Intro
Discover the INR meaning in medical terms, including International Normalized Ratio, blood clotting, and coagulation, to understand its significance in healthcare and patient care management.
The medical field is filled with abbreviations and acronyms that can be confusing for those who are not familiar with them. One such term is INR, which stands for International Normalized Ratio. It is a test used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot and is primarily used to monitor patients on warfarin therapy. Warfarin is a blood thinner that is prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming or growing. The INR test is crucial in ensuring that patients on warfarin therapy are within the therapeutic range, as being outside of this range can increase the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
The importance of INR cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in patient care. For individuals taking warfarin, regular INR checks are necessary to ensure that their blood is within the optimal range. If the INR is too high, it means that the blood is too thin, and the patient is at risk of bleeding. On the other hand, if the INR is too low, it means that the blood is not thin enough, and the patient is at risk of developing blood clots. Therefore, understanding INR and its significance is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The concept of INR is not new, and its use has been widespread in the medical field for several decades. However, with advancements in medical technology and the development of new anticoagulants, the role of INR in patient care continues to evolve. As a result, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest information and guidelines regarding INR and its applications in medicine. In this article, we will delve into the world of INR, exploring its meaning, significance, and implications in medical terms.
What is INR?

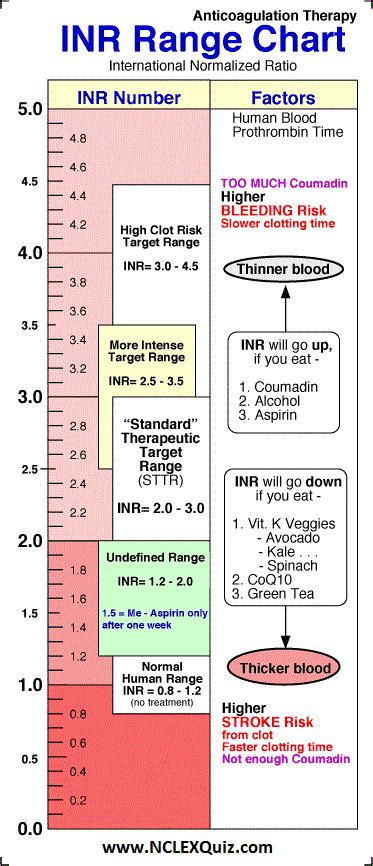
The INR test is commonly used to monitor patients on warfarin therapy, as well as to diagnose and manage bleeding disorders. It is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of warfarin in preventing blood clots and to adjust the dosage as needed. The INR range is typically between 0.8 and 1.2 for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications. For patients on warfarin therapy, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0, although this can vary depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated.
How is INR Measured?
There are several methods that can be used to measure INR, including:
- Prothrombin time (PT) test: This is the most common method used to measure INR. It involves adding a substance called tissue factor to the blood sample, which triggers blood clotting.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) test: This test measures the time it takes for blood to clot in the presence of a substance called partial thromboplastin.
- Thrombin time (TT) test: This test measures the time it takes for blood to clot in the presence of thrombin, a substance that converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific needs of the patient and the laboratory.
What are the Benefits of INR?

- Monitoring warfarin therapy: INR is used to monitor the effectiveness of warfarin in preventing blood clots and to adjust the dosage as needed.
- Diagnosing bleeding disorders: INR can be used to diagnose bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- Evaluating the risk of bleeding: INR can be used to evaluate the risk of bleeding in patients who are taking anticoagulant medications.
- Reducing the risk of thrombosis: INR can be used to reduce the risk of thrombosis in patients who are at high risk of developing blood clots.
Overall, the INR test is a valuable tool in the management of patients on warfarin therapy and in the diagnosis and treatment of bleeding disorders.
What are the Risks and Complications of INR?
