Intro
The world of grains is incredibly diverse, offering a wide range of options that cater to different tastes, dietary needs, and cultural preferences. Grains are a staple food in many parts of the world, providing essential nutrients, fiber, and energy. Understanding the various types of grains can help individuals make informed choices about their diet, explore new recipes, and appreciate the cultural significance of these foods.
Grains have been a cornerstone of human nutrition for thousands of years, with evidence of grain cultivation dating back to ancient civilizations. They are a rich source of carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose and used by the body for energy. Additionally, whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious choice for those seeking to maintain a healthy diet.
The importance of grains extends beyond their nutritional value, as they also play a significant role in food security, sustainable agriculture, and cultural heritage. Different regions around the world have their unique grain preferences, reflecting local traditions, climate conditions, and historical influences. For instance, rice is a staple in many Asian countries, while wheat and barley are more commonly consumed in Western societies. Exploring the diverse world of grains can be a fascinating journey, offering insights into the culinary practices, agricultural systems, and social norms of various cultures.
Types Of Grains

There are numerous types of grains, each with its distinct characteristics, uses, and nutritional profile. Broadly, grains can be categorized into two main groups: whole grains and refined grains. Whole grains include the bran, germ, and endosperm of the grain, providing more fiber, nutrients, and health benefits compared to refined grains, which are processed to remove the bran and germ.
Some of the most commonly consumed grains include wheat, rice, corn, oats, barley, quinoa, and rye. Each of these grains has its unique properties and uses in cooking. For example, wheat is often used to make bread, pasta, and cereals, while rice is a staple in many cuisines, served as a side dish or used as an ingredient in various recipes.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are considered the healthier option due to their higher content of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are less processed, retaining more of their natural nutrients and antioxidants. Examples of whole grains include brown rice, whole wheat, oats, and quinoa. Incorporating whole grains into one's diet can have several health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.Benefits Of Grains

The benefits of grains are multifaceted, ranging from their nutritional value to their role in sustainable agriculture and food security. Here are some key benefits of grains:
- Nutritional Value: Grains are a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Whole grains, in particular, are rich in nutrients and antioxidants.
- Energy Source: Grains are an excellent source of energy due to their carbohydrate content, making them an ideal food for individuals with high energy requirements.
- Food Security: Grains are a staple food in many parts of the world, contributing significantly to food security, especially in regions where other food sources may be scarce.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Grain production can be managed sustainably, incorporating practices that reduce environmental impact, such as crop rotation and organic farming methods.
Grain-Based Diets
Grain-based diets are common in many cultures, with grains serving as the primary source of nutrition. These diets can be highly nutritious if they include a variety of whole grains, which provide a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. A well-planned grain-based diet can help maintain a healthy weight, support digestive health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.Grain Production And Trade

Grain production and trade play a vital role in the global food system, with many countries relying on grain imports to meet their food needs. The global grain market is influenced by factors such as climate change, agricultural policies, and economic trends. Understanding the dynamics of grain production and trade can provide insights into issues related to food security, sustainability, and economic development.
The process of grain production involves several stages, from planting and harvesting to processing and distribution. Advances in agricultural technology have improved grain yields and efficiency, allowing for more food to be produced with fewer resources. However, these advances also raise concerns about the environmental impact of large-scale farming and the potential for genetic modification of grain crops.
Sustainable Grain Production
Sustainable grain production is crucial for maintaining soil health, conserving water, and reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture. Practices such as organic farming, crop rotation, and precision agriculture can help achieve these goals. Additionally, supporting local grain producers and choosing sustainable grain products can contribute to a more environmentally friendly food system.Culinary Uses Of Grains

