Intro
Learn about Listeria symptoms in pregnancy, including foodborne illness risks, prenatal complications, and maternal health concerns, to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a critical period in a woman's life, filled with excitement, anticipation, and a multitude of physical changes. While many women experience a healthy pregnancy, there are certain health risks that can pose a threat to both the mother and the unborn baby. One such risk is listeria, a type of bacterial infection that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Listeria symptoms in pregnancy can be subtle, making it essential for expectant mothers to be aware of the warning signs and take necessary precautions to prevent infection.
Listeria is a type of foodborne illness caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. It can be found in contaminated food, water, and soil, and can also be spread through contact with infected animals or people. Pregnant women are more susceptible to listeria due to their weakened immune system, which can make it harder for their body to fight off the infection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pregnant women are 10 times more likely to get listeriosis than non-pregnant women.
The risk of listeria infection during pregnancy is a significant concern, as it can lead to serious health complications for both the mother and the baby. Listeria can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, and low birth weight, making it crucial for expectant mothers to be aware of the symptoms and take preventive measures. In this article, we will delve into the world of listeria, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies, as well as providing valuable insights and advice for pregnant women to minimize their risk of infection.
Listeria Infection Causes and Risk Factors
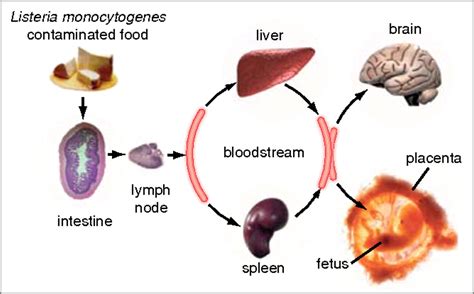
- Age: Pregnant women over 65 years old are at higher risk of listeria infection
- Weakened immune system: Women with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to listeria
- Pregnancy complications: Women with pregnancy complications, such as placenta previa or preeclampsia, are at higher risk of listeria infection
Foodborne Listeria Risks
Listeria can be found in a variety of foods, including: * Unpasteurized dairy products, such as raw milk and soft cheeses * Hot dogs and deli meats * Refrigerated pâtés and meat spreads * Unwashed raw vegetables and fruits * Contaminated soil and waterListeria Symptoms in Pregnancy
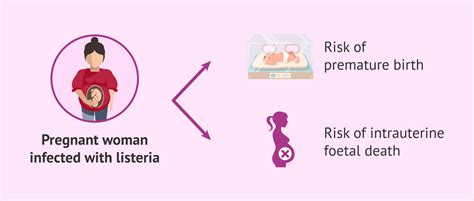
In some cases, listeria can cause more severe symptoms, such as:
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Septicemia
- Stillbirth or miscarriage
Diagnosing Listeria Infection
Listeria infection can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Laboratory tests may include: * Blood tests to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes * Urine tests to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes * Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, to monitor fetal developmentTreatment and Prevention Strategies

Prevention strategies for listeria infection include:
- Avoiding high-risk foods, such as unpasteurized dairy products and hot dogs
- Cooking food thoroughly, especially meat and poultry
- Washing hands frequently, especially after handling raw meat or vegetables
- Avoiding cross-contamination of food and surfaces
- Keeping the refrigerator at a temperature below 40°F (4°C)
Safe Food Handling Practices
To minimize the risk of listeria infection, pregnant women should follow safe food handling practices, including: * Washing hands frequently with soap and water * Separating raw meat and vegetables from ready-to-eat foods * Cooking food thoroughly, especially meat and poultry * Refrigerating perishable foods promptly * Avoiding cross-contamination of food and surfacesComplications of Listeria Infection
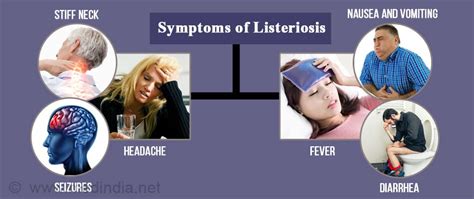
Neonatal Listeriosis
Neonatal listeriosis is a serious infection that can occur in newborns. Symptoms may include: * Fever * Lethargy * Poor feeding * Vomiting * Diarrhea * Respiratory distressConclusion and Next Steps

If you are pregnant and have concerns about listeria infection, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and guidance on how to minimize your risk of infection.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with listeria infection in the comments below. Have you or someone you know been affected by listeria? What steps have you taken to minimize your risk of infection? Share your story and help raise awareness about this critical health issue.
What is listeria, and how is it transmitted?
+Listeria is a type of bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. It can be found in contaminated food, water, and soil, and can also be spread through contact with infected animals or people.
What are the symptoms of listeria infection in pregnancy?
+Listeria symptoms in pregnancy can be subtle and may resemble flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, muscle aches, headache, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
How can I prevent listeria infection during pregnancy?
+To prevent listeria infection, pregnant women should follow safe food handling practices, avoid high-risk foods, cook food thoroughly, and wash hands frequently. They should also avoid cross-contamination of food and surfaces and keep the refrigerator at a temperature below 40°F (4°C).
What are the complications of listeria infection in pregnancy?
+Listeria infection can cause serious complications for both the mother and the baby, including miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, low birth weight, and neonatal listeriosis.
How is listeria infection diagnosed and treated?
+Listeria infection can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, such as ampicillin or penicillin, and in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor the mother and the baby.
