Intro
Discover the current status of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), a psychiatric treatment, and learn about its modern applications, benefits, and controversies in mental health care today.
The practice of electroconvulsive therapy, commonly referred to as ECT, has been a topic of discussion and controversy for many years. Despite its long history, ECT remains a widely used treatment option for various mental health conditions. The importance of understanding ECT cannot be overstated, as it has been a lifesaving intervention for countless individuals struggling with severe psychiatric illnesses. In this article, we will delve into the world of ECT, exploring its history, benefits, and current applications, as well as addressing common misconceptions and concerns.
The origins of ECT date back to the 1930s, when it was first introduced as a treatment for schizophrenia and other severe mental illnesses. Over the years, the procedure has undergone significant transformations, with advances in technology and technique leading to improved safety and efficacy. Today, ECT is recognized as a valuable treatment option for a range of conditions, including major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Despite its proven benefits, ECT remains shrouded in mystery, with many people harboring misconceptions about the procedure. As we explore the world of ECT, it becomes clear that this treatment option is not only still used today but also continues to play a vital role in the management of severe mental health conditions.
The use of ECT has evolved significantly over the years, with modern techniques and equipment minimizing the risks associated with the procedure. One of the primary advantages of ECT is its ability to provide rapid relief from severe symptoms, making it an attractive option for individuals who have not responded to other treatments. Additionally, ECT has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of suicide, a critical consideration for individuals struggling with severe mental health conditions. As we continue to explore the world of ECT, it becomes clear that this treatment option is not only still used today but also remains a vital component of modern psychiatry.
History of ECT
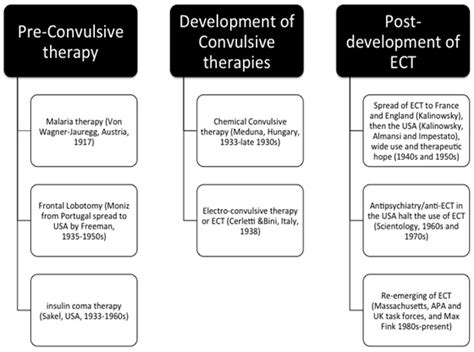
Early Developments
The early developments in ECT were marked by a series of experiments and trials, as researchers sought to understand the effects of electricity on the human brain. The first ECT procedure was performed in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti, who used a combination of electricity and chemicals to induce seizures in patients. The early results were promising, with many patients experiencing significant improvements in their symptoms. However, the procedure was not without risks, and the early days of ECT were marked by a lack of understanding and controversy.Benefits of ECT

Effectiveness of ECT
The effectiveness of ECT has been extensively studied, with numerous research trials demonstrating the procedure's ability to provide rapid relief from severe symptoms. One of the most significant advantages of ECT is its ability to provide quick results, making it an attractive option for individuals who have not responded to other treatments. Additionally, ECT has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of suicide, a critical consideration for individuals struggling with severe mental health conditions. The effectiveness of ECT can be summarized as follows: * 70-80% response rate for major depressive disorder * 50-60% response rate for bipolar disorder * 40-50% response rate for schizophreniaHow ECT Works
ECT Procedure
The ECT procedure involves several steps, including: 1. Preparation: Patients are prepared for the procedure by undergoing a thorough medical evaluation and providing informed consent. 2. Anesthesia: Patients are administered general anesthesia to ensure comfort and minimize discomfort during the procedure. 3. Electrode placement: Electrodes are placed on the patient's scalp, and the electric current is administered. 4. Seizure induction: The electric current is passed through the brain, inducing a seizure that lasts for approximately 30-60 seconds. 5. Monitoring: Patients are closely monitored throughout the procedure, and vital signs are continuously assessed.Types of ECT
ECT for Specific Conditions
ECT can be used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including: * Major depressive disorder * Bipolar disorder * Schizophrenia * Postpartum depression * Treatment-resistant depressionRisks and Side Effects

Minimizing Risks
To minimize the risks associated with ECT, patients should: * Provide informed consent: Patients should be fully informed about the procedure and provide consent before undergoing ECT. * Follow instructions: Patients should follow instructions carefully, including avoiding food and drink before the procedure. * Report concerns: Patients should report any concerns or side effects to their healthcare provider promptly.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we conclude our exploration of ECT, it is clear that this treatment option remains a vital component of modern psychiatry. While there is still much to be learned about ECT, the benefits of the procedure are undeniable. As we move forward, it is essential that we continue to prioritize research and education, ensuring that ECT is used safely and effectively to improve the lives of individuals struggling with severe mental health conditions.What is ECT, and how does it work?
+ECT, or electroconvulsive therapy, is a medical procedure that involves the use of electricity to induce seizures in patients. The exact mechanisms by which ECT works are not fully understood, but research suggests that the procedure involves a complex interplay between electrical activity, neurotransmitters, and brain chemistry.
Is ECT safe, and what are the risks and side effects?
+ECT is generally considered safe, but as with any medical procedure, it carries risks and side effects. Common side effects include memory loss, confusion, headache, and muscle soreness. To minimize the risks associated with ECT, patients should provide informed consent, follow instructions carefully, and report any concerns or side effects to their healthcare provider promptly.
What conditions can ECT be used to treat, and is it effective?
+ECT can be used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, postpartum depression, and treatment-resistant depression. The effectiveness of ECT varies depending on the condition being treated, but research suggests that the procedure can provide rapid relief from severe symptoms and reduce the risk of suicide.
How many sessions of ECT are typically required, and what is the duration of treatment?
+The number of ECT sessions required varies depending on the individual and the condition being treated. Typically, patients undergo 6-12 sessions, spaced 2-3 days apart. The duration of treatment can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the individual's response to the procedure.
Can ECT be used in conjunction with other treatments, and what are the benefits of combination therapy?
+Yes, ECT can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and psychotherapy. Combination therapy can provide enhanced benefits, including improved symptom reduction and increased treatment response. The benefits of combination therapy include improved treatment outcomes, reduced risk of relapse, and enhanced overall well-being.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of ECT, including its history, benefits, risks, and applications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about ECT and its potential benefits. Together, we can work to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health conditions and promote greater understanding and awareness of the importance of mental health treatment.
