Intro
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It is a bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, which can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission. Therefore, it is essential to get tested for chlamydia if you are sexually active or have had unprotected sex with a new partner. In this article, we will discuss the importance of testing for chlamydia, the different types of tests available, and how to get tested.
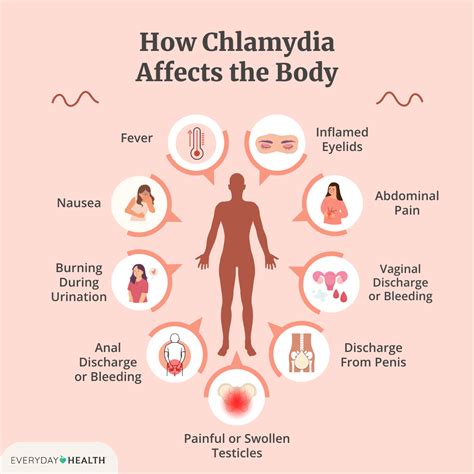
Chlamydia is often referred to as a "silent" infection, as many people who are infected do not experience any symptoms. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), up to 70% of women and 50% of men with chlamydia do not show any symptoms. This makes it difficult to diagnose the infection without a test. However, if symptoms do occur, they may include abnormal vaginal discharge, painful urination, or abdominal pain in women, and discharge from the penis, painful urination, or testicular pain in men.
The importance of testing for chlamydia cannot be overstated. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission. In addition, chlamydia can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy, which is a life-threatening condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Furthermore, chlamydia can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth, which can lead to serious health complications for the baby.
Types of Chlamydia Tests

Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)
NAATs are the most commonly used tests for chlamydia, as they are highly sensitive and can detect the presence of chlamydia DNA in urine or swab samples. These tests involve collecting a sample of urine or cells from the cervix or urethra and using a special machine to amplify the DNA. NAATs can detect the presence of chlamydia even if the person is not showing any symptoms.Cell Cultures
Cell cultures involve collecting a sample of cells from the cervix or urethra and growing them in a laboratory to detect the presence of chlamydia. This test is less commonly used than NAATs, as it is more time-consuming and less sensitive. However, cell cultures can still be used to detect the presence of chlamydia, especially in people who are experiencing symptoms.Serological Tests
Serological tests involve measuring the levels of antibodies against chlamydia in the blood. These tests are less commonly used than NAATs or cell cultures, as they are less sensitive and can take longer to produce results. However, serological tests can still be used to detect the presence of chlamydia, especially in people who are experiencing symptoms.How to Get Tested for Chlamydia

- Make an appointment with your healthcare provider or visit a local clinic that offers STI testing.
- Discuss your sexual history and any symptoms you may be experiencing with your healthcare provider.
- Provide a urine sample or have a swab taken from your cervix or urethra.
- Wait for the test results, which can take anywhere from a few minutes to a few days.
Where to Get Tested for Chlamydia
There are several places where you can get tested for chlamydia, including:- Your healthcare provider's office
- Local clinics that offer STI testing
- Community health centers
- Urgent care centers
- Online testing services
What to Expect During the Test
The chlamydia test is a simple and painless procedure. If you are getting a urine test, you will be asked to provide a urine sample in a cup. If you are getting a swab test, a healthcare provider will insert a swab into your cervix or urethra to collect a sample of cells. The test results will be available within a few minutes to a few days, depending on the type of test used.Treatment and Prevention of Chlamydia
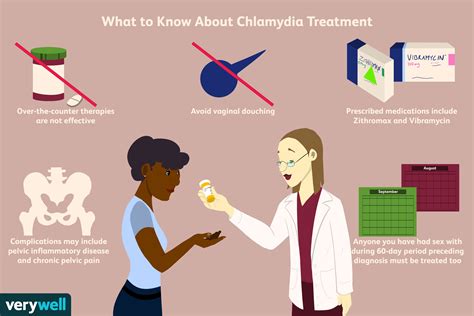
- Take the antibiotics as directed and complete the full course of treatment.
- Avoid having sex until you have completed the treatment and your symptoms have disappeared.
- Use condoms or dental dams during sex to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Get tested regularly for chlamydia and other STIs.
- Practice safe sex and avoid having unprotected sex with new partners.
Complications of Untreated Chlamydia
If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, such as:- Infertility
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Premature birth
Prevention of Chlamydia
The best way to prevent chlamydia is to practice safe sex and avoid having unprotected sex with new partners. Here are some tips for preventing chlamydia:- Use condoms or dental dams during sex.
- Get tested regularly for chlamydia and other STIs.
- Avoid having sex with multiple partners.
- Practice safe sex and avoid having unprotected sex with new partners.
- Get vaccinated against human papillomavirus (HPV), which can reduce the risk of cervical cancer and other health complications.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of testing for chlamydia. If you have any questions or concerns about chlamydia or other STIs, please leave a comment below or contact a healthcare provider for more information.
What is chlamydia?
+Chlamydia is a bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, which can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner.
What are the symptoms of chlamydia?
+The symptoms of chlamydia can include abnormal vaginal discharge, painful urination, or abdominal pain in women, and discharge from the penis, painful urination, or testicular pain in men. However, many people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
How is chlamydia treated?
+Chlamydia is treated with antibiotics, which are prescribed by a healthcare provider. It is essential to take the antibiotics as directed and to complete the full course of treatment, even if your symptoms disappear before you finish the medication.
Can chlamydia be prevented?
+Yes, chlamydia can be prevented by practicing safe sex, getting tested regularly, and avoiding having unprotected sex with new partners. Using condoms or dental dams during sex can also reduce the risk of transmission.
What are the complications of untreated chlamydia?
+If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, increased risk of HIV transmission, ectopic pregnancy, and premature birth.