Intro
Learn about ischemia medical definition, causes, symptoms, and treatment. Understand blood flow restriction, cardiac ischemia, and peripheral artery disease, and how to manage ischemic conditions for overall well-being.
Ischemia is a medical term that refers to a condition where there is a reduction or cessation of blood flow to a body part, causing a lack of oxygen and nutrients to be delivered to the tissues. This can lead to damage or dysfunction of the affected area, and if left untreated, can result in permanent damage or even death of the tissue. Ischemia can occur in any part of the body, but it is most commonly associated with the heart, brain, and limbs. Understanding the concept of ischemia is crucial in the field of medicine, as it can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
The importance of understanding ischemia cannot be overstated. Ischemia is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it is a major contributor to the development of various diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Furthermore, ischemia can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ischemia, healthcare professionals can provide effective care and improve patient outcomes.
Ischemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including atherosclerosis, blood clots, and trauma. Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque, which can reduce blood flow to the affected area. Blood clots can also block blood flow, causing ischemia. Trauma, such as injuries or surgery, can also disrupt blood flow and lead to ischemia. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, can increase the risk of developing ischemia.
Types of Ischemia

There are several types of ischemia, including cardiac ischemia, cerebral ischemia, and peripheral ischemia. Cardiac ischemia occurs when there is a reduction in blood flow to the heart muscle, which can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. Cerebral ischemia occurs when there is a reduction in blood flow to the brain, which can cause symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and difficulty speaking. Peripheral ischemia occurs when there is a reduction in blood flow to the limbs, which can cause symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness.
Cardiac Ischemia
Cardiac ischemia is a type of ischemia that occurs when there is a reduction in blood flow to the heart muscle. This can be caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. Cardiac ischemia can cause a range of symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. If left untreated, cardiac ischemia can lead to a heart attack, which can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle.Symptoms of Ischemia
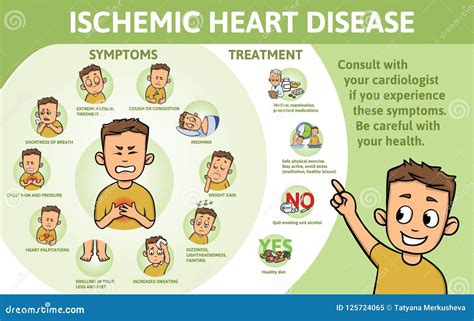
The symptoms of ischemia can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of ischemia include pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. In some cases, ischemia can cause no symptoms at all, which is known as silent ischemia. Silent ischemia can be particularly dangerous, as it can lead to permanent damage or even death of the tissue without any warning signs.
Diagnosis of Ischemia
Diagnosing ischemia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare professionals may use tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and angiogram to diagnose ischemia. An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart, while an echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart. An angiogram uses X-rays and a special dye to visualize the blood vessels and diagnose blockages.Treatment Options for Ischemia
Treatment options for ischemia depend on the location and severity of the condition. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms. Medications such as aspirin, beta blockers, and statins can also help reduce the risk of ischemia. In more severe cases, surgery or angioplasty may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected area.
Prevention of Ischemia
Preventing ischemia involves reducing the risk factors that contribute to the development of the condition. This can include quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet. Additionally, managing underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure can help reduce the risk of ischemia. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can also help identify any potential problems early on, which can improve treatment outcomes.Complications of Ischemia
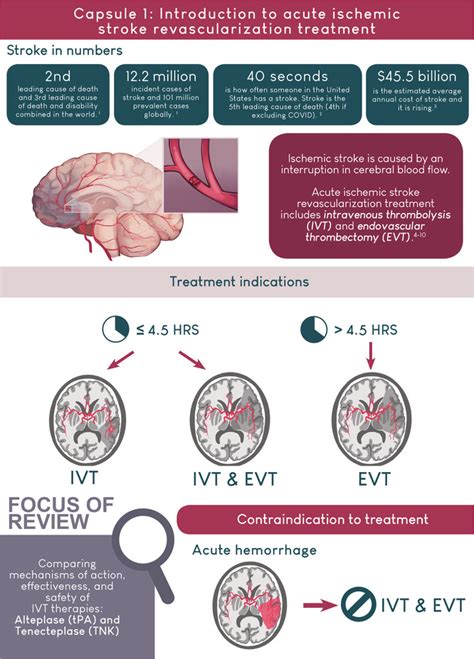
If left untreated, ischemia can lead to a range of complications, including permanent damage or even death of the tissue. In the case of cardiac ischemia, this can lead to a heart attack, which can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle. Cerebral ischemia can lead to a stroke, which can cause permanent damage to the brain. Peripheral ischemia can lead to gangrene, which can result in the loss of a limb.
Current Research on Ischemia
Current research on ischemia is focused on developing new treatments and improving patient outcomes. This includes the development of new medications and surgical techniques, as well as the use of stem cells and gene therapy to repair damaged tissue. Additionally, researchers are working to improve our understanding of the underlying causes of ischemia, which can help identify new targets for treatment.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, ischemia is a complex medical condition that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ischemia is crucial in providing effective care and improving patient outcomes. By continuing to research and develop new treatments, we can improve our understanding of ischemia and develop more effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
Final Thoughts
Ischemia is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the risks and taking steps to prevent ischemia, individuals can reduce their risk of developing the condition. Additionally, by staying informed about the latest research and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and improve their overall health and well-being.What is ischemia?
+Ischemia is a medical term that refers to a condition where there is a reduction or cessation of blood flow to a body part, causing a lack of oxygen and nutrients to be delivered to the tissues.
What are the symptoms of ischemia?
+The symptoms of ischemia can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition, but common symptoms include pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
How is ischemia diagnosed?
+Diagnosing ischemia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and angiogram.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of ischemia, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you have any personal experiences with ischemia or would like to share your thoughts on this topic, we would love to hear from you.
