Intro
Stay updated on Covid strain symptoms, variants, and outbreaks. Learn about infection signs, vaccine efficacy, and prevention measures amidst the pandemics evolving landscape and new wave mutations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been an unprecedented global health crisis, affecting millions of people worldwide. As the virus continues to evolve, new strains have emerged, bringing with them concerns about increased transmissibility, severity, and potential impacts on public health. One of the critical aspects of managing the pandemic is understanding the symptoms associated with these new strains. This knowledge is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of further spread. The symptoms of COVID-19 can vary widely among individuals, and the emergence of new strains has added complexity to this landscape.
The initial strains of COVID-19 presented with a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Common symptoms included fever, dry cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. However, as new strains have emerged, there have been reports of additional symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, sore throat, and gastrointestinal issues. The variability in symptoms can make diagnosis challenging, especially in cases where individuals may not exhibit the classic signs of COVID-19. Furthermore, some people may be asymptomatic, meaning they do not display any symptoms at all, despite being infected and capable of transmitting the virus to others.
The ongoing evolution of COVID-19 strains necessitates continuous monitoring and updates on symptomatology. Healthcare professionals, researchers, and the general public must stay informed about the latest developments to ensure timely and effective responses to the pandemic. This includes understanding the differences in symptoms between various strains, the potential for increased severity or transmissibility, and the implications for vaccination strategies and public health measures. By staying abreast of the latest information, we can better navigate the challenges posed by COVID-19 and work towards mitigating its impact on global health.
Covid Strain Symptoms Overview

Common Symptoms Across Strains
Some symptoms are common across various COVID-19 strains, including: - Fever - Cough - Fatigue - Shortness of breath - Loss of taste and smell - Sore throat - Headache - Muscle or body aches - Diarrhea - Nausea or vomiting These symptoms can appear 2-14 days after exposure to the virus and may vary in severity and duration. It's essential to note that not everyone will develop all of these symptoms, and some may experience additional symptoms not listed here.Variants and Their Symptoms
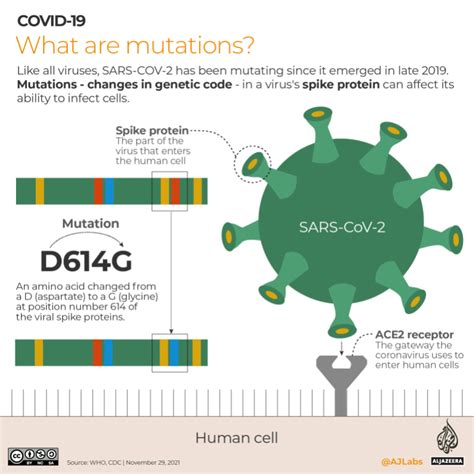
Factors Influencing Symptom Severity
The severity of COVID-19 symptoms can be influenced by several factors, including: 1. **Age**: Older adults are at higher risk of developing severe symptoms. 2. **Underlying Health Conditions**: Individuals with conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and lung disease may experience more severe symptoms. 3. **Vaccination Status**: Vaccinated individuals are less likely to develop severe symptoms and require hospitalization. 4. **Strain of the Virus**: Different strains may have varying levels of transmissibility and severity. 5. **Immune Response**: The body's immune response plays a crucial role in determining the severity of symptoms.Diagnosis and Treatment
Vaccination Efforts
Vaccination has been instrumental in controlling the pandemic, with various vaccines approved for emergency use worldwide. These vaccines have undergone rigorous testing for safety and efficacy and have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe illness and hospitalization due to COVID-19. Booster shots have also been recommended to maintain and enhance immunity over time, especially in light of emerging variants.Public Health Measures

Global Response
The global response to COVID-19 has been multifaceted, involving international cooperation, national policies, and community-level actions. This includes sharing data and research, developing and distributing vaccines, implementing public health measures, and providing economic and social support to affected populations.Future Directions
Personal Responsibility
Each individual has a role to play in managing the pandemic. This includes staying informed about COVID-19, adhering to public health guidelines, getting vaccinated, and supporting those affected by the pandemic. By working together, we can mitigate the effects of COVID-19 and look towards a healthier future.What are the common symptoms of COVID-19 across different strains?
+Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, loss of taste and smell, sore throat, headache, muscle or body aches, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting. However, the specific symptoms can vary depending on the strain and individual factors.
How do vaccines help in preventing COVID-19?
+Vaccines offer protection against COVID-19 by stimulating the body's immune system to recognize and fight the virus, thereby reducing the risk of infection, severe illness, and death. Booster shots can enhance and maintain this protection over time.
What public health measures are most effective in controlling the spread of COVID-19?
+Effective measures include mask-wearing, physical distancing, hand hygiene, avoiding crowds, and quarantine or isolation when necessary. These actions, combined with vaccination, are crucial in managing the pandemic.
As we navigate the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic, staying informed and proactive is key. By understanding the symptoms of different strains, adhering to public health guidelines, and supporting global efforts to combat the virus, we can work towards a future where COVID-19 is under control. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments below, and to consider sharing this article with others to promote awareness and action against COVID-19. Together, we can make a difference and look forward to a healthier, safer world for all.
