Intro
Discover effective inguinal hernia treatment options, including laparoscopic repair, open surgery, and watchful waiting, to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications, with expert guidance on hernia repair and management.
Inguinal hernias are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, typically in the inguinal canal. This can cause discomfort, pain, and other complications if left untreated. Fortunately, there are various inguinal hernia treatment options available, ranging from non-surgical approaches to surgical interventions. In this article, we will delve into the different treatment options, their benefits, and what to expect during the recovery process.
The importance of seeking medical attention for an inguinal hernia cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the hernia can become strangulated, cutting off blood supply to the affected tissue, which can lead to serious health complications. Moreover, inguinal hernias can affect daily activities, causing pain and discomfort during physical exertion, lifting, or even coughing. By exploring the available treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and alleviate symptoms to improve their overall quality of life.
Inguinal hernias can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans. Once diagnosed, the treatment approach will depend on the size and severity of the hernia, as well as the individual's overall health. For small, asymptomatic hernias, a watchful waiting approach may be recommended, where the doctor monitors the hernia for any changes or complications. However, for larger, symptomatic hernias, surgical intervention is often necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Inguinal Hernia Treatment Options

There are two primary surgical approaches for inguinal hernia repair: open hernia repair and laparoscopic hernia repair. Open hernia repair involves making an incision in the groin area to push the hernia back into place and reinforce the abdominal wall with mesh. Laparoscopic hernia repair, on the other hand, involves making several small incisions through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted to repair the hernia. Both approaches have their benefits and drawbacks, and the choice of surgery will depend on the individual's specific condition and the surgeon's expertise.
Open Hernia Repair
Open hernia repair is a traditional surgical approach that involves making an incision in the groin area to access the hernia. This approach allows the surgeon to directly visualize the hernia and surrounding tissue, making it easier to repair the defect. The benefits of open hernia repair include: * Lower risk of complications during surgery * Faster recovery time compared to laparoscopic surgery * Less expensive than laparoscopic surgery However, open hernia repair also has some drawbacks, including: * Larger incision, which can lead to more post-operative pain and scarring * Higher risk of wound infection and complications * Longer hospital stay compared to laparoscopic surgeryLaparoscopic Hernia Repair
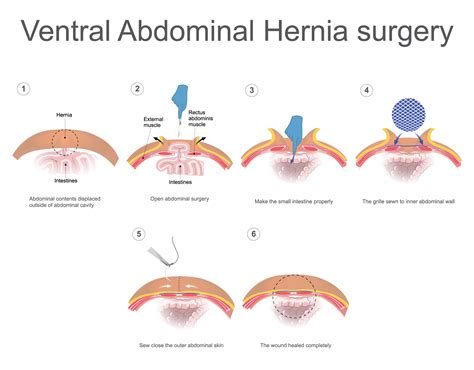
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive surgical approach that involves making several small incisions through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. This approach allows the surgeon to visualize the hernia and surrounding tissue on a video monitor, making it easier to repair the defect. The benefits of laparoscopic hernia repair include:
- Smaller incisions, which can lead to less post-operative pain and scarring
- Faster recovery time compared to open hernia repair
- Lower risk of wound infection and complications However, laparoscopic hernia repair also has some drawbacks, including:
- Higher risk of complications during surgery, such as bowel injury or bleeding
- More expensive than open hernia repair
- Requires specialized training and equipment
Robotic Hernia Repair
Robotic hernia repair is a relatively new surgical approach that combines the benefits of laparoscopic surgery with the precision and dexterity of robotic technology. This approach allows the surgeon to visualize the hernia and surrounding tissue in high definition, making it easier to repair the defect. The benefits of robotic hernia repair include: * Improved visualization and precision during surgery * Reduced risk of complications during surgery * Faster recovery time compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery However, robotic hernia repair also has some drawbacks, including: * Higher cost compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery * Limited availability of robotic technology and trained surgeons * Longer operating time compared to traditional laparoscopic surgeryNon-Surgical Treatment Options
For small, asymptomatic inguinal hernias, non-surgical treatment options may be recommended. These approaches aim to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications without the need for surgery. The benefits of non-surgical treatment options include:
- Avoidance of surgical risks and complications
- Reduced recovery time compared to surgical interventions
- Lower cost compared to surgical interventions However, non-surgical treatment options also have some drawbacks, including:
- Limited effectiveness in alleviating symptoms and preventing complications
- Requires regular monitoring and follow-up appointments
- May not be suitable for larger, symptomatic hernias
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting is a non-surgical approach that involves monitoring the hernia for any changes or complications. This approach is often recommended for small, asymptomatic hernias that are not causing any symptoms or discomfort. The benefits of watchful waiting include: * Avoidance of surgical risks and complications * Reduced cost compared to surgical interventions * Allows for monitoring of the hernia to determine if surgery is necessary However, watchful waiting also has some drawbacks, including: * Limited effectiveness in preventing complications * Requires regular monitoring and follow-up appointments * May not be suitable for larger, symptomatic herniasPrevention and Lifestyle Changes

While inguinal hernias can be treated with surgery or non-surgical approaches, prevention and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing a hernia in the first place. The benefits of prevention and lifestyle changes include:
- Reduced risk of developing a hernia
- Improved overall health and well-being
- Reduced risk of complications and symptoms Some prevention and lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of developing a hernia include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the abdominal wall
- Avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or straining
- Engaging in regular exercise to improve core strength and flexibility
- Eating a balanced diet to improve overall health and well-being
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet and nutrition can play a crucial role in preventing and managing inguinal hernias. A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help improve overall health and well-being, reducing the risk of complications and symptoms. Some foods that can help prevent and manage inguinal hernias include: * Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Foods high in protein, such as lean meats, fish, and legumes * Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and nuts * Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and other fruits and vegetablesConclusion and Next Steps

Inguinal hernias are a common health issue that can be treated with surgery or non-surgical approaches. By understanding the different treatment options, benefits, and drawbacks, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and alleviate symptoms to improve their overall quality of life. Prevention and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and engaging in regular exercise, can also help reduce the risk of developing a hernia in the first place. If you are experiencing symptoms or have been diagnosed with an inguinal hernia, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with inguinal hernias in the comments section below. Have you undergone surgery or non-surgical treatment for an inguinal hernia? What were your experiences, and what advice would you give to others who are facing similar challenges? By sharing your stories and insights, you can help others better understand their options and make informed decisions about their care.
What are the symptoms of an inguinal hernia?
+The symptoms of an inguinal hernia may include a bulge or swelling in the groin area, discomfort or pain, especially when coughing, lifting, or bending, and a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the groin area.
What are the risks and complications of inguinal hernia surgery?
+The risks and complications of inguinal hernia surgery may include bleeding, infection, nerve damage, and recurrence of the hernia. It is essential to discuss these risks and complications with your surgeon before undergoing surgery.
Can inguinal hernias be prevented?
+While inguinal hernias cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and engaging in regular exercise, can help reduce the risk of developing a hernia.
