Intro
Master intramuscular injection techniques with 5 expert tips, covering muscle selection, needle placement, and safety precautions for optimal injection outcomes, minimizing risks and ensuring effective medication delivery.
Intramuscular injections are a common medical procedure used to administer medications, vaccines, and other substances directly into the muscle tissue. This method of administration allows for faster absorption and longer-lasting effects compared to subcutaneous injections. However, it requires proper technique to ensure safety and effectiveness. In this article, we will discuss the importance of proper technique, benefits, and steps involved in administering intramuscular injections, as well as provide tips for healthcare professionals and individuals who self-administer injections.
The technique used for intramuscular injections is crucial to prevent complications such as nerve damage, infection, and incorrect medication absorption. Incorrect technique can lead to serious health issues, making it essential to follow established guidelines and protocols. Moreover, the benefits of intramuscular injections, including faster absorption rates and longer-lasting effects, make them a preferred method for administering certain medications. As the demand for intramuscular injections continues to grow, it is essential to educate healthcare professionals and individuals on the proper technique and best practices.
Intramuscular injections are used for various purposes, including vaccination, medication administration, and hormone replacement therapy. The most common sites for intramuscular injections are the deltoid muscle, vastus lateralis muscle, and gluteal muscle. Each site has its specific guidelines and considerations, making it essential to choose the correct site based on the medication, patient's age, and medical condition. Furthermore, the choice of needle size and syringe type also plays a critical role in ensuring safe and effective administration.
Intramuscular Injection Technique
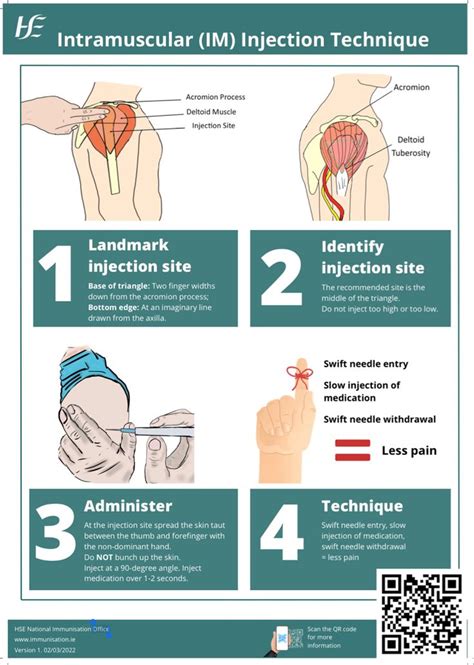
Preparation and Equipment
The preparation and equipment used for intramuscular injections are critical to ensuring safe and effective administration. This includes using sterile needles and syringes, preparing the injection site, and administering the medication at the correct angle and depth. The choice of needle size and syringe type also plays a critical role in ensuring safe and effective administration. For example, a 22-25 gauge needle is recommended for intramuscular injections, while a 1-2 ml syringe is suitable for most medications.Benefits of Intramuscular Injections
Common Sites for Intramuscular Injections
The most common sites for intramuscular injections are the deltoid muscle, vastus lateralis muscle, and gluteal muscle. Each site has its specific guidelines and considerations, making it essential to choose the correct site based on the medication, patient's age, and medical condition. For example, the deltoid muscle is recommended for vaccinations and medications that require rapid absorption, while the vastus lateralis muscle is suitable for medications that require slower absorption rates.Tips for Administering Intramuscular Injections
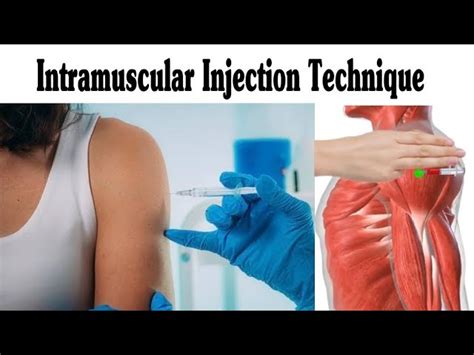
Complications and Adverse Reactions
Intramuscular injections can cause complications and adverse reactions, such as nerve damage, infection, and incorrect medication absorption. It is essential to monitor the patient for any signs of complications or adverse reactions after administering the injection. This includes monitoring for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and pain, and monitoring for signs of nerve damage, such as numbness, tingling, and weakness.Best Practices for Intramuscular Injections

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, intramuscular injections are a common medical procedure used to administer medications, vaccines, and other substances directly into the muscle tissue. The technique used for intramuscular injections is crucial to prevent complications and ensure safety and effectiveness. By following established guidelines and protocols, healthcare professionals and individuals can ensure safe and effective administration of intramuscular injections. Future directions for intramuscular injections include the development of new medications and technologies that can improve the safety and effectiveness of intramuscular injections.What is the most common site for intramuscular injections?
+The most common site for intramuscular injections is the deltoid muscle, followed by the vastus lateralis muscle and gluteal muscle.
What is the recommended needle size for intramuscular injections?
+A 22-25 gauge needle is recommended for intramuscular injections.
What are the benefits of intramuscular injections?
+Intramuscular injections offer several benefits, including faster absorption rates and longer-lasting effects, reduced risk of gastrointestinal side effects, and improved patient compliance.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information on intramuscular injections, including the technique, benefits, and best practices. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
