Intro
Potassium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including muscle contractions, nerve impulses, and heart function. Abnormal potassium levels can lead to serious health complications, making it essential to monitor potassium levels through lab tests. In this article, we will delve into the importance of lab tests for potassium levels, the different types of tests available, and what the results mean.
Potassium levels are crucial for maintaining proper bodily functions. Even slight deviations from normal potassium levels can cause significant health issues. For instance, low potassium levels (hypokalemia) can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias, while high potassium levels (hyperkalemia) can cause cardiac arrest, muscle paralysis, and respiratory failure. Therefore, it is essential to undergo lab tests to determine potassium levels and take corrective measures if necessary.
The human body regulates potassium levels tightly, and any imbalance can have severe consequences. Potassium helps maintain fluid balance, regulates blood pressure, and supports bone health. Moreover, potassium is essential for the proper functioning of nerves and muscles. With the help of lab tests, healthcare professionals can diagnose and treat potassium-related disorders, preventing long-term damage to the body. By understanding the importance of potassium and the role of lab tests, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal potassium levels and overall health.
Types of Lab Tests for Potassium Levels
There are several types of lab tests available to measure potassium levels. The most common test is the serum potassium test, which measures the amount of potassium in the blood. This test is usually performed as part of a routine blood test or to diagnose and monitor conditions such as kidney disease, heart disease, and hormonal imbalances. Other tests, such as the urine potassium test and the blood gas test, can also be used to evaluate potassium levels.
Serum Potassium Test
The serum potassium test is a blood test that measures the amount of potassium in the blood. This test is usually performed in a healthcare setting, and the results are available within a few hours. The test involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The normal range for potassium levels in the blood is between 3.5 and 5.0 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).Urine Potassium Test
The urine potassium test measures the amount of potassium in the urine. This test is usually performed to evaluate kidney function and to diagnose conditions such as kidney disease. The test involves collecting a urine sample over a 24-hour period, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The normal range for potassium levels in the urine is between 25 and 120 milliequivalents per 24 hours.Interpreting Lab Test Results

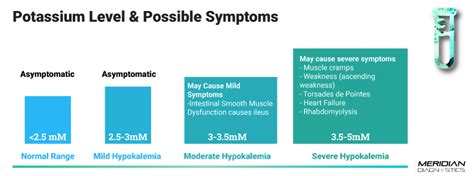
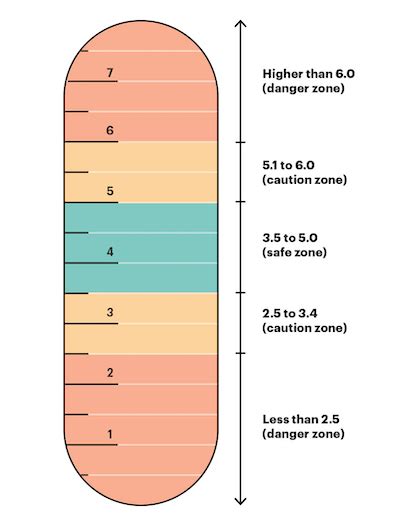
Interpreting lab test results for potassium levels requires a thorough understanding of the normal ranges and the factors that can affect potassium levels. The normal range for potassium levels in the blood is between 3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L. Levels below 3.5 mEq/L indicate hypokalemia, while levels above 5.0 mEq/L indicate hyperkalemia.
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a condition characterized by low potassium levels in the blood. The symptoms of hypokalemia include muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias. Severe hypokalemia can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and even death. Treatment for hypokalemia usually involves potassium supplements and addressing the underlying cause of the condition.Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is a condition characterized by high potassium levels in the blood. The symptoms of hyperkalemia include muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias. Severe hyperkalemia can lead to cardiac arrest, muscle paralysis, and respiratory failure. Treatment for hyperkalemia usually involves medications that help remove excess potassium from the body and addressing the underlying cause of the condition.Causes of Abnormal Potassium Levels
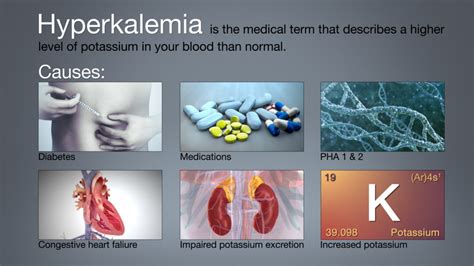
Abnormal potassium levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disease, heart disease, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. Other factors, such as diet, dehydration, and certain medical conditions, can also affect potassium levels.
Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is a common cause of abnormal potassium levels. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating potassium levels, and kidney disease can disrupt this process. Individuals with kidney disease may experience hyperkalemia or hypokalemia, depending on the severity of the disease.Heart Disease
Heart disease is another common cause of abnormal potassium levels. Certain heart conditions, such as heart failure, can lead to hyperkalemia or hypokalemia. Additionally, some medications used to treat heart disease can affect potassium levels.Prevention and Treatment of Abnormal Potassium Levels
Preventing and treating abnormal potassium levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatment. Individuals can take steps to maintain optimal potassium levels by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain medications.
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes can help maintain optimal potassium levels. Foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes, can help prevent hypokalemia. Additionally, avoiding foods high in salt and sugar can help reduce the risk of hyperkalemia.Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and stress management, can also help maintain optimal potassium levels. Exercise can help improve kidney function, while stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce the risk of hyperkalemia.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, lab tests for potassium levels are essential for maintaining optimal health. By understanding the importance of potassium and the role of lab tests, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and treat abnormal potassium levels. If you are concerned about your potassium levels or have questions about lab tests, consult with your healthcare provider. They can help you determine the best course of action and provide guidance on maintaining optimal potassium levels.
What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
+The symptoms of hypokalemia include muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias. Severe hypokalemia can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and even death.
What are the causes of hyperkalemia?
+Hyperkalemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disease, heart disease, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. Other factors, such as diet, dehydration, and certain medical conditions, can also affect potassium levels.
How can I maintain optimal potassium levels?
+Individuals can maintain optimal potassium levels by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain medications. Foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes, can help prevent hypokalemia. Additionally, avoiding foods high in salt and sugar can help reduce the risk of hyperkalemia.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about lab tests for potassium levels. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the importance of potassium and lab tests. Together, we can maintain optimal health and prevent complications related to abnormal potassium levels.
