Intro
Unlock the secrets of your liver health with our comprehensive Liver Blood Test Results Guide, covering ALT, AST, and GGT levels, liver function, and abnormal results, to help you understand your liver health and take proactive steps towards wellness.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in our overall health, responsible for filtering toxins, producing bile, and regulating various bodily functions. When it comes to assessing liver health, blood tests are a crucial diagnostic tool. Liver blood test results can help identify potential issues, monitor existing conditions, and guide treatment decisions. Understanding what these tests measure and how to interpret the results is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals concerned about their liver health.
Liver function tests, also known as liver panels, typically include a series of tests that evaluate various aspects of liver function. These tests can detect liver damage, inflammation, or disease, allowing for early intervention and potentially improving outcomes. The importance of liver blood tests cannot be overstated, as liver diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer, can have severe consequences if left undiagnosed or untreated. By understanding liver blood test results, individuals can better navigate their health, making informed decisions about their well-being.
The complexity of liver function and the variety of tests available can make interpreting liver blood test results seem daunting. However, breaking down the key components and understanding what each test measures can simplify the process. From alanine transaminase (ALT) to bilirubin levels, each test provides valuable insights into liver health. Whether you're a healthcare professional seeking to refine your diagnostic skills or an individual looking to understand your test results, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of liver blood tests, their interpretation, and the implications for health and treatment.
Liver Function Tests: An Overview
Liver function tests are a group of tests used to assess the state of the liver and its ability to perform its vital functions. These tests can be categorized into several types, each measuring different aspects of liver health. The most common liver function tests include:
- Alanine Transaminase (ALT): Measures the level of ALT, an enzyme found primarily in the liver. Elevated levels can indicate liver damage or disease.
- Aspartate Transaminase (AST): Similar to ALT, AST measures another enzyme found in the liver, as well as in muscles. High levels can suggest liver damage or muscle disease.
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): This test measures the level of ALP, an enzyme related to the liver and bones. Elevated levels can indicate liver disease, bone disorders, or other conditions.
- Bilirubin: Measures the level of bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. High levels can indicate liver dysfunction or a disorder affecting the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT): This test measures the level of GGT, an enzyme found in the liver. Elevated levels can suggest liver disease, alcohol use, or other conditions.
Interpreting Liver Blood Test Results

Interpreting liver blood test results requires considering the individual's overall health, symptoms, and medical history. Normal ranges for these tests can vary slightly between laboratories, but generally:
- ALT and AST levels are considered normal when they are below 40 IU/L.
- ALP levels typically range from 30 to 120 IU/L.
- Bilirubin levels are usually considered normal when they are below 1.2 mg/dL.
- GGT levels are typically normal when they are below 60 IU/L.
Elevated levels of these enzymes and substances can indicate liver damage or disease. For instance, high ALT and AST levels may suggest hepatitis or liver injury, while elevated bilirubin levels could indicate jaundice or a liver disorder affecting the processing of bilirubin.
Understanding Elevated Liver Enzymes
Elevated liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, are a common finding in liver blood tests. These elevations can result from various conditions, including: - Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E) - Alcoholic liver disease - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) - Autoimmune hepatitis - Liver cancer - Medication-induced liver injuryEach of these conditions has distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. For example, viral hepatitis may require antiviral medication, while alcoholic liver disease necessitates cessation of alcohol consumption.
Liver Disease Diagnosis and Management
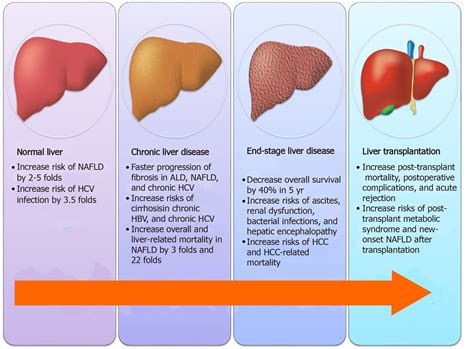
Diagnosing liver disease often involves a combination of liver blood tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or MRI), and sometimes a liver biopsy. Management and treatment of liver diseases depend on the underlying cause and can include:
- Medications to treat the underlying condition (e.g., antivirals for hepatitis)
- Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss for NAFLD or cessation of alcohol use for alcoholic liver disease
- Surgical interventions, such as liver transplantation in advanced cases of liver failure
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for preventing the progression of liver disease and improving outcomes.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing liver disease or managing existing conditions often involves lifestyle changes and preventive measures, including: - Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of NAFLD - Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption - Practicing safe sex and avoiding intravenous drug use to prevent viral hepatitis - Getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B - Avoiding exposure to toxins and certain medications that can harm the liverBy adopting these preventive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing liver disease.
Advanced Liver Disease and Liver Transplantation
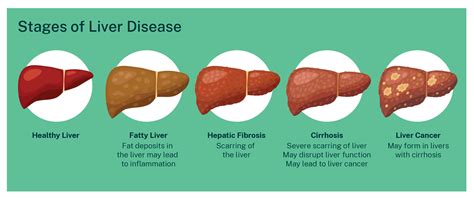
In cases where liver disease progresses to advanced stages, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, liver transplantation may be the only viable treatment option. Liver transplantation involves surgically replacing the diseased liver with a healthy liver from a donor. This procedure is a life-saving intervention for individuals with end-stage liver disease.
The process of liver transplantation includes:
- Evaluation for transplantation suitability
- Placement on a transplant waiting list
- Surgery to remove the diseased liver and implant the donor liver
- Post-transplant care and immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection
Liver transplantation offers a second chance at life for many individuals with advanced liver disease, highlighting the importance of organ donation and the need for increased awareness about liver health.
Living with a Liver Transplant
After receiving a liver transplant, individuals must adhere to a lifelong regimen of immunosuppressive medications to prevent the body from rejecting the new liver. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor liver function, adjust medication as needed, and address any potential complications early.Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances, is also essential for the long-term success of the transplant.
Future Directions in Liver Disease Management

Research into liver diseases is ongoing, with promising developments in areas such as:
- Gene therapy for inherited liver diseases
- Novel antiviral treatments for hepatitis
- Stem cell therapies for liver regeneration
- Personalized medicine approaches for tailored treatment plans
These advancements hold potential for improving the diagnosis, treatment, and management of liver diseases, offering hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for affected individuals.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are being explored for their potential to enhance liver disease diagnosis and treatment. For example, AI can help analyze medical images more accurately and quickly, potentially leading to earlier detection of liver diseases.Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine and digital health platforms can improve access to care for individuals with liver diseases, especially those in remote or underserved areas.
Conclusion and Next Steps

Understanding liver blood test results and the implications for liver health is a critical step towards maintaining overall well-being. By recognizing the importance of liver function, adopting preventive measures, and seeking medical care when necessary, individuals can play an active role in protecting their liver health.
For those diagnosed with liver disease, a comprehensive treatment plan, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing medical care can significantly improve outcomes. As research continues to advance our understanding and management of liver diseases, there is hope for more effective treatments and better quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions regarding liver health and blood test results in the comments below. Your engagement can help foster a community of support and awareness, promoting better liver health for everyone.
What is the purpose of liver function tests?
+Liver function tests are used to assess the state of the liver and its ability to perform its vital functions, helping to diagnose liver damage or disease.
How often should liver blood tests be performed?
+The frequency of liver blood tests depends on individual health needs and risk factors. Individuals with liver disease or at high risk may need regular testing, while others may only require occasional screening.
Can liver disease be prevented?
+Yes, many forms of liver disease can be prevented through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, practicing safe sex, and getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
