Intro
Stay updated on Covid Variant Symptoms with latest news on Omicron, Delta, and new strains, including common signs, vaccination effects, and global health trends.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been an unprecedented global health crisis, affecting millions of people worldwide. As the virus continues to mutate, new variants have emerged, bringing with them concerns about increased transmissibility, severity, and impact on public health. One of the key aspects of understanding these variants is recognizing their symptoms, which can vary from person to person and from one variant to another. Staying informed about the latest developments in COVID-19 variant symptoms is crucial for individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike.
Understanding the symptoms of COVID-19 variants is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in the early detection and diagnosis of the disease, which is critical for providing appropriate care and preventing further transmission. Secondly, recognizing the symptoms can inform public health strategies, such as vaccination campaigns, contact tracing, and quarantine measures. Lastly, awareness of the symptoms can empower individuals to take preventive measures, such as getting vaccinated, wearing masks, and practicing social distancing.
The evolution of COVID-19 variants has been rapid, with new strains emerging and spreading globally. Each variant has its unique characteristics, including differences in symptomatology. For instance, some variants may cause more severe respiratory symptoms, while others may lead to milder symptoms that are often mistaken for the common cold or flu. The variability in symptoms poses a challenge for healthcare systems, as it requires continuous updating of diagnostic criteria and treatment protocols.
Introduction to COVID-19 Variants

The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health authorities have been closely monitoring the emergence of COVID-19 variants. These variants are classified based on their genetic mutations, which can affect the virus's transmissibility, virulence, and ability to evade the immune system. Some of the notable variants include the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron variants, each with its own set of characteristics and implications for public health.
Alpha Variant Symptoms
The Alpha variant, first identified in the United Kingdom, was one of the earliest variants of concern. It was associated with increased transmissibility and a higher risk of hospitalization and death. The symptoms of the Alpha variant were similar to those of the original COVID-19 strain, including fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. However, some individuals infected with the Alpha variant reported more severe symptoms, such as pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Key Symptoms of the Alpha Variant
Some of the key symptoms of the Alpha variant include: - High fever - Persistent cough - Fatigue - Shortness of breath - Chest pain or pressure - Loss of appetite - Headache - Sore throat - Runny nose - DiarrheaBeta Variant Symptoms
The Beta variant, first detected in South Africa, was another variant of concern due to its potential to evade the immune system. The symptoms of the Beta variant were generally milder than those of the Alpha variant but could still lead to severe illness in vulnerable populations. Common symptoms included headache, sore throat, and muscle pain, in addition to the typical COVID-19 symptoms like fever and cough.
Key Symptoms of the Beta Variant
Some of the key symptoms of the Beta variant include: - Mild fever - Headache - Sore throat - Muscle pain - Fatigue - Cough - Shortness of breath - Loss of taste or smell - Nausea or vomiting - DiarrheaGamma Variant Symptoms

