Intro
Discover causes and treatments for an inflamed salivary gland, including symptoms, diagnosis, and remedies for salivary gland inflammation, swelling, and infection, to alleviate pain and promote healing.
The salivary glands are an essential part of our digestive system, responsible for producing saliva that helps break down food and maintain oral health. However, like any other part of the body, they can become inflamed, leading to discomfort and pain. Inflamed salivary glands, also known as sialadenitis, can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, blockages, and autoimmune disorders. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for inflamed salivary glands is crucial for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being.
Inflamed salivary glands can be a painful and debilitating condition, affecting daily activities such as eating, speaking, and even sleeping. The condition can be acute or chronic, with acute cases often resolving on their own with proper treatment, while chronic cases may require ongoing management and care. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated inflamed salivary glands can lead to complications such as abscesses, fistulas, or even cancer.
The salivary glands play a vital role in our oral health, producing saliva that helps to neutralize acids, break down food, and protect teeth from decay. There are three main salivary glands: the parotid gland, submandibular gland, and sublingual gland. Each gland has a unique function and can be affected by inflammation, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. Understanding the anatomy and function of the salivary glands is essential for diagnosing and treating inflamed salivary glands.
Inflamed Salivary Gland Causes

Types of Inflamed Salivary Gland
There are several types of inflamed salivary glands, including acute and chronic sialadenitis. Acute sialadenitis is a sudden onset of inflammation, often caused by infection or blockage, while chronic sialadenitis is a long-term condition, often caused by autoimmune disorders or recurrent infections. Other types of inflamed salivary glands include recurrent parotitis, which affects the parotid gland, and submandibular sialadenitis, which affects the submandibular gland.Inflamed Salivary Gland Symptoms
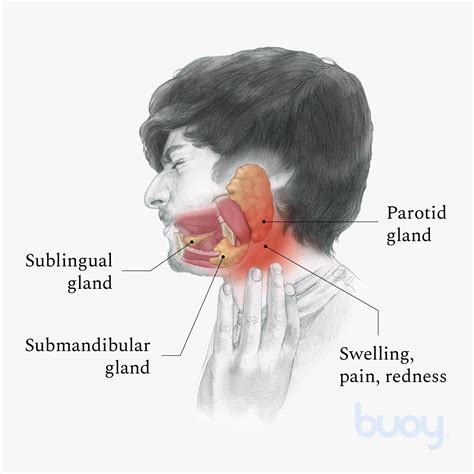
Diagnosing Inflamed Salivary Gland
Diagnosing inflamed salivary glands typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. A physical examination may reveal swelling, redness, and tenderness of the affected gland, while a medical history may reveal underlying conditions or risk factors. Diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or laboratory tests, may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.Inflamed Salivary Gland Treatment

Home Remedies for Inflamed Salivary Gland
There are several home remedies that can help to manage symptoms and promote healing of inflamed salivary glands. These include applying warm compresses to the affected area, sucking on sugar-free candy or lozenges to stimulate saliva production, and avoiding spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the mouth and throat. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other fluids can also help to thin out saliva and promote healing.Inflamed Salivary Gland Complications

Preventing Inflamed Salivary Gland
Preventing inflamed salivary glands involves practicing good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants such as tobacco and spicy foods. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can also help to identify and treat underlying conditions that may contribute to inflamed salivary glands. Avoiding trauma to the face and mouth, such as from sports injuries or falls, can also help to prevent inflamed salivary glands.Inflamed Salivary Gland and Nutrition
Nutritional Supplements for Inflamed Salivary Gland
Certain nutritional supplements, such as vitamin C and zinc, may also help to support saliva production and overall oral health. Vitamin C, in particular, has antioxidant properties that may help to reduce inflammation and promote healing. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements, as they may interact with other medications or have adverse effects.Inflamed Salivary Gland and Lifestyle

Managing Stress and Anxiety with Inflamed Salivary Gland
Managing stress and anxiety is essential for managing symptoms and promoting healing of inflamed salivary glands. This can involve practicing relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or visualization, and seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional. Getting enough sleep and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can also help to reduce stress and anxiety.What are the symptoms of inflamed salivary glands?
+The symptoms of inflamed salivary glands can include pain and swelling of the affected gland, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and a foul taste or odor in the mouth.
How are inflamed salivary glands diagnosed?
+Inflamed salivary glands are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or laboratory tests.
What are the treatment options for inflamed salivary glands?
+Treatment options for inflamed salivary glands depend on the cause and severity of the condition, but may include antibiotics, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory medications, as well as self-care measures such as staying hydrated and practicing good oral hygiene.
Can inflamed salivary glands be prevented?
+Yes, inflamed salivary glands can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants such as tobacco and spicy foods.
What are the complications of untreated inflamed salivary glands?
+Untreated inflamed salivary glands can lead to complications such as abscesses, fistulas, or even cancer.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of inflamed salivary glands, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Remember to prioritize your oral health and take steps to prevent inflamed salivary glands, such as practicing good oral hygiene and staying hydrated. By working together, we can promote healthy salivary glands and overall well-being. Share this article with others to help raise awareness about the importance of salivary gland health, and let's work together to create a healthier and happier community.
