Intro
Elevated sodium levels can lead to increased Na levels, causing hypernatremia, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalance, emphasizing the importance of monitoring and managing sodium intake to prevent related health complications.
The human body is a complex system that relies on a delicate balance of various substances to function properly. One of the essential substances is sodium, which plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. However, when sodium levels in the body become elevated, it can lead to a range of health problems. Increased Na levels, also known as hypernatremia, can have severe consequences if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of sodium and explore the causes, symptoms, and effects of increased Na levels in the body.
Sodium is an essential mineral that helps regulate the amount of water in the body. It also facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contractions. The body tightly regulates sodium levels, and even small changes can have significant effects. Normally, the kidneys help maintain sodium balance by adjusting the amount of sodium excreted in the urine. However, when the kidneys are not functioning properly or when there is an excess of sodium in the diet, sodium levels can become elevated. This can lead to a range of health problems, from mild to life-threatening.
The importance of maintaining healthy sodium levels cannot be overstated. Elevated sodium levels can lead to a range of complications, including seizures, coma, and even death. Furthermore, increased Na levels can also exacerbate existing health conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and kidney disease. It is essential to understand the causes and symptoms of hypernatremia to take preventative measures and seek medical attention if necessary. In the following sections, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and effects of increased Na levels in more detail.
Causes of Increased Na Levels
Increased Na levels can be caused by a range of factors, including dehydration, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Dehydration is one of the most common causes of hypernatremia, as it reduces the amount of water in the body, leading to a concentration of sodium. Certain medications, such as diuretics, can also increase sodium levels by reducing the amount of water in the body. Additionally, underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, and liver disease, can also contribute to elevated sodium levels.
Some of the other causes of increased Na levels include:
- Excessive sodium intake through diet or supplements
- Hormonal imbalances, such as Cushing's syndrome or hyperaldosteronism
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes insipidus or primary hyperparathyroidism
- Use of certain medications, such as steroids or certain antidepressants
It is essential to note that increased Na levels can be caused by a range of factors, and a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Symptoms of Increased Na Levels
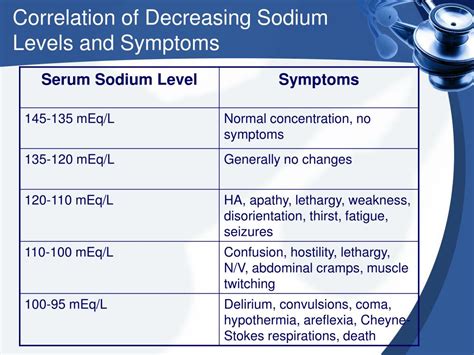
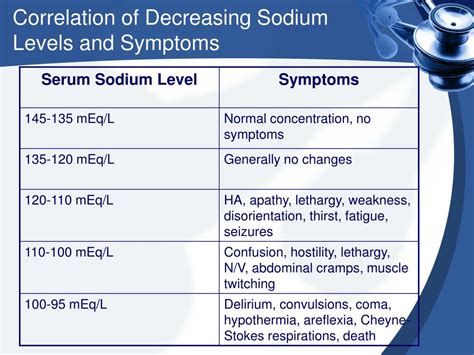
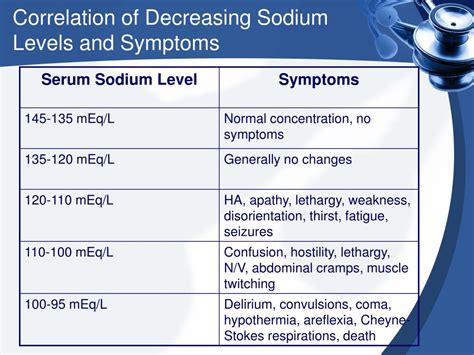
The symptoms of increased Na levels can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Mild cases of hypernatremia may not produce any noticeable symptoms, while more severe cases can lead to a range of complications. Some of the common symptoms of increased Na levels include:
- Thirst and dry mouth
- Dark yellow or brown urine
- Fatigue and weakness
- Headache and confusion
- Seizures and coma (in severe cases)
In addition to these symptoms, increased Na levels can also lead to a range of other complications, including:
- Kidney damage and disease
- Heart problems, such as high blood pressure and heart failure
- Muscle weakness and cramps
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as prompt treatment can help prevent long-term damage and complications.
Diagnosis of Increased Na Levels
The diagnosis of increased Na levels typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to look for signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth and dark urine. They may also ask questions about your medical history, including your diet, medication use, and underlying medical conditions.Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and urine tests, can help confirm the diagnosis of hypernatremia. These tests can measure the levels of sodium and other electrolytes in the body, as well as assess kidney function and other underlying medical conditions.
Effects of Increased Na Levels

Increased Na levels can have a range of effects on the body, from mild to life-threatening. Some of the effects of hypernatremia include:
- Dehydration: Elevated sodium levels can lead to dehydration, as the body tries to dilute the sodium by holding onto water.
- Kidney damage: Hypernatremia can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease.
- Heart problems: Increased Na levels can lead to high blood pressure, heart failure, and other heart problems.
- Muscle weakness: Elevated sodium levels can cause muscle weakness and cramps.
- Numbness and tingling: Hypernatremia can cause numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
In severe cases, increased Na levels can lead to life-threatening complications, such as seizures, coma, and even death.
Treatment of Increased Na Levels
The treatment of increased Na levels depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases of hypernatremia may be treated with fluid replacement and dietary changes, while more severe cases may require hospitalization and medical treatment.Some of the common treatments for hypernatremia include:
- Fluid replacement: Replacing lost fluids with water or electrolyte-rich solutions can help dilute sodium levels.
- Dietary changes: Reducing sodium intake and increasing water intake can help manage hypernatremia.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can help reduce sodium levels and manage underlying medical conditions.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide close monitoring and treatment.
It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for increased Na levels.
Prevention of Increased Na Levels
Preventing increased Na levels requires a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical check-ups. Some of the ways to prevent hypernatremia include:
- Reducing sodium intake: Limiting sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day can help prevent hypernatremia.
- Increasing water intake: Drinking plenty of water can help dilute sodium levels and prevent dehydration.
- Monitoring urine output: Monitoring urine output can help identify signs of dehydration and hypernatremia.
- Regular medical check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help identify underlying medical conditions and prevent complications.
Additionally, it is essential to:
- Avoid excessive sodium intake through diet or supplements
- Manage underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease and heart failure
- Use medications as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare provider
By taking these steps, you can help prevent increased Na levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Increased Na levels can have severe consequences if left untreated. It is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and effects of hypernatremia to take preventative measures and seek medical attention if necessary. By working with a healthcare provider and making lifestyle modifications, you can help manage and prevent increased Na levels.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with increased Na levels in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by hypernatremia.
What are the common causes of increased Na levels?
+Increased Na levels can be caused by dehydration, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease and heart failure.
What are the symptoms of increased Na levels?
+The symptoms of increased Na levels can include thirst and dry mouth, dark yellow or brown urine, fatigue and weakness, headache and confusion, and seizures and coma in severe cases.
How can I prevent increased Na levels?
+Preventing increased Na levels requires a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical check-ups. This can include reducing sodium intake, increasing water intake, monitoring urine output, and managing underlying medical conditions.