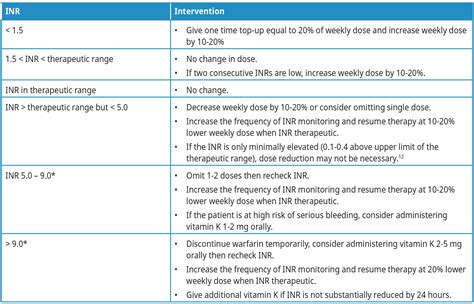
- Bleeding: Patients on warfarin therapy are at risk of bleeding, particularly if their INR is too high.
- Thrombosis: Patients on warfarin therapy are at risk of thrombosis, particularly if their INR is too low.
- Interaction with other medications: Warfarin can interact with other medications, including antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications, which can affect the INR.
- Dietary restrictions: Patients on warfarin therapy may need to follow a special diet to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
It is essential to discuss these risks and complications with a healthcare professional and to follow their advice carefully.
How to Manage INR?
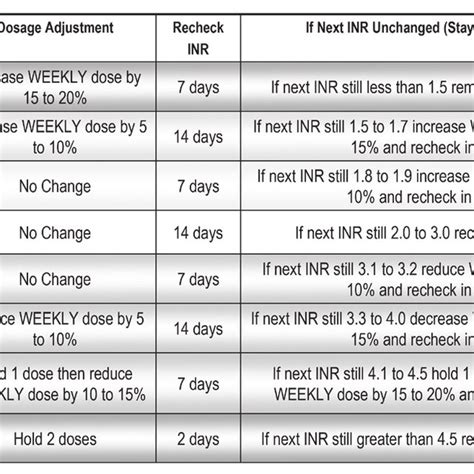
- Regular blood tests: Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor the INR and adjust the warfarin dosage as needed.
- Dietary restrictions: Patients on warfarin therapy may need to follow a special diet to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
- Medication management: Patients on warfarin therapy need to be careful when taking other medications, as they can interact with warfarin and affect the INR.
- Lifestyle modifications: Patients on warfarin therapy may need to make lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding contact sports or heavy lifting, to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage INR and to follow their advice carefully.
INR and Pregnancy
- Warfarin and pregnancy: Warfarin is not recommended during pregnancy, as it can increase the risk of birth defects and bleeding complications.
- Alternative anticoagulants: Alternative anticoagulants, such as heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin, may be recommended during pregnancy.
- INR monitoring: INR monitoring is essential during pregnancy to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
- Dietary restrictions: Patients on warfarin therapy during pregnancy may need to follow a special diet to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage INR during pregnancy and to follow their advice carefully.
INR and Surgery
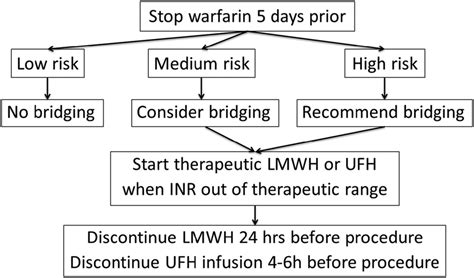
- Warfarin and surgery: Warfarin is typically stopped before surgery to minimize the risk of bleeding complications.
- Alternative anticoagulants: Alternative anticoagulants, such as heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin, may be recommended during surgery.
- INR monitoring: INR monitoring is essential during surgery to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
- Dietary restrictions: Patients on warfarin therapy during surgery may need to follow a special diet to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage INR during surgery and to follow their advice carefully.
FAQs
What is the normal range for INR?
+The normal range for INR is typically between 0.8 and 1.2 for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications. For patients on warfarin therapy, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0.
How often should INR be monitored?
+INR should be monitored regularly, typically every 1-4 weeks, depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated.
What are the risks of high INR?
+The risks of high INR include bleeding, particularly if the INR is too high. Patients on warfarin therapy are at risk of bleeding, particularly if their INR is too high.
In conclusion, INR is a crucial test in the management of patients on warfarin therapy and in the diagnosis and treatment of bleeding disorders. Understanding INR and its significance is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can take an active role in managing their INR and minimizing the risk of bleeding or thrombosis. If you have any questions or concerns about INR, be sure to discuss them with a healthcare professional. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about INR, and take the first step towards taking control of your health.
