Intro
Discover 5 ways to get strep throat, including close contact, contaminated food, and poor hygiene, and learn about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this bacterial infection, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis.
Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a highly contagious infection caused by the group A Streptococcus bacteria. It is a common illness that affects people of all ages, but it is most prevalent among children and adolescents. The infection can spread quickly, and it is essential to understand the ways it can be transmitted to take preventive measures. In this article, we will discuss the various ways to get strep throat and provide valuable insights into its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Strep throat is a significant health concern, and its impact should not be underestimated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), strep throat affects approximately 10 million people in the United States each year. The infection can lead to severe complications, such as kidney inflammation and rheumatic fever, if left untreated. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of strep throat and seek medical attention promptly.
The transmission of strep throat can occur through various means, and it is essential to be aware of the risks to minimize the chances of infection. The bacteria that cause strep throat can survive on surfaces, clothing, and personal items, making it easy to spread the infection. Moreover, people with strep throat can be contagious for up to 24 hours before symptoms appear, making it challenging to identify the source of the infection.
Understanding Strep Throat Transmission

Strep throat transmission can occur through direct contact with an infected person, contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The bacteria can enter the body through the nose, mouth, or eyes, and it can take 2-5 days for symptoms to appear after exposure. Understanding the transmission dynamics of strep throat is vital to develop effective prevention strategies.
Risk Factors for Strep Throat
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of getting strep throat. These include: * Age: Children and adolescents are more susceptible to strep throat due to their underdeveloped immune systems. * Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive medications, are more prone to strep throat. * Close living quarters: Living in close proximity to others, such as in dormitories or military barracks, can increase the risk of transmission. * Poor hygiene: Failure to practice good hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly, can facilitate the spread of the infection.5 Common Ways to Get Strep Throat
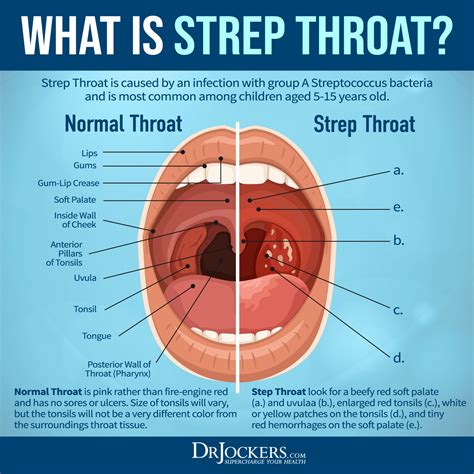
Here are five common ways to get strep throat:
- Direct Contact: Strep throat can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, such as touching, shaking hands, or sharing personal items.
- Airborne Transmission: The bacteria that cause strep throat can be transmitted through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing droplets that contain the bacteria.
- Contaminated Surfaces: Strep throat bacteria can survive on surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops, for extended periods. Touching these surfaces and then touching the face can lead to infection.
- Shared Food and Drinks: Sharing food, drinks, or utensils with an infected person can spread the bacteria, as they can survive on these items for a short period.
- Poor Hygiene: Failure to practice good hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, and after blowing the nose, coughing or sneezing, can increase the risk of getting strep throat.
Preventing Strep Throat
Preventing strep throat requires a combination of good hygiene practices, avoidance of close contact with infected individuals, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Some effective prevention strategies include: * Washing hands frequently with soap and water * Avoiding close contact with people who have strep throat * Not sharing personal items, such as utensils, glasses, or towels * Keeping surfaces and objects clean and disinfected * Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy diet to boost the immune systemDiagnosing and Treating Strep Throat
Diagnosing strep throat typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a rapid strep test or throat culture. If the test results are positive, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
Untreated strep throat can lead to severe complications, such as: * Kidney inflammation (poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis) * Rheumatic fever * Abscesses or pockets of pus in the throat * Sinusitis or infection of the sinuses * Ear infectionsManaging Strep Throat Symptoms
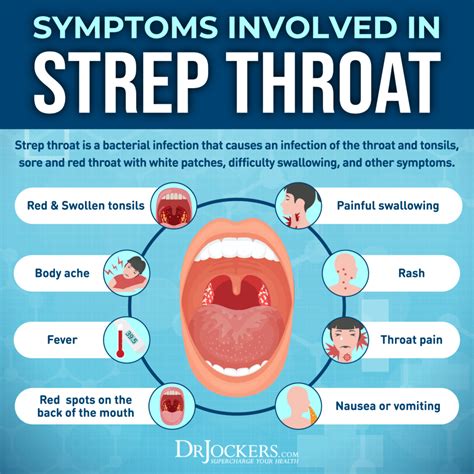
Managing strep throat symptoms is crucial to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Some effective ways to manage symptoms include:
- Getting plenty of rest
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Using a humidifier to add moisture to the air
- Gargling with salt water to reduce throat pain
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Some signs that require immediate medical attention include: * Severe throat pain or difficulty swallowing * High fever (over 101°F) * White patches or pus on the tonsils * Swollen or tender lymph nodes in the neck * Difficulty breathing or shortness of breathConclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, strep throat is a contagious infection that can be spread through various means. Understanding the transmission dynamics, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial to minimize the risk of infection. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent complications. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, we can reduce the incidence of strep throat and promote overall health and well-being.
We encourage readers to share their experiences with strep throat, ask questions, or provide feedback on this article. Your input is valuable to us, and we appreciate your engagement. If you have any concerns or questions, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. Let's work together to promote health and wellness in our communities.
What are the common symptoms of strep throat?
+Common symptoms of strep throat include sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and white patches or pus on the tonsils.
How long does it take for strep throat symptoms to appear?
+Strep throat symptoms can take 2-5 days to appear after exposure to the bacteria.
Can strep throat be treated without antibiotics?
+No, strep throat requires antibiotic treatment to clear the infection and prevent complications.
