Intro
Heal chemical burns fast with effective treatments and remedies, reducing scarring and promoting wound healing, while minimizing burn pain and inflammation with natural burn care and first aid techniques.
Chemical burns can be extremely painful and potentially disfiguring, making it essential to know how to heal them quickly and effectively. The severity of a chemical burn can vary greatly, depending on the type of chemical involved, the duration of exposure, and the extent of the burn. In this article, we will explore the importance of prompt treatment and provide guidance on how to heal chemical burns fast.
Chemical burns can occur in various settings, including workplaces, homes, and laboratories. They can be caused by a wide range of substances, such as acids, bases, and other corrosive materials. The initial treatment of a chemical burn is crucial in determining the outcome, and it is essential to act quickly to minimize the damage. If you or someone you know has suffered a chemical burn, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately.
The first step in treating a chemical burn is to remove the affected clothing and jewelry, as these can retain the chemical and continue to cause damage. Next, the burn should be rinsed with cool or lukewarm water to help neutralize the chemical and reduce the pain. It is essential to avoid using hot water, as this can activate the chemical and worsen the burn. After rinsing, the burn should be covered with a non-stick dressing or bandage to protect it from further irritation and promote healing.
Understanding Chemical Burns
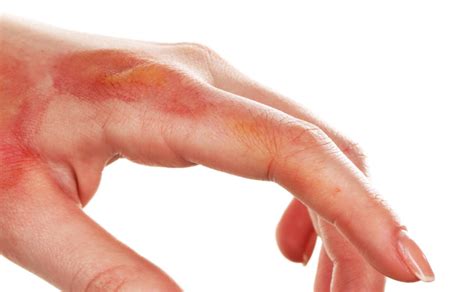
Chemical burns can be classified into different types, depending on the severity of the damage. First-degree chemical burns affect only the outer layer of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Second-degree chemical burns extend into the middle layer of the skin, resulting in blisters, redness, and swelling. Third-degree chemical burns are the most severe, penetrating through all layers of the skin and potentially causing permanent damage.
Causes of Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can be caused by a wide range of substances, including: * Acids, such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid * Bases, such as sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide * Other corrosive materials, such as bleach and ammonia * Chemicals used in cleaning products, such as drain cleaners and oven cleaners * Chemicals used in industrial processes, such as manufacturing and constructionTreatment Options for Chemical Burns

The treatment of chemical burns depends on the severity of the burn and the type of chemical involved. In general, the goals of treatment are to:
- Neutralize the chemical and stop the burning process
- Clean and decontaminate the affected area
- Promote healing and prevent infection
- Manage pain and discomfort
For minor chemical burns, treatment may involve rinsing the affected area with cool or lukewarm water, applying a topical antibiotic ointment, and covering the burn with a non-stick dressing or bandage. For more severe chemical burns, treatment may involve hospitalization, surgical debridement, and the use of specialized dressings and topical treatments.
Home Remedies for Chemical Burns
While medical treatment is essential for chemical burns, there are some home remedies that can help promote healing and reduce discomfort. These include: * Applying a cool compress to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation * Using topical creams or gels, such as aloe vera or silicone, to promote healing and reduce scarring * Taking over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage pain and discomfort * Keeping the affected area clean and dry to prevent infectionPrevention of Chemical Burns

Prevention is key when it comes to chemical burns. To reduce the risk of chemical burns, it is essential to:
- Handle chemicals with care, wearing protective clothing and gloves
- Follow safety instructions and guidelines when working with chemicals
- Keep chemicals out of reach of children and pets
- Use chemicals in well-ventilated areas to prevent inhalation of fumes
- Dispose of chemicals properly, following local regulations and guidelines
Chemical Burn Safety in the Workplace
Chemical burns can occur in various workplaces, including laboratories, manufacturing facilities, and construction sites. To reduce the risk of chemical burns in the workplace, employers should: * Provide training on the safe handling of chemicals * Ensure that employees wear protective clothing and equipment * Implement safety protocols and procedures for handling chemicals * Conduct regular inspections to ensure compliance with safety regulationsComplications of Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can lead to various complications, including:
- Infection: Bacteria can infect the burn, leading to serious complications, such as sepsis and organ failure.
- Scarring: Chemical burns can result in significant scarring, which can be permanent and disfiguring.
- Nerve damage: Chemical burns can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and permanent nerve damage.
- Respiratory problems: Inhaling chemical fumes can lead to respiratory problems, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Long-term Effects of Chemical Burns
The long-term effects of chemical burns can be significant, depending on the severity of the burn and the type of chemical involved. Some potential long-term effects include: * Permanent scarring and disfigurement * Nerve damage and numbness * Respiratory problems and lung damage * Increased risk of skin cancer and other skin conditionsConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, chemical burns can be extremely painful and potentially disfiguring, making it essential to know how to heal them quickly and effectively. By understanding the causes and treatment options for chemical burns, individuals can take steps to prevent these injuries and promote healing. If you or someone you know has suffered a chemical burn, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately and follow the treatment plan recommended by a healthcare professional.
To learn more about chemical burns and how to prevent them, we invite you to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can reduce the risk of chemical burns and promote a safer and healthier environment for everyone.
What are the most common causes of chemical burns?
+Chemical burns can be caused by a wide range of substances, including acids, bases, and other corrosive materials. Common causes of chemical burns include cleaning products, industrial chemicals, and laboratory accidents.
How can I prevent chemical burns in the workplace?
+To reduce the risk of chemical burns in the workplace, employers should provide training on the safe handling of chemicals, ensure that employees wear protective clothing and equipment, and implement safety protocols and procedures for handling chemicals.
What are the long-term effects of chemical burns?
+The long-term effects of chemical burns can be significant, depending on the severity of the burn and the type of chemical involved. Potential long-term effects include permanent scarring and disfigurement, nerve damage and numbness, respiratory problems and lung damage, and increased risk of skin cancer and other skin conditions.
