Intro
Discover if aspirin is an NSAID, exploring its classification, uses, and differences from other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and antiplatelet agents.
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, is one of the most widely used medications worldwide. It has been used for over a century to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent blood clots. One of the most common questions about aspirin is whether it is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). To answer this question, let's dive into the world of aspirin and explore its properties, uses, and classification.
Aspirin has been used for various purposes, including relieving headaches, reducing fever, and preventing heart attacks and strokes. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that cause pain, inflammation, and fever. Aspirin works by blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for producing prostaglandins. By inhibiting COX, aspirin reduces the production of prostaglandins, thereby relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
The classification of aspirin is a topic of interest, and it is often debated whether it is an NSAID. To understand this classification, let's first define what an NSAID is. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications that reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and lower fever. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that cause inflammation and pain. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac.
Is Aspirin an NSAID?

Aspirin is often classified as an NSAID because it shares many similarities with other NSAIDs. Like other NSAIDs, aspirin works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which reduces inflammation and relieves pain. Aspirin also has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic (fever-reducing) effects, which are characteristic of NSAIDs. However, some sources may argue that aspirin is not a true NSAID due to its unique mechanism of action and its ability to inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.
Unique Properties of Aspirin
Aspirin has several unique properties that set it apart from other NSAIDs. One of its most notable properties is its ability to inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. COX-1 is responsible for producing prostaglandins that protect the stomach lining, while COX-2 is responsible for producing prostaglandins that cause inflammation and pain. Aspirin's ability to inhibit both enzymes makes it a versatile medication that can relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent blood clots.Benefits of Aspirin

Aspirin has several benefits that make it a widely used medication. Some of its benefits include:
- Relieving pain and reducing inflammation
- Preventing heart attacks and strokes
- Reducing the risk of colon cancer
- Relieving headaches and migraines
- Reducing fever and relieving symptoms of colds and flu
Risks and Side Effects of Aspirin
While aspirin is generally safe and effective, it can cause several risks and side effects. Some of the most common side effects of aspirin include: * Stomach upset and bleeding * Allergic reactions * Ringing in the ears * Dizziness and drowsiness * Interaction with other medicationsWorking Mechanism of Aspirin
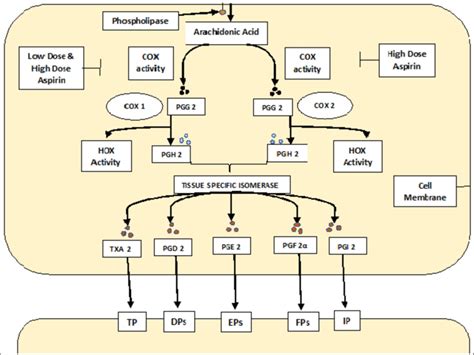
Aspirin works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that cause pain, inflammation, and fever. Its mechanism of action involves blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for producing prostaglandins. By inhibiting COX, aspirin reduces the production of prostaglandins, thereby relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
Steps to Take Aspirin Safely
To take aspirin safely, follow these steps: 1. Consult with your doctor before taking aspirin, especially if you have any medical conditions or take other medications. 2. Take the recommended dose of aspirin, which is usually 81-100 mg per day. 3. Avoid taking aspirin with other medications that may interact with it, such as blood thinners or NSAIDs. 4. Monitor your body for any side effects, such as stomach upset or bleeding. 5. Avoid taking aspirin for extended periods, as it may increase the risk of side effects.Practical Examples of Aspirin Use
Aspirin is widely used for various purposes, including:
- Relieving headaches and migraines
- Reducing fever and relieving symptoms of colds and flu
- Preventing heart attacks and strokes
- Relieving pain and reducing inflammation
- Reducing the risk of colon cancer
Statistical Data on Aspirin Use
According to statistical data, aspirin is one of the most widely used medications worldwide. In the United States alone, over 100 million people take aspirin every day. Aspirin is also widely used in other countries, with over 1 billion people taking it worldwide.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, aspirin is a versatile medication that has been used for over a century to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent blood clots. While it is often classified as an NSAID, aspirin has several unique properties that set it apart from other NSAIDs. To use aspirin safely, follow the recommended dose, consult with your doctor, and monitor your body for any side effects.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with aspirin in the comments below. Have you used aspirin for pain relief or to prevent heart attacks and strokes? What are your thoughts on the benefits and risks of aspirin? Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of aspirin and its proper use.
What is the recommended dose of aspirin?
+The recommended dose of aspirin is usually 81-100 mg per day.
Can I take aspirin with other medications?
+No, you should not take aspirin with other medications that may interact with it, such as blood thinners or NSAIDs.
What are the risks and side effects of aspirin?
+The risks and side effects of aspirin include stomach upset and bleeding, allergic reactions, ringing in the ears, dizziness and drowsiness, and interaction with other medications.
