Intro
Learn how to pop a boil safely with proper techniques, avoiding infection and scarring, using sterile tools and aftercare methods to promote healing and prevent further complications like abscesses or cysts.
Popping a boil can be a tempting solution when dealing with the pain and discomfort it causes, but it's essential to approach this situation with caution. Boils are infections of the skin that can lead to serious complications if not treated properly. Understanding the risks and taking the right steps is crucial to safely manage and treat boils. The importance of proper treatment cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the healing process and prevents potential long-term damage.
Boils are typically caused by bacterial infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common culprit. They can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, and buttocks. The infection starts in the oil glands or hair follicles and can spread to surrounding tissues if left untreated. The symptoms of a boil include a red, painful lump filled with pus, which can grow in size as the infection progresses. It's critical to recognize these symptoms early on to prevent the boil from becoming more severe.
The temptation to pop a boil often arises from the desire to relieve pressure and pain. However, popping a boil can push bacteria deeper into the skin, leading to more severe infections, scarring, and potentially life-threatening conditions like sepsis or meningitis. Instead of resorting to popping, it's vital to understand the proper methods for treating and managing boils safely. This includes applying warm compresses to bring the pus to the surface, using over-the-counter pain relievers, and maintaining good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection. In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary, such as draining the boil or prescribing antibiotics.
Understanding Boils and Their Treatment
To treat boils effectively, it's essential to understand their causes and the various treatment options available. Boils can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor hygiene, infected hair follicles, and certain medical conditions that weaken the immune system. Treatment typically involves promoting drainage of the pus, either through home remedies or medical procedures, and addressing any underlying conditions that may have contributed to the boil's formation. Home remedies include applying warm compresses to the boil several times a day, which helps to bring the pus to the surface and encourage drainage. It's also crucial to keep the boil and surrounding area clean to prevent the spread of infection.
Home Remedies for Boil Treatment
Some of the most effective home remedies for treating boils include: - Applying warm compresses to the affected area - Using antibacterial soap to keep the area clean - Applying tea tree oil, which has natural antibacterial properties - Taking over-the-counter pain relievers to manage discomfortThese remedies can help to manage symptoms and promote healing. However, if the boil does not improve with home treatment, or if it worsens, seeking medical attention is necessary.
Medical Treatment for Boils

In cases where home remedies are not effective, or if the boil is particularly large or severe, medical treatment may be required. This can involve the doctor draining the boil, either by making a small incision or using a needle to aspirate the pus. In some instances, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the underlying bacterial infection. It's vital to follow the doctor's instructions carefully to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Preventing Boils
Prevention is a critical aspect of managing boils. This includes practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and keeping the skin clean, especially in areas prone to boils. Wearing loose, clean clothing can also help to reduce friction and prevent irritation, which can lead to boil formation. Maintaining a healthy diet and managing any underlying medical conditions can also contribute to preventing boils.Surgical Drainage of Boils
In some cases, surgical drainage may be necessary to treat a boil. This procedure involves making a small incision in the boil to allow the pus to drain out. The area is then cleaned and dressed to promote healing. Surgical drainage is typically performed in a doctor's office or clinic and may require local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Aftercare Following Boil Drainage
After a boil has been drained, either through home remedies or medical intervention, proper aftercare is essential to promote healing and prevent infection. This includes keeping the area clean, applying topical antibiotics if prescribed, and changing dressings as directed by a healthcare provider. It's also important to monitor the area for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or fever, and to seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.Complications of Untreated Boils
Untreated boils can lead to serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body, the formation of abscesses, and in rare cases, life-threatening conditions such as sepsis or meningitis. Sepsis occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream, causing a systemic infection that can be fatal if not treated promptly. Meningitis is an infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and can be caused by bacteria from an untreated boil.
Recognizing the Signs of Complications
Recognizing the signs of complications early on is crucial for effective treatment. These signs include increased pain, redness, or swelling around the boil, fever, and general feelings of illness. If any of these symptoms occur, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately.Managing Boil Scars
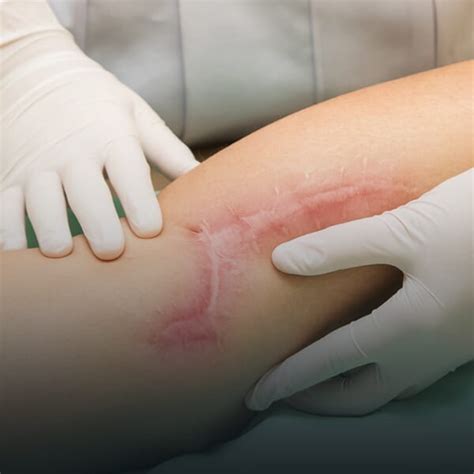
After a boil has healed, it may leave behind a scar. Managing these scars can help to minimize their appearance and promote skin health. This includes using topical creams or gels to reduce the size and color of the scar, protecting the area from the sun to prevent further darkening, and maintaining good skin hygiene to prevent future breakouts.
Preventing Future Boil Formation
Preventing future boil formation is key to maintaining skin health. This includes practicing good hygiene, managing any underlying medical conditions, and avoiding tight clothing that can cause friction and irritation. By taking these steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing boils and promote overall skin well-being.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, popping a boil is not a recommended solution due to the risk of pushing bacteria deeper into the skin and causing more severe infections. Instead, understanding the causes of boils, recognizing their symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, whether through home remedies or medical intervention, is crucial for safe and effective management. By prioritizing skin health and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing boils and promote overall well-being.
We invite readers to share their experiences with boils and their treatments in the comments below. Have you ever had a boil and if so, how did you treat it? What home remedies have you found to be effective? Your insights can help others who are dealing with similar issues. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
What are the common causes of boils?
+Boils are commonly caused by bacterial infections, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, poor hygiene, and infected hair follicles.
How can I treat a boil at home?
+Home treatment for boils includes applying warm compresses to promote drainage, using antibacterial soap to keep the area clean, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers to manage discomfort.
When should I seek medical attention for a boil?
+Seek medical attention if the boil does not improve with home treatment, if it worsens, or if you experience signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, or fever.
