Intro
Understand hypothyroidism blood test results, including TSH, free T4, and T3 levels, to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders, symptoms, and treatment options.
Hypothyroidism is a common health condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, which are crucial for regulating various bodily functions. One of the primary methods for diagnosing hypothyroidism is through blood tests, which measure the levels of thyroid hormones and other related substances in the blood. Understanding the results of these blood tests is essential for diagnosis, treatment, and management of hypothyroidism. In this article, we will delve into the world of hypothyroidism blood test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what steps to take after receiving the results.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in maintaining the body's metabolic rate, energy levels, and overall health. When the thyroid gland is underactive, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and hair loss. Blood tests are a crucial tool for diagnosing hypothyroidism, as they can detect abnormalities in thyroid hormone levels. The most common blood tests used to diagnose hypothyroidism include the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test, Free Thyroxine (FT4) test, and Free Triiodothyronine (FT3) test. Each of these tests provides valuable information about the thyroid gland's function and can help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage hypothyroidism.
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism can be a life-changing experience, and understanding the blood test results is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. The results of these blood tests can be complex and may require interpretation by a healthcare professional. However, having a basic understanding of what the results mean can help individuals take a more active role in their healthcare. In the following sections, we will explore the different aspects of hypothyroidism blood test results, including the various tests used, how to interpret the results, and what steps to take after receiving the results.
Understanding Thyroid Function Tests
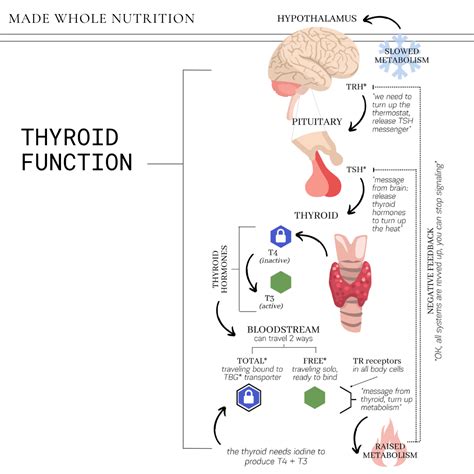
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test
The TSH test is a sensitive test that can detect even slight changes in thyroid function. The normal range for TSH is typically between 0.4 and 4.5 milliunits per liter (mU/L), but this range may vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status. A high TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is underactive, while a low TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is overactive. The TSH test is often used in combination with other tests, such as the FT4 and FT3 tests, to confirm the diagnosis of hypothyroidism.Interpreting Blood Test Results
- A high TSH level (>4.5 mU/L) indicates hypothyroidism.
- A low TSH level (<0.4 mU/L) indicates hyperthyroidism.
- A normal TSH level (0.4-4.5 mU/L) indicates normal thyroid function.
- A low FT4 level (<0.8 ng/dL) indicates hypothyroidism.
- A low FT3 level (<2.5 pg/mL) indicates hypothyroidism.
Free Thyroxine (FT4) Test
The FT4 test measures the level of free thyroxine in the blood. Free thyroxine is the biologically active form of thyroxine, which is the primary thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland. The normal range for FT4 is typically between 0.8 and 1.8 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL), but this range may vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status. A low FT4 level indicates hypothyroidism, while a high FT4 level indicates hyperthyroidism.Treatment and Management of Hypothyroidism
- Take thyroid hormone replacement medication as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Monitor blood test results regularly to adjust medication dosage.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Avoid certain medications and substances that can interfere with thyroid function.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Hypothyroidism
In addition to thyroid hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes can help manage hypothyroidism. The following are some lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health:- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly, such as walking or yoga.
- Get enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing.
Complications and Risks of Untreated Hypothyroidism
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
- Osteoporosis and bone fractures
- Infertility and pregnancy complications
- Cognitive impairment and dementia
- Depression and anxiety
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood test results and thyroid function is essential for managing hypothyroidism. The following are some reasons why regular monitoring is important:- Adjust medication dosage as needed
- Monitor for potential complications and risks
- Evaluate the effectiveness of treatment
- Make lifestyle changes to improve overall health
Conclusion and Next Steps

- Consult with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan.
- Make lifestyle changes to improve overall health.
- Monitor blood test results regularly to adjust medication dosage.
- Seek support from family, friends, or support groups.
We encourage you to share your experiences and questions about hypothyroidism in the comments below. Your input can help others better understand the condition and its management. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from the information.
What is hypothyroidism?
+Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin.
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
+Hypothyroidism is typically diagnosed through blood tests, including the TSH, FT4, and FT3 tests, which measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood.
What are the treatment options for hypothyroidism?
+The primary treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones to replace the missing hormones. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also help manage symptoms.