Grains are incredibly versatile, with a wide range of culinary uses across different cultures. From traditional dishes like sushi (made with Japanese rice) and pasta (made from wheat) to modern creations like grain salads and bowls, grains can be prepared in numerous ways to suit various tastes and dietary preferences.
Some popular culinary uses of grains include:
- Baking: Grains like wheat, rye, and oats are used to make bread, cakes, and pastries.
- Side Dishes: Rice, quinoa, and barley are often served as side dishes, accompanied by vegetables, meats, or sauces.
- Breakfast Foods: Oats and wheat are commonly used in breakfast cereals and porridges.
- Snacks: Grains like corn and rice are used to make snack foods such as chips and crackers.
Grain Recipes
Exploring grain recipes from around the world can be a fascinating culinary adventure, introducing individuals to new flavors, textures, and cooking techniques. For example, trying out a traditional Japanese recipe for onigiri (triangular rice balls) or an Indian recipe for biryani (a mixed rice dish) can be a great way to experience the diversity of grain-based cuisine.Health Considerations
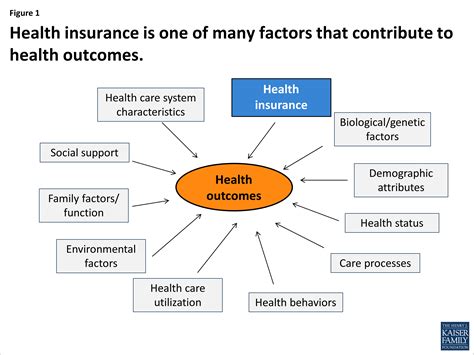
While grains are a nutritious food group, there are several health considerations to be aware of, particularly for individuals with specific dietary needs or restrictions. For instance, some people may have gluten intolerance or celiac disease, requiring them to avoid gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye.
Other health considerations include:
- Glycemic Index: Some grains, especially refined grains, have a high glycemic index, which can cause a spike in blood sugar levels.
- Allergies and Intolerances: Besides gluten, some individuals may be allergic or intolerant to other grains, such as corn or rice.
- Phytic Acid: Whole grains contain phytic acid, a compound that can inhibit the absorption of minerals like zinc and iron.
Nutritional Balance
Achieving nutritional balance is key when consuming grains as part of a healthy diet. This involves choosing whole grains over refined grains, varying grain sources, and ensuring that grain intake is balanced with other food groups like fruits, vegetables, proteins, and healthy fats.Future Of Grains

The future of grains is closely tied to global challenges such as climate change, population growth, and sustainable development. As the world seeks to feed a growing population while minimizing environmental impact, grains will play a critical role. Innovations in grain production, such as precision agriculture and vertical farming, may offer solutions to these challenges.
Moreover, the development of new grain varieties that are more resilient to climate change, have higher nutritional content, or are more efficient in water use can contribute to a more sustainable food system. Consumer trends towards healthier, more sustainable, and locally sourced foods are also expected to influence the grain industry, with a potential shift towards more organic and specialty grain production.
Sustainability And Innovation
Sustainability and innovation are at the forefront of the grain industry's future, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving grain yields, reducing environmental footprint, and enhancing nutritional quality. As consumers become more aware of the environmental and health implications of their food choices, the demand for sustainable and nutritious grain products is likely to increase.What are the health benefits of whole grains?
+Whole grains offer several health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer, due to their high content of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
How can I incorporate more whole grains into my diet?
+You can incorporate more whole grains into your diet by choosing whole grain bread, brown rice instead of white rice, whole grain pasta, and oats for breakfast. Also, try to vary your grain sources to get a broad range of nutrients.
Are all grains gluten-free?
+No, not all grains are gluten-free. Grains like wheat, barley, and rye contain gluten. However, grains such as rice, quinoa, and corn are naturally gluten-free, making them suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of food production, sustainability, and health, grains will undoubtedly remain a vital component of our diets and agricultural systems. By exploring the diverse world of grains, understanding their nutritional benefits, and embracing sustainable production practices, we can work towards a future where grains contribute to a healthier, more sustainable food system for all. Whether you're a food enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or someone interested in sustainable living, the world of grains has much to offer, inviting you to delve deeper into its richness and diversity. So, take the first step today, and discover the wonderful world of grains for yourself.
