Intro
Discover how Ivermectin kills parasites through 5 effective methods, targeting internal parasites, worms, and microorganisms, utilizing antiparasitic properties.
The fight against parasites is a longstanding one, with various treatments and medications being developed over the years to combat these unwanted invaders. One such medication that has gained significant attention in recent times is Ivermectin, a powerful anti-parasitic drug that has been used to treat a wide range of parasitic infections. But how exactly does Ivermectin kill parasites? In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms of action of Ivermectin and explore the different ways it eliminates parasites from the body.
Ivermectin has been widely used for decades to treat parasitic infections in both humans and animals. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of parasites, including nematodes, arthropods, and protozoa, has made it a staple in the treatment of parasitic diseases. But what makes Ivermectin so effective against parasites? The answer lies in its unique mechanism of action, which involves targeting specific channels and receptors in the parasite's nervous system. By understanding how Ivermectin works, we can better appreciate its importance in the fight against parasitic infections.
The importance of Ivermectin in the treatment of parasitic infections cannot be overstated. With millions of people worldwide suffering from parasitic diseases, the need for effective treatments is paramount. Ivermectin has filled this gap, providing a safe and effective way to eliminate parasites from the body. But how does it do it? Let's take a closer look at the different ways Ivermectin kills parasites.
Introduction to Ivermectin
Ivermectin is a semi-synthetic derivative of avermectin, a naturally occurring compound produced by the bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. It was first introduced in the 1980s as a veterinary medication, but its use soon expanded to human medicine due to its efficacy against a wide range of parasites. Ivermectin works by targeting the parasite's nervous system, specifically the glutamate-gated chloride channels. By binding to these channels, Ivermectin increases the flow of chloride ions into the parasite's nerve cells, leading to hyperpolarization and eventual paralysis.
5 Ways Ivermectin Kills Parasites

Ivermectin kills parasites in several ways, including:
- Paralyzing the parasite's nervous system, making it unable to move or feed
- Disrupting the parasite's reproductive cycle, preventing it from multiplying
- Damaging the parasite's cuticle, leading to dehydration and death
- Interfering with the parasite's nutrient uptake, starving it of essential nutrients
- Stimulating the host's immune system to attack and eliminate the parasite
Paralyzing the Parasite's Nervous System
Ivermectin's primary mechanism of action is to paralyze the parasite's nervous system. By binding to the glutamate-gated chloride channels, Ivermectin increases the flow of chloride ions into the parasite's nerve cells, leading to hyperpolarization and eventual paralysis. This paralysis prevents the parasite from moving, feeding, or reproducing, ultimately leading to its death.Benefits of Using Ivermectin

The benefits of using Ivermectin to treat parasitic infections are numerous. Some of the advantages of Ivermectin include:
- High efficacy against a broad spectrum of parasites
- Low toxicity and side effects
- Easy to administer, either orally or topically
- Cost-effective compared to other anti-parasitic medications
- Can be used to treat a wide range of parasitic diseases, including river blindness, lymphatic filariasis, and strongyloidiasis
Disrupting the Parasite's Reproductive Cycle
Ivermectin also disrupts the parasite's reproductive cycle, preventing it from multiplying and spreading. By targeting the parasite's reproductive organs, Ivermectin prevents the production of eggs or larvae, ultimately leading to a decline in the parasite population.Working Mechanism of Ivermectin
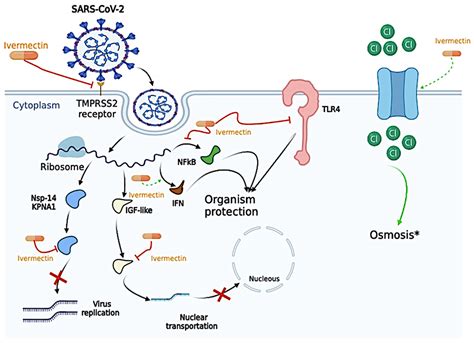
The working mechanism of Ivermectin involves several key steps:
- Binding to glutamate-gated chloride channels: Ivermectin binds to the glutamate-gated chloride channels in the parasite's nervous system, increasing the flow of chloride ions into the nerve cells.
- Hyperpolarization: The increased flow of chloride ions leads to hyperpolarization of the nerve cells, making it difficult for the parasite to transmit nerve impulses.
- Paralysis: The paralysis of the parasite's nervous system prevents it from moving, feeding, or reproducing, ultimately leading to its death.
Damaging the Parasite's Cuticle
Ivermectin also damages the parasite's cuticle, leading to dehydration and death. The cuticle is the outer layer of the parasite's body, and damage to this layer can lead to water loss and eventual death.Steps to Take Ivermectin

To take Ivermectin, follow these steps:
- Consult a healthcare professional to determine the correct dosage and treatment duration
- Take the medication orally, usually with water
- Follow the recommended treatment schedule to ensure maximum efficacy
- Monitor for side effects and report any adverse reactions to a healthcare professional
Interfering with the Parasite's Nutrient Uptake
Ivermectin also interferes with the parasite's nutrient uptake, starving it of essential nutrients. By targeting the parasite's nutrient uptake mechanisms, Ivermectin prevents the parasite from obtaining the necessary nutrients for survival, ultimately leading to its death.Precautions and Side Effects

While Ivermectin is generally safe and effective, there are some precautions and side effects to be aware of:
- Ivermectin can cause allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing
- It can also cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- In rare cases, Ivermectin can cause neurological side effects, such as dizziness, headaches, and seizures
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare professional before taking Ivermectin
Stimulating the Host's Immune System
Ivermectin also stimulates the host's immune system to attack and eliminate the parasite. By activating the host's immune cells, such as macrophages and T-cells, Ivermectin helps to eliminate the parasite from the body.What is Ivermectin used for?
+Ivermectin is used to treat a wide range of parasitic infections, including river blindness, lymphatic filariasis, and strongyloidiasis.
How does Ivermectin work?
+Ivermectin works by targeting the parasite's nervous system, specifically the glutamate-gated chloride channels, leading to hyperpolarization and eventual paralysis.
What are the benefits of using Ivermectin?
+The benefits of using Ivermectin include high efficacy against a broad spectrum of parasites, low toxicity and side effects, and cost-effectiveness compared to other anti-parasitic medications.
In conclusion, Ivermectin is a powerful anti-parasitic medication that kills parasites in several ways, including paralyzing the parasite's nervous system, disrupting the parasite's reproductive cycle, damaging the parasite's cuticle, interfering with the parasite's nutrient uptake, and stimulating the host's immune system. With its high efficacy, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness, Ivermectin has become a staple in the treatment of parasitic diseases. If you have any questions or concerns about Ivermectin or parasitic infections, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Let's work together to raise awareness about the importance of parasitic disease treatment and the benefits of using Ivermectin.
