Intro
Discover how a liver panel works, revealing 7 key ways to diagnose liver health, including liver function tests, enzyme levels, and bilirubin checks, to detect liver damage, disease, and dysfunction.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. It is responsible for filtering toxins, producing bile, and regulating various bodily functions. A liver panel, also known as a liver function test, is a series of blood tests that help assess the health and functioning of the liver. In this article, we will delve into the world of liver panels and explore how they work, their benefits, and what the results can indicate about our liver health.
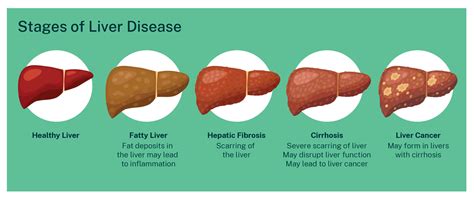
The liver is a complex organ that performs numerous functions, including detoxification, metabolism, and production of essential proteins. It is also responsible for storing glycogen, regulating blood sugar levels, and producing bile to aid in digestion. Given its critical role, it is essential to monitor liver health regularly, especially for individuals who are at risk of liver damage or disease. A liver panel is a valuable tool that helps healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor liver conditions, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Liver panels typically include a range of tests that measure various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood. These tests can help identify liver damage or disease, as well as monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Some common tests included in a liver panel are alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), and bilirubin. Each of these tests provides valuable information about liver function and can help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage liver conditions.
What is a Liver Panel?
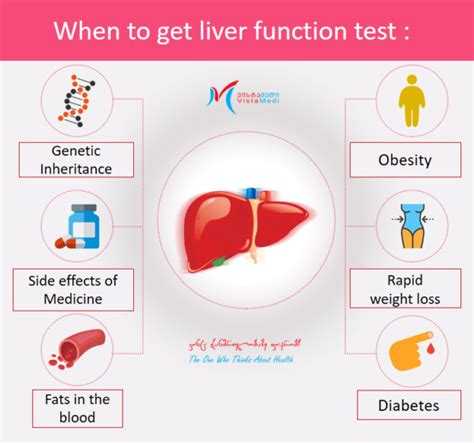
Benefits of a Liver Panel
The benefits of a liver panel are numerous. It can help healthcare professionals diagnose liver conditions, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. It can also help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and identify potential liver damage or disease. Additionally, a liver panel can help healthcare professionals assess the risk of liver disease in individuals who are at risk, such as those with a family history of liver disease or those who have been exposed to hepatitis.How Does a Liver Panel Work?
Tests Included in a Liver Panel
Some common tests included in a liver panel are: * Alanine transaminase (ALT): This test measures the level of ALT in the blood, which can indicate liver cell damage. * Aspartate transaminase (AST): This test measures the level of AST in the blood, which can indicate liver cell damage. * Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): This test measures the level of ALP in the blood, which can indicate bile duct obstruction or liver cell damage. * Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): This test measures the level of GGT in the blood, which can indicate liver cell damage or bile duct obstruction. * Bilirubin: This test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood, which can indicate liver cell damage or bile duct obstruction.Interpreting Liver Panel Results
What Do Abnormal Results Mean?
Abnormal results on a liver panel can indicate liver damage or disease. Some possible causes of abnormal results include: * Liver cell damage: Elevated levels of ALT or AST can indicate liver cell damage, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. * Bile duct obstruction: Elevated levels of ALP or GGT can indicate bile duct obstruction, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including gallstones, tumors, or inflammation. * Liver protein production: Abnormal levels of liver proteins, such as albumin or globulin, can indicate liver damage or disease.Risk Factors for Liver Disease
Reducing the Risk of Liver Disease
There are several ways to reduce the risk of liver disease, including: * Maintaining a healthy weight * Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption * Getting vaccinated against hepatitis * Practicing safe sex * Avoiding sharing needles or other equipmentLiver Panel and Diagnosis
Using a Liver Panel to Diagnose Liver Conditions
A liver panel can be used to diagnose liver conditions in several ways: * Identifying liver cell damage: Elevated levels of ALT or AST can indicate liver cell damage, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. * Identifying bile duct obstruction: Elevated levels of ALP or GGT can indicate bile duct obstruction, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including gallstones, tumors, or inflammation. * Monitoring liver protein production: Abnormal levels of liver proteins, such as albumin or globulin, can indicate liver damage or disease.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with liver panels in the comments section below. Have you had a liver panel test? What were your results, and how did you use the information to improve your liver health? Your feedback and insights can help others better understand the importance of liver health and the role of liver panels in maintaining it.
What is a liver panel test?
+A liver panel test is a series of blood tests that measure various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood to assess liver function and health.
What are the benefits of a liver panel test?
+The benefits of a liver panel test include diagnosing liver conditions, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, and identifying potential liver damage or disease.
What are the risk factors for liver disease?
+Risk factors for liver disease include family history of liver disease, exposure to hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
How can I reduce my risk of liver disease?
+You can reduce your risk of liver disease by maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, getting vaccinated against hepatitis, practicing safe sex, and avoiding sharing needles or other equipment.
What are the common tests included in a liver panel?
+Common tests included in a liver panel are alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), and bilirubin.
