Intro
Discover 5 isosorbide uses, including heart health, angina treatment, and blood vessel dilation, with benefits for cardiovascular conditions, coronary artery disease, and stroke prevention, exploring its medical applications and therapeutic effects.
The importance of understanding various medical treatments and their applications cannot be overstated. In the realm of cardiovascular health, several medications and compounds play crucial roles in managing conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. One such compound that has garnered significant attention for its therapeutic benefits is Isosorbide. Isosorbide is used in various medical scenarios, primarily for its vasodilatory effects, which make it an essential component in the treatment of certain heart conditions. Its ability to improve blood flow and reduce the workload on the heart makes it a valuable asset in cardiovascular medicine.
Isosorbide's uses extend beyond its most commonly known application, showcasing its versatility and potential in addressing different aspects of cardiovascular health. From managing angina pectoris to its potential role in other medical conditions, the breadth of Isosorbide's applications underscores its significance in modern medicine. As research continues to uncover the full spectrum of Isosorbide's effects and potential uses, its importance in the medical community is likely to grow. This article will delve into the various uses of Isosorbide, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and the conditions it treats, providing a comprehensive overview of its role in healthcare.
The therapeutic applications of Isosorbide are rooted in its pharmacological properties, which allow it to act as a potent vasodilator. By relaxing the smooth muscles in blood vessel walls, Isosorbide facilitates the dilation of these vessels, thereby improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure. This action is particularly beneficial in conditions where increased blood flow is necessary to prevent tissue damage or to alleviate symptoms associated with reduced blood flow. As such, Isosorbide finds its place in the treatment regimens of various cardiovascular conditions, where its vasodilatory effects can be leveraged to improve patient outcomes.
Isosorbide for Angina Pectoris
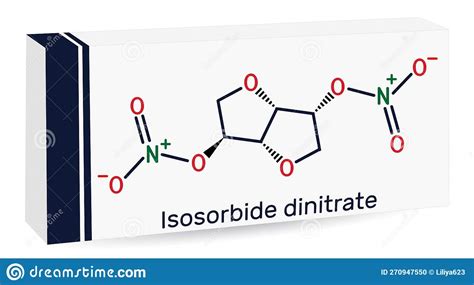
Isosorbide in Heart Failure
Isosorbide for Esophageal Spasms
Isosorbide Dinitrate vs. Isosorbide Mononitrate

Side Effects and Precautions

Key Considerations for Patients
When taking Isosorbide, patients should be aware of the following: - The importance of adhering to the prescribed dosage to minimize side effects and ensure therapeutic efficacy. - The potential for tolerance development with continuous use, which may necessitate dose adjustment or alternative treatment strategies. - The need to stand up slowly from a sitting or lying position to reduce the risk of orthostatic hypotension. - The importance of regular follow-up with healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and adjust the regimen as necessary.Future Directions and Research

Emerging Trends and Technologies
Emerging trends in drug delivery systems and nanotechnology may offer novel approaches to enhancing the bioavailability and targeted delivery of Isosorbide, potentially reducing side effects and improving patient compliance. Additionally, advancements in personalized medicine could allow for more tailored treatment regimens, taking into account individual patient characteristics and genetic profiles to optimize the therapeutic benefits of Isosorbide.What is the primary use of Isosorbide in medicine?
+Isosorbide is primarily used in the management of angina pectoris, due to its vasodilatory effects which help in reducing the workload on the heart and improving blood flow to the myocardium.
How does Isosorbide work to alleviate symptoms of angina?
+Isosorbide works by dilating peripheral blood vessels, which reduces the preload on the heart and subsequently decreases the heart's oxygen demand. This action helps in alleviating the symptoms of angina, such as chest pain and discomfort.
What are the common side effects associated with Isosorbide use?
+The common side effects of Isosorbide include headache, dizziness, and orthostatic hypotension. These side effects are generally related to its vasodilatory action and can often be managed through dose adjustment or patient education.
In conclusion, Isosorbide plays a critical role in the management of various cardiovascular conditions, primarily through its vasodilatory effects. Its applications extend beyond angina pectoris, showcasing its potential in addressing different aspects of cardiovascular health. As research continues to explore the full spectrum of Isosorbide's effects and potential uses, its importance in modern medicine is poised to grow. For individuals seeking to understand more about Isosorbide and its uses, engaging with healthcare professionals and staying updated on the latest research findings can provide valuable insights into its therapeutic benefits and potential applications. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Isosorbide, contributing to a broader discussion on its role in healthcare and its potential to improve patient outcomes.
