Intro
Unlock the secrets of LDH blood test results, understanding lactate dehydrogenase levels, enzyme elevations, and diagnostic implications for liver and tissue damage, with expert insights on test interpretation and related health conditions.
The LDH blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of lactate dehydrogenase, an enzyme found in various tissues throughout the body. Elevated LDH levels can indicate tissue damage or disease, making it a valuable marker for diagnosing and monitoring a range of medical conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of LDH blood test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what factors can influence their accuracy.
The importance of understanding LDH blood test results cannot be overstated. By grasping the significance of these results, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care, and individuals can better comprehend their health status. Whether you are a medical professional or simply looking to understand your test results, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to LDH blood tests.
LDH blood tests are commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as liver disease, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. The test is also used to assess tissue damage after a heart attack or other traumatic injuries. With its wide range of applications, it is essential to understand the intricacies of LDH blood test results to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
What is LDH?
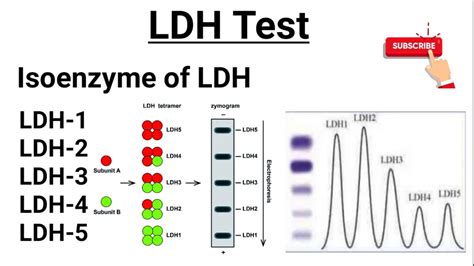
How is the LDH Test Performed?
The LDH test is a relatively simple procedure that involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the level of LDH is measured using a specialized assay. The results are typically reported in units per liter (U/L) or international units per liter (IU/L).Interpreting LDH Blood Test Results
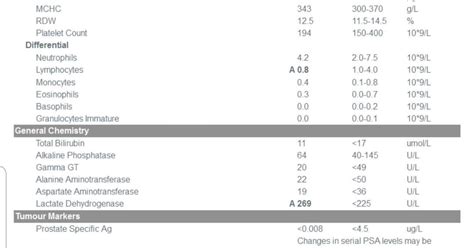
Elevated LDH levels can indicate tissue damage or disease. For example, high LDH levels may be seen in individuals with liver disease, heart disease, or certain types of cancer. On the other hand, low LDH levels are relatively rare and may indicate a deficiency in the enzyme or a condition such as anemia.
Factors that Influence LDH Levels
Several factors can influence LDH levels, including: * Age: LDH levels tend to increase with age * Sex: LDH levels are generally higher in men than in women * Pregnancy: LDH levels may be elevated during pregnancy * Exercise: Intense exercise can increase LDH levels * Certain medications: Some medications, such as statins and anticonvulsants, can affect LDH levelsLDH Isoenzymes
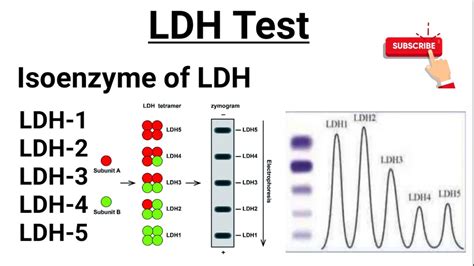
Clinical Significance of LDH Isoenzymes
The clinical significance of LDH isoenzymes lies in their ability to provide tissue-specific information. For example: * Elevated LDH-1 levels may indicate heart damage or disease * Elevated LDH-5 levels may indicate liver or muscle damage * Elevated LDH-2 levels may indicate kidney damage or diseaseCommon Conditions Associated with Elevated LDH Levels
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of conditions associated with elevated LDH levels depend on the underlying cause. For example: * Liver disease: Treatment may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery * Heart disease: Treatment may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery * Cancer: Treatment may involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery * Muscle disease: Treatment may involve physical therapy, medications, or surgeryLimitations and Potential Drawbacks
Future Directions
Future directions for the LDH test include the development of more sensitive and specific assays, as well as the exploration of new clinical applications. For example: * The use of LDH as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and monitoring * The use of LDH to monitor tissue damage and disease in real-timeWhat is the normal range for LDH levels?
+The normal range for LDH levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other health factors. In general, a normal LDH range is between 100 and 190 U/L.
What does an elevated LDH level indicate?
+An elevated LDH level can indicate tissue damage or disease, such as liver disease, heart disease, or certain types of cancer.
How is the LDH test performed?
+The LDH test involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the limitations of the LDH test?
+The LDH test has several limitations, including the fact that elevated LDH levels are not specific to a particular condition or disease, and that LDH levels can be influenced by a range of factors.
What is the clinical significance of LDH isoenzymes?
+The clinical significance of LDH isoenzymes lies in their ability to provide tissue-specific information, which can be used to diagnose and monitor a range of medical conditions.
In conclusion, understanding LDH blood test results is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring a range of medical conditions. By grasping the significance of these results, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care, and individuals can better comprehend their health status. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about LDH blood tests in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
