preventing Recurrent Kidney Infections
To prevent recurrent kidney infections, individuals should: - Follow the prevention strategies mentioned earlier - Take all prescribed antibiotics as directed - Attend follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to ensure the infection has been fully cleared - Consider additional preventative measures, such as taking a daily antibiotic, for those at high risk of recurrent infectionsConclusion and Next Steps

For those who have experienced a kidney infection, it is crucial to follow the treatment plan and take preventative measures to avoid future infections. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a kidney infection, do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Engaging in discussions about kidney health, sharing personal experiences, and educating others on the importance of urinary tract health can also contribute to a community that values and promotes well-being.
What are the common symptoms of kidney infections?
+Kidney infection symptoms can include severe back pain, fever, chills, painful urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
How can I prevent kidney infections?
+Prevention strategies include drinking plenty of water, urinating when needed, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding the use of scented soaps or douches.
What are the complications of untreated kidney infections?
+Untreated kidney infections can lead to permanent kidney damage, sepsis, and kidney failure, emphasizing the importance of timely medical intervention.
