Intro
Discover the normal range values for INR, a crucial blood clotting test. Learn about INR normal range, blood thinning, and coagulation, and understand how to interpret INR results for optimal health management and thrombosis prevention.
The International Normalized Ratio, commonly referred to as INR, is a crucial metric used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot. It is primarily used to monitor patients on warfarin therapy, ensuring their blood is within the therapeutic range, neither too prone to clotting nor too prone to bleeding. Understanding INR normal range values is vital for managing anticoagulation therapy effectively.
For individuals not on anticoagulant therapy, the normal INR range is typically between 0.9 and 1.1. This range indicates that the blood is clotting at a normal rate. However, for patients on warfarin or other anticoagulants, the target INR range varies depending on the medical condition being treated. For example, patients with mechanical heart valves may require a higher INR target (usually between 2.0 and 3.0) to prevent valve thrombosis, while those with atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis might have a target range of 2.0 to 3.0.
The significance of maintaining an INR within the therapeutic range cannot be overstated. Values below the target range may indicate insufficient anticoagulation, increasing the risk of thromboembolic events. Conversely, INR values above the target range suggest over-anticoagulation, which can lead to an increased risk of bleeding complications. Therefore, regular monitoring of INR levels is essential for patients on anticoagulant therapy to adjust their medication doses as needed and maintain the delicate balance between clotting and bleeding risks.
Understanding INR Normal Range Values

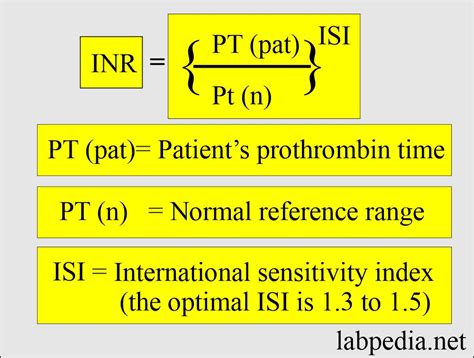
To comprehend INR normal range values fully, it's essential to delve into how INR is measured and what factors can influence these measurements. The INR is calculated from the results of a prothrombin time (PT) test, which measures how long it takes for blood to clot. The PT result is then compared to a standard to derive the INR, allowing for a standardized measurement that can be compared across different laboratories.
Factors Influencing INR Levels
Several factors can influence INR levels, including diet, other medications, and certain medical conditions. For instance, vitamin K, found in leafy green vegetables, can affect warfarin's efficacy, potentially altering INR levels. Similarly, medications like antibiotics can interact with warfarin, necessitating closer monitoring of INR values. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing anticoagulation therapy effectively and minimizing the risk of complications.Importance of Regular INR Monitoring
Regular monitoring of INR levels is vital for patients on warfarin therapy. This monitoring helps in adjusting the dose of warfarin to maintain the INR within the target range, thereby minimizing the risks associated with both under-anticoagulation and over-anticoagulation. The frequency of INR monitoring can vary depending on the stability of the patient's INR values and their individual risk factors for bleeding or thrombosis.
Consequences of INR Levels Outside the Normal Range
INR levels outside the therapeutic range can have significant consequences. An INR below the target range may increase the risk of thromboembolic events, such as stroke or deep vein thrombosis, while an INR above the target range can increase the risk of bleeding, ranging from minor bruising to life-threatening hemorrhages. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the signs of both under-anticoagulation and over-anticoagulation and to seek medical attention promptly if any concerns arise.Management of INR Levels
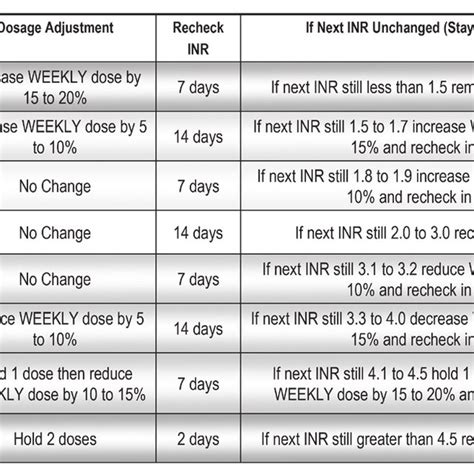
The management of INR levels involves a combination of regular monitoring, dietary advice, and adjustment of warfarin doses as needed. Patients are often advised to maintain a consistent diet, especially regarding vitamin K intake, to minimize fluctuations in INR levels. Additionally, any changes in medications or health status should be reported to the healthcare provider to ensure timely adjustments to the anticoagulation regimen.
Dietary Considerations for INR Management
Diet plays a critical role in INR management, particularly concerning foods high in vitamin K. While it is not necessary to completely avoid these foods, maintaining a consistent intake can help in stabilizing INR levels. Foods rich in vitamin K include leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli, as well as certain oils like canola and soybean oil. Patients should aim for a balanced diet and discuss any specific dietary concerns with their healthcare provider.Challenges in INR Management

Despite the importance of maintaining INR within the therapeutic range, several challenges exist in INR management. These include variability in patient response to warfarin, interactions with other medications, and the need for regular blood tests, which can be inconvenient for some patients. Additionally, achieving and maintaining the target INR range can be difficult, especially in patients with fluctuating health statuses or those who have difficulty adhering to their medication regimen.
Future Directions in Anticoagulation Therapy
Research into new anticoagulants and management strategies aims to address some of the challenges associated with warfarin therapy. Novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) have been developed, offering a more predictable anticoagulant effect without the need for regular INR monitoring. However, these medications come with their own set of considerations, including higher costs and specific reversal strategies in the event of bleeding.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding INR normal range values and the factors that influence them is crucial for the effective management of anticoagulation therapy. By recognizing the importance of regular INR monitoring, being aware of dietary considerations, and understanding the challenges and future directions in INR management, patients and healthcare providers can work together to minimize risks and maximize the benefits of anticoagulant therapy.
If you found this information helpful and would like to learn more about managing INR levels or have questions regarding anticoagulation therapy, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others who might benefit from it. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in creating a community that supports informed healthcare decisions.
What is the normal INR range for individuals not on anticoagulant therapy?
+The normal INR range for individuals not on anticoagulant therapy is typically between 0.9 and 1.1.
Why is regular INR monitoring important for patients on warfarin therapy?
+Regular INR monitoring is crucial for adjusting warfarin doses to maintain the INR within the therapeutic range, minimizing the risks of thromboembolic events and bleeding complications.
What foods can affect INR levels in patients on warfarin therapy?
+Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, broccoli), and certain oils (canola, soybean oil), can affect INR levels. Consistency in diet is key to minimizing fluctuations in INR.
