Intro
Effectively treat pneumonia with targeted therapies, managing symptoms and preventing complications through antibiotics, respiratory support, and holistic approaches, ensuring swift recovery and minimizing risks.
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that affects millions of people worldwide each year. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with compromised immune systems. Despite its severity, pneumonia is a treatable condition, and with prompt and effective treatment, most people can recover fully. In this article, we will delve into the importance of treating pneumonia effectively, exploring the various treatment options, and discussing the key strategies for managing this complex condition.
Pneumonia is a multifaceted disease that can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The most common cause of pneumonia is the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is responsible for approximately 30-50% of all cases. Other common causes of pneumonia include Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Legionella pneumophila. The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common signs and symptoms include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. If left untreated, pneumonia can lead to serious complications, such as respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death.
The importance of treating pneumonia effectively cannot be overstated. Prompt and effective treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. In addition, treating pneumonia effectively can also help to reduce the spread of the disease, as people with untreated pneumonia can transmit the infection to others. Furthermore, effective treatment can also help to reduce the economic burden of pneumonia, which is a significant public health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is one of the most common causes of hospitalization and death worldwide, resulting in significant healthcare costs and lost productivity.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
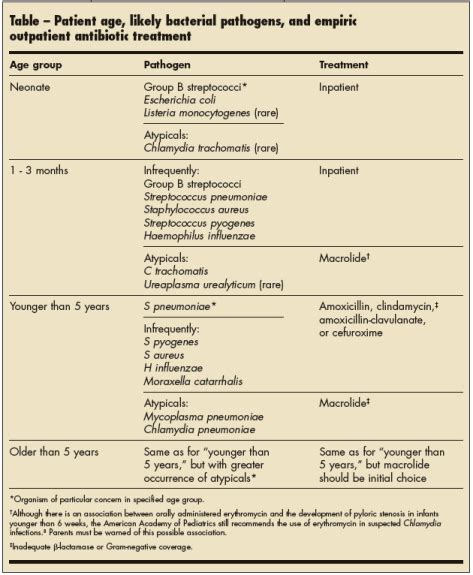
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is the cornerstone of pneumonia treatment. The goal of antibiotic therapy is to eradicate the underlying pathogen, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of pneumonia, as well as the patient's medical history and allergy status. For example, patients with mild pneumonia may be treated with oral antibiotics, such as amoxicillin or azithromycin, while those with severe pneumonia may require intravenous antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone or vancomycin.Managing Pneumonia Symptoms
Preventing Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is a critical aspect of managing this complex condition. Vaccination is a key strategy for preventing pneumonia, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) are two commonly used vaccines that can help prevent pneumonia. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, and avoiding close contact with people who have pneumonia can also help prevent the spread of the disease.Complications of Pneumonia
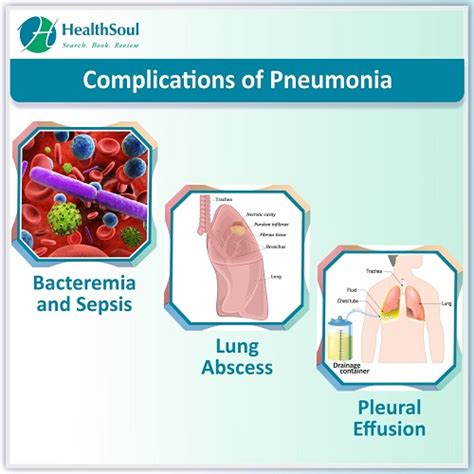
Managing Complications
Managing complications of pneumonia requires prompt and effective treatment. Patients with respiratory failure may require mechanical ventilation, while those with sepsis may require intensive care and supportive therapy. Additionally, patients with long-term complications of pneumonia may require ongoing management and treatment, such as oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation.Pneumonia in Special Populations

Treatment Considerations
Treatment considerations for pneumonia in special populations include the use of age-specific vaccines, such as the PCV and PPSV, and the use of antibiotics that are effective against common pathogens in these populations. Additionally, patients with compromised immune systems may require more aggressive treatment, such as combination antibiotic therapy, to manage pneumonia effectively.Current Research and Developments

Future Directions
Future directions in pneumonia treatment include the development of more effective and targeted therapies, as well as the use of personalized medicine approaches to manage pneumonia. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia, as well as to predict patient outcomes and identify high-risk populations.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with pneumonia treatment in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about pneumonia treatment and management. By working together, we can improve outcomes and reduce the burden of pneumonia worldwide.
What are the most common causes of pneumonia?
+The most common causes of pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Legionella pneumophila.
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
+Pneumonia is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays and blood tests.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
+The symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Can pneumonia be prevented?
+Yes, pneumonia can be prevented through vaccination, good hygiene practices, and avoiding close contact with people who have pneumonia.
What are the complications of pneumonia?
+The complications of pneumonia include respiratory failure, sepsis, and long-term complications, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchiectasis.