The Gamma variant, identified in Brazil, shared some similarities with the Alpha and Beta variants in terms of its genetic mutations. However, its symptom profile was distinct, with a higher prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Respiratory symptoms, such as cough and shortness of breath, were also common but tended to be less severe than in the Alpha variant.
Key Symptoms of the Gamma Variant
Some of the key symptoms of the Gamma variant include: - Fever - Cough - Shortness of breath - Fatigue - Headache - Sore throat - Nausea or vomiting - Diarrhea - Abdominal pain - Loss of appetiteDelta Variant Symptoms
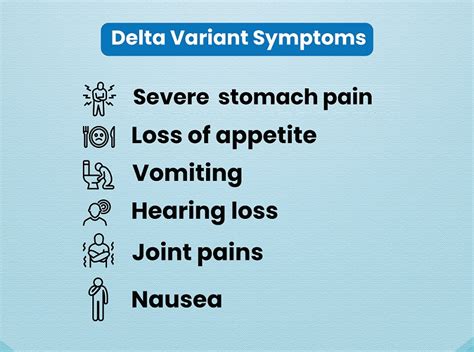
The Delta variant, first identified in India, became a dominant strain globally due to its high transmissibility. The symptoms of the Delta variant were often more severe and included a higher risk of hospitalization and death, particularly among unvaccinated individuals. Common symptoms included fever, cough, and shortness of breath, as well as more severe manifestations like pneumonia and respiratory failure.
Key Symptoms of the Delta Variant
Some of the key symptoms of the Delta variant include: - High fever - Persistent cough - Shortness of breath - Fatigue - Chest pain or pressure - Loss of appetite - Headache - Sore throat - Runny nose - DiarrheaOmicron Variant Symptoms
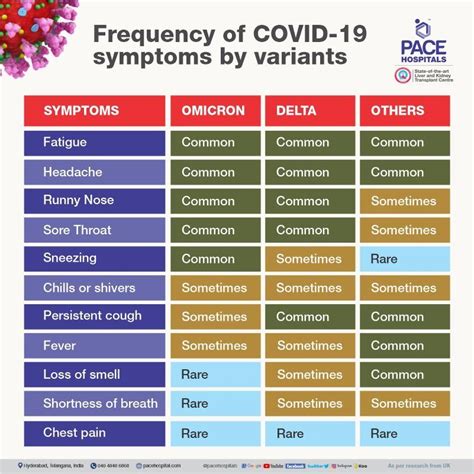
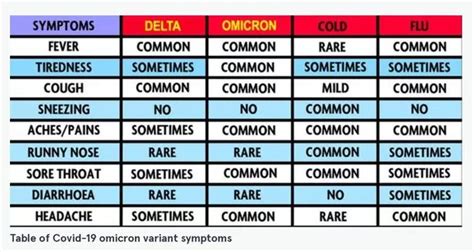
The Omicron variant, first detected in South Africa, marked a significant shift in the pandemic due to its high transmissibility and ability to evade immune responses. The symptoms of the Omicron variant tend to be milder, with many individuals experiencing symptoms similar to the common cold, such as runny nose, sore throat, and fatigue. However, the variant can still cause severe illness, particularly in older adults and those with underlying health conditions.
Key Symptoms of the Omicron Variant
Some of the key symptoms of the Omicron variant include: - Mild fever - Runny nose - Sore throat - Fatigue - Cough - Shortness of breath - Headache - Loss of taste or smell - Nausea or vomiting - DiarrheaVaccination and Prevention

Vaccination remains one of the most effective strategies for preventing COVID-19 and reducing the risk of severe illness and death. The development of vaccines that target specific variants has been a critical aspect of the global response to the pandemic. In addition to vaccination, preventive measures such as wearing masks, practicing social distancing, and improving ventilation can significantly reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
Key Prevention Strategies
Some of the key prevention strategies include: - Getting vaccinated with the recommended doses - Wearing masks in public places - Practicing social distancing - Avoiding crowded areas - Improving ventilation in indoor spaces - Frequently washing hands with soap and water - Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sickConclusion and Future Directions

The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of global cooperation, scientific research, and public health preparedness. As new variants emerge, it is crucial to continue monitoring their symptoms, transmission patterns, and impact on public health. The development of effective vaccines, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic interventions will be critical in managing the pandemic and reducing its socioeconomic burden.
The future directions in managing COVID-19 variants will likely involve a multi-faceted approach, including enhanced surveillance, rapid diagnostic testing, and targeted vaccination campaigns. Additionally, promoting public awareness and adherence to preventive measures will be essential in controlling the spread of the virus. As the world continues to navigate the challenges of the pandemic, it is clear that a comprehensive and coordinated response will be necessary to mitigate its effects and protect global health.
What are the most common symptoms of COVID-19 variants?
+The most common symptoms of COVID-19 variants include fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, headache, sore throat, and loss of taste or smell. However, the specific symptoms can vary depending on the variant and the individual's immune response.
How can I protect myself from COVID-19 variants?
+To protect yourself from COVID-19 variants, get vaccinated with the recommended doses, wear masks in public places, practice social distancing, avoid crowded areas, and frequently wash your hands with soap and water.
What is the role of vaccination in preventing COVID-19 variants?
+Vaccination plays a critical role in preventing COVID-19 variants by reducing the risk of severe illness and death. Vaccines can also help prevent the transmission of the virus, thereby reducing the spread of variants.
We invite readers to share their thoughts, experiences, and questions regarding COVID-19 variants and their symptoms. Your engagement can help foster a community of informed individuals who are better equipped to navigate the challenges of the pandemic. Please feel free to comment below, share this article with others, or take specific actions to protect yourself and your community from COVID-19 variants.
