Intro
Discover key facts about the Immunoglobulin A test, including its role in diagnosing immune disorders, measuring IgA levels, and understanding its significance in mucosal immunity and autoimmune diseases.
The immunoglobulin A (IgA) test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess the levels of IgA antibodies in the blood. IgA is a type of antibody that plays a vital role in the immune system, particularly in the mucous membranes of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the IgA test, its working mechanism, and its applications in clinical practice.
IgA is the most abundant antibody in the human body, and its primary function is to protect the mucous membranes from invading pathogens. The IgA test is used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and allergies. The test measures the levels of IgA in the blood, which can help healthcare professionals identify underlying immune system disorders. For instance, low levels of IgA can indicate an increased risk of infections, while high levels can suggest an autoimmune disorder or an allergic reaction.
The IgA test is a valuable tool in clinical practice, and its applications continue to expand as research advances. The test can help diagnose conditions such as selective IgA deficiency, common variable immunodeficiency, and IgA nephropathy. Additionally, the IgA test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for these conditions. With the increasing prevalence of immune system disorders, the importance of the IgA test cannot be overstated. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits, working mechanisms, and applications of the IgA test in greater detail.
What is Immunoglobulin A?
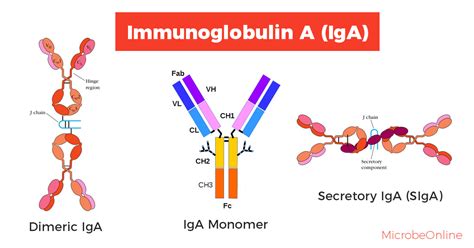
IgA has several functions, including neutralizing pathogens, removing toxins, and regulating the immune response. It is also involved in the development of mucosal immunity, which is essential for protecting the body against infections. IgA deficiency is a common condition that can increase the risk of infections, particularly in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
Types of Immunoglobulin A
There are two types of IgA: IgA1 and IgA2. IgA1 is the most abundant form of IgA and is primarily found in the serum, while IgA2 is found in the mucous membranes. Both types of IgA play important roles in the immune system, and their levels can be measured using the IgA test.How Does the Immunoglobulin A Test Work?
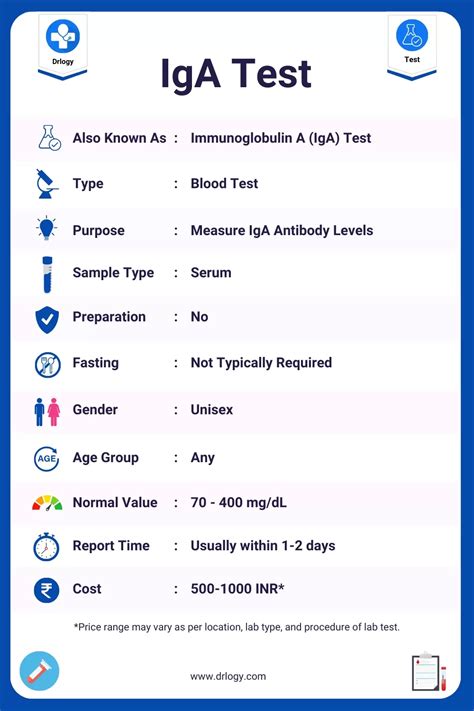
The IgA test can measure the levels of total IgA, as well as the levels of IgA1 and IgA2. The results of the test are typically reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). The normal range for IgA levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but generally, a level of 70-400 mg/dL is considered normal.
Interpreting the Results of the Immunoglobulin A Test
The results of the IgA test can be interpreted in various ways, depending on the underlying condition being diagnosed or monitored. For instance, low levels of IgA can indicate an increased risk of infections, while high levels can suggest an autoimmune disorder or an allergic reaction.Here are some possible interpretations of the IgA test results:
- Low IgA levels (<70 mg/dL): May indicate an increased risk of infections, particularly in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
- Normal IgA levels (70-400 mg/dL): Indicates a normal immune response.
- High IgA levels (>400 mg/dL): May suggest an autoimmune disorder, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, or an allergic reaction.
Benefits of the Immunoglobulin A Test
The IgA test is a valuable tool in clinical practice, and its benefits continue to expand as research advances. The test can help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage various conditions, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Applications of the Immunoglobulin A Test
The IgA test has various applications in clinical practice, including: * Diagnosing and monitoring immune system disorders, such as selective IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. * Identifying underlying causes of recurrent infections, particularly in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. * Monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for immune system disorders. * Providing valuable information for the diagnosis and management of autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.The IgA test can also be used to monitor the levels of IgA in individuals with conditions such as IgA nephropathy, a type of kidney disease characterized by the deposition of IgA antibodies in the kidneys.
Immunoglobulin A Test Procedure
The IgA test procedure is relatively simple and straightforward, and the results can provide valuable information for the diagnosis and management of various conditions.
Preparation for the Immunoglobulin A Test
To prepare for the IgA test, individuals should: * Fast for at least 8 hours before the test to ensure accurate results. * Avoid taking any medications that may interfere with the test results. * Inform their healthcare professional about any underlying medical conditions or allergies. * Follow any specific instructions provided by their healthcare professional.By following these steps, individuals can ensure that their IgA test results are accurate and reliable.
Common Conditions Diagnosed with the Immunoglobulin A Test
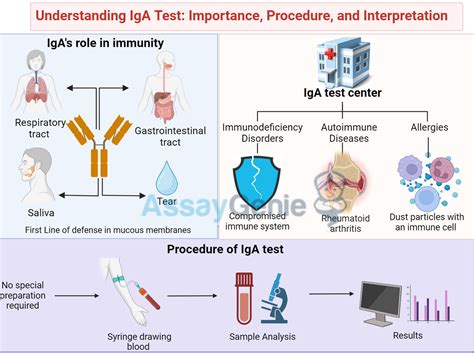
The IgA test can provide valuable information for the diagnosis and management of these conditions, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Treatment Options for Conditions Diagnosed with the Immunoglobulin A Test
The treatment options for conditions diagnosed with the IgA test vary depending on the underlying condition. For instance: * Selective IgA deficiency: Treatment may involve antibiotics to prevent infections, as well as immunoglobulin replacement therapy to replace low levels of IgA. * Common variable immunodeficiency: Treatment may involve immunoglobulin replacement therapy to replace low levels of IgA, IgG, and IgM, as well as antibiotics to prevent infections. * IgA nephropathy: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression, as well as lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms. * Rheumatoid arthritis: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression, as well as lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms. * Lupus: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression, as well as lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms.By understanding the treatment options for conditions diagnosed with the IgA test, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and management.
What is the normal range for IgA levels?
+The normal range for IgA levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but generally, a level of 70-400 mg/dL is considered normal.
What are the benefits of the IgA test?
+The IgA test has several benefits, including diagnosing and monitoring immune system disorders, identifying underlying causes of recurrent infections, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments.
What conditions can be diagnosed with the IgA test?
+The IgA test can be used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including selective IgA deficiency, common variable immunodeficiency, IgA nephropathy, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
In summary, the IgA test is a valuable tool in clinical practice, providing valuable information for the diagnosis and management of various conditions. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and applications of the IgA test, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and management. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the IgA test in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
