Intro
Understand INR blood test results and their implications. Learn about International Normalized Ratio, blood clotting, and warfarin therapy management, including normal ranges and abnormal results.
The International Normalized Ratio (INR) blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot. This test is essential for patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, to ensure their blood is clotting at the right rate. An INR test result can help healthcare providers determine if a patient's blood is too prone to clotting, which can lead to conditions like deep vein thrombosis, or if it's too thin, increasing the risk of bleeding. In this article, we will delve into the world of INR blood test results, explaining what they mean, how they're interpreted, and what patients can expect from this test.
The INR test is a vital component of healthcare, particularly for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, mechanical heart valves, or a history of blood clots. By understanding INR test results, patients can better manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. With the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, the importance of INR testing cannot be overstated. As we explore the intricacies of INR blood test results, we'll also discuss the benefits and limitations of this test, as well as provide practical examples and statistical data to illustrate its significance.
What is an INR Blood Test?
Why is the INR Test Important?
The INR test is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps healthcare providers monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. By adjusting the dosage of these medications, healthcare providers can ensure that patients are receiving the optimal treatment for their condition. Secondly, the INR test helps identify patients who are at risk of bleeding or clotting complications. For example, patients with a high INR result may be at risk of bleeding, while those with a low INR result may be at risk of clotting.Interpreting INR Test Results
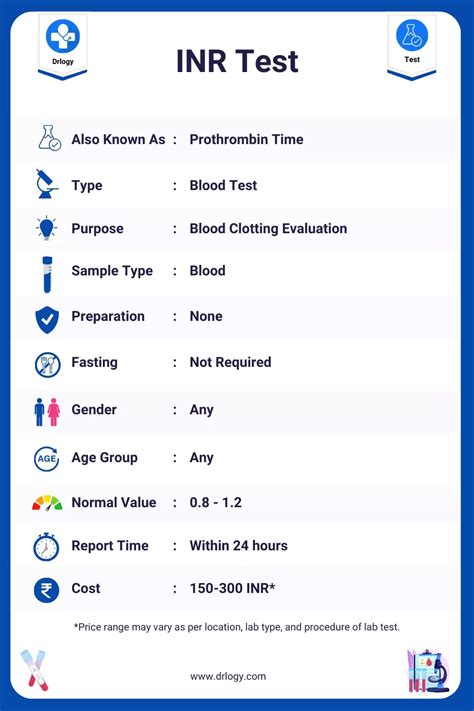
Factors that Affect INR Test Results
Several factors can affect INR test results, including: * Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications, can interact with anticoagulant medications and affect INR results. * Diet: Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy greens, can affect warfarin's effectiveness and INR results. * Lifestyle: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical activity can also impact INR results. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, can affect the way the body processes anticoagulant medications and impact INR results.Benefits and Limitations of INR Testing

However, INR testing also has some limitations:
- Variability: INR results can vary depending on the laboratory and testing equipment used.
- Limited accuracy: INR results may not always accurately reflect a patient's clotting status.
- Frequent testing: Patients may require frequent INR testing, which can be inconvenient and time-consuming.
Practical Examples of INR Testing
To illustrate the importance of INR testing, let's consider a few practical examples: * A 65-year-old patient with atrial fibrillation is taking warfarin to prevent stroke. Regular INR testing helps the healthcare provider adjust the warfarin dosage to ensure the patient's INR result remains within the target range. * A 40-year-old patient with a mechanical heart valve requires regular INR testing to ensure their blood is clotting at the right rate. The healthcare provider adjusts the patient's anticoagulant medication based on the INR results to minimize the risk of complications.Statistical Data on INR Testing
Future Directions for INR Testing
As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see advancements in INR testing, including: * Point-of-care testing: Patients may be able to perform INR tests at home using portable devices. * Genetic testing: Genetic testing may help identify patients who are more likely to experience INR variability. * Artificial intelligence: AI algorithms may be used to analyze INR results and predict patient outcomes.What is the normal INR range for a healthy individual?
+The normal INR range for a healthy individual is typically between 0.9 and 1.1.
How often should I get an INR test if I'm taking warfarin?
+The frequency of INR testing depends on individual factors, such as the condition being treated and the patient's response to warfarin. Typically, patients require INR testing every 1-4 weeks.
Can I eat foods high in vitamin K while taking warfarin?
+Yes, but it's essential to maintain a consistent diet and inform your healthcare provider about any changes. Foods high in vitamin K can affect warfarin's effectiveness and INR results.
As we conclude our exploration of INR blood test results, we encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this knowledge. By working together, we can improve our understanding of INR testing and promote better patient outcomes. Take the first step today by discussing INR testing with your healthcare provider and learning more about how this test can help you manage your condition effectively.
