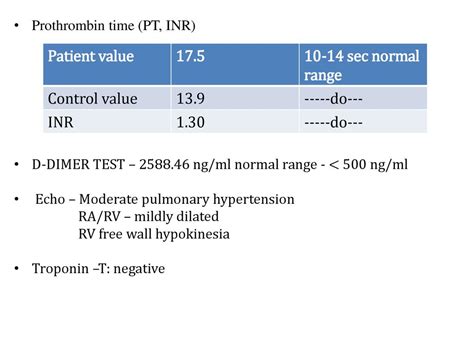
Intro
Discover normal INR levels explained, including ideal ranges, fluctuation causes, and warfarin therapy management for optimal blood clotting, stroke prevention, and cardiovascular health.
Normal INR levels are a crucial aspect of blood coagulation, and understanding their significance is essential for individuals taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a test used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot, which helps healthcare professionals assess the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy. In this article, we will delve into the world of INR levels, exploring their importance, the factors that influence them, and the steps individuals can take to maintain optimal INR levels.
The INR test is a vital tool for monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy, as it helps prevent both thrombosis and bleeding complications. By measuring the INR level, healthcare professionals can adjust the dosage of anticoagulant medications to ensure that the blood is neither too prone to clotting nor too prone to bleeding. This delicate balance is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of individuals with conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism.
The importance of normal INR levels cannot be overstated, as they play a critical role in preventing serious health complications. For instance, an INR level that is too low may indicate that the blood is too prone to clotting, which can increase the risk of thrombosis and stroke. On the other hand, an INR level that is too high may indicate that the blood is too prone to bleeding, which can increase the risk of hemorrhage and other bleeding-related complications. Therefore, it is essential for individuals taking anticoagulant medications to regularly monitor their INR levels and adjust their treatment plans accordingly.
Understanding INR Levels

To comprehend the significance of INR levels, it is essential to understand how they are measured and interpreted. The INR test is typically performed using a blood sample, which is then analyzed to determine the time it takes for the blood to clot. The results are expressed as a ratio, with a normal INR level ranging from 0.8 to 1.2. Individuals taking anticoagulant medications usually aim for an INR level between 2.0 and 3.0, although this may vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual's overall health.
Factors Influencing INR Levels
Several factors can influence INR levels, including diet, medications, and underlying health conditions. For instance, consuming foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables, can affect INR levels, as vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood coagulation. Additionally, certain medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents, can interact with anticoagulant medications and alter INR levels. It is essential for individuals to be aware of these factors and take steps to minimize their impact on INR levels.Maintaining Optimal INR Levels
To maintain optimal INR levels, individuals can take several steps. Firstly, it is essential to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan and take anticoagulant medications as directed. Secondly, individuals should be aware of the foods and medications that can affect INR levels and take steps to minimize their impact. Regular monitoring of INR levels is also crucial, as it allows healthcare professionals to adjust the treatment plan as needed. Additionally, individuals can maintain a healthy lifestyle by engaging in regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress.
Practical Tips for Managing INR Levels
Here are some practical tips for managing INR levels: * Keep a record of INR test results and medication dosages * Be aware of the foods and medications that can affect INR levels * Maintain a consistent diet and lifestyle * Avoid making significant changes to diet or lifestyle without consulting a healthcare professional * Attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professionalCommon Challenges and Complications
Despite the importance of maintaining optimal INR levels, individuals may face several challenges and complications. For instance, some individuals may experience difficulty adhering to their treatment plan, which can lead to fluctuations in INR levels. Others may experience bleeding or thrombotic complications, which can be serious and potentially life-threatening. It is essential for individuals to be aware of these challenges and complications and take steps to mitigate their impact.
Bleeding and Thrombotic Complications
Bleeding and thrombotic complications are two of the most significant challenges associated with anticoagulant therapy. Bleeding complications can range from minor bruising to life-threatening hemorrhage, while thrombotic complications can increase the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular events. To minimize the risk of these complications, individuals should work closely with their healthcare professionals to maintain optimal INR levels and adjust their treatment plans as needed.Advanced INR Management Strategies

In recent years, advanced INR management strategies have emerged, offering individuals more effective and convenient ways to manage their INR levels. For instance, point-of-care INR testing devices allow individuals to monitor their INR levels at home, reducing the need for frequent laboratory tests. Additionally, anticoagulant medications with more predictable pharmacokinetics have been developed, making it easier for individuals to maintain optimal INR levels.
Point-of-Care INR Testing
Point-of-care INR testing devices have revolutionized the way individuals manage their INR levels. These devices allow individuals to perform INR tests at home, using a small blood sample and a portable testing device. The results are then transmitted to a healthcare professional, who can adjust the treatment plan as needed. Point-of-care INR testing offers several benefits, including increased convenience, improved accuracy, and enhanced patient engagement.Future Directions in INR Management
As our understanding of INR levels and anticoagulant therapy continues to evolve, new directions in INR management are emerging. For instance, researchers are exploring the use of genetic testing to predict an individual's response to anticoagulant medications, allowing for more personalized treatment plans. Additionally, the development of novel anticoagulant medications with improved safety and efficacy profiles is ongoing, offering individuals more effective and convenient treatment options.
Personalized Medicine and INR Management
Personalized medicine is an emerging field that involves tailoring treatment plans to an individual's unique genetic and environmental profile. In the context of INR management, personalized medicine offers several benefits, including improved treatment outcomes, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced patient satisfaction. By using genetic testing and other advanced diagnostic tools, healthcare professionals can create personalized treatment plans that take into account an individual's unique characteristics and needs.What is a normal INR level?
+A normal INR level ranges from 0.8 to 1.2, although this may vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual's overall health.
How often should I monitor my INR levels?
+The frequency of INR monitoring depends on several factors, including the individual's condition, treatment plan, and overall health. Typically, INR levels are monitored every 2-4 weeks, although this may vary depending on the specific circumstances.
What are the risks of anticoagulant therapy?
+The risks of anticoagulant therapy include bleeding and thrombotic complications, which can be serious and potentially life-threatening. However, these risks can be minimized by maintaining optimal INR levels and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
In conclusion, maintaining optimal INR levels is a critical aspect of anticoagulant therapy, and individuals should be aware of the factors that influence INR levels and take steps to minimize their impact. By working closely with healthcare professionals, adhering to treatment plans, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with INR management, and to ask any questions you may have about this important topic.
