Intro
Discover how Loperamide provides rapid diarrhea relief, alleviating symptoms of acute and chronic diarrhea, including travelers diarrhea, with its anti-diarrheal properties, offering fast and effective treatment for gastrointestinal issues.
Diarrhea is a common health issue that affects people of all ages, causing discomfort, dehydration, and disruption to daily life. While it can be caused by various factors, including viral or bacterial infections, food intolerance, and underlying medical conditions, the primary goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. One of the most widely used medications for diarrhea relief is loperamide, which has been a staple in many medicine cabinets for decades. In this article, we will delve into the world of loperamide, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications, as well as discussing its potential side effects and interactions.
The importance of effective diarrhea treatment cannot be overstated, as it can lead to severe dehydration, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with compromised immune systems. Loperamide has been shown to be a highly effective medication in managing diarrhea symptoms, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities with minimal disruption. Moreover, its widespread availability and relatively low cost make it an accessible treatment option for people around the world. As we explore the topic of loperamide for diarrhea relief, we will examine the science behind its effectiveness, its potential benefits and drawbacks, and provide practical guidance on how to use it safely and effectively.
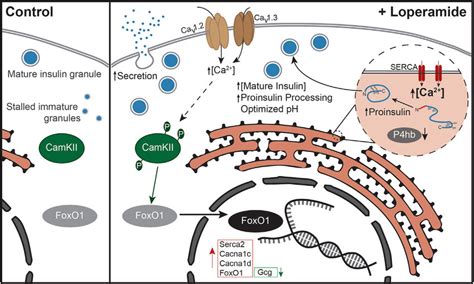
Loperamide works by slowing down the movement of the gut, allowing the body to absorb more water and electrolytes from the fecal material, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of diarrhea episodes. This mechanism of action is made possible by loperamide's ability to bind to opioid receptors in the intestinal wall, which in turn reduces the contraction of intestinal muscles and decreases the secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestine. As a result, loperamide provides rapid relief from diarrhea symptoms, often within a few hours of administration. Furthermore, its effectiveness in managing diarrhea has been extensively studied, with numerous clinical trials demonstrating its superiority over placebo in reducing stool frequency and improving stool consistency.
Loperamide Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Loperamide
The benefits of loperamide for diarrhea relief are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using loperamide include: * Rapid relief from diarrhea symptoms, often within a few hours of administration * Effective in reducing stool frequency and improving stool consistency * Available over-the-counter, making it easily accessible to individuals in need * Relatively low cost compared to other diarrhea treatments * Can be used in combination with other medications, such as antibiotics, to treat underlying infections * Suitable for use in a variety of populations, including adults, children, and individuals with compromised immune systemsLoperamide Side Effects and Interactions

Loperamide Dosage and Administration
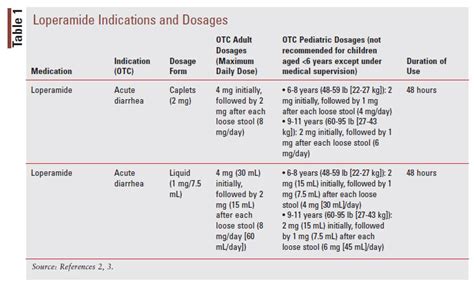
The dosage and administration of loperamide vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition. Generally, the recommended dose of loperamide for adults is 4mg after the first loose stool, followed by 2mg after each subsequent loose stool, up to a maximum of 16mg per day. For children, the recommended dose is 1-2mg after the first loose stool, followed by 1mg after each subsequent loose stool, up to a maximum of 8mg per day. It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure effective treatment.Loperamide vs. Other Diarrhea Treatments
Practical Applications of Loperamide
Loperamide has a wide range of practical applications, from treating acute diarrhea episodes to managing chronic diarrhea conditions. Some examples of practical applications of loperamide include: * Traveler's diarrhea: Loperamide can be used to treat diarrhea caused by bacterial or viral infections while traveling abroad. * Food poisoning: Loperamide can be used to treat diarrhea caused by food poisoning, reducing the risk of dehydration and other complications. * Inflammatory bowel disease: Loperamide can be used to manage chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. * Cancer treatment: Loperamide can be used to manage diarrhea caused by cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.Loperamide and Pregnancy
Loperamide and Breastfeeding
Loperamide is excreted in breast milk, and its effects on nursing infants are not well understood. While loperamide is generally considered safe to use during breastfeeding, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication. Loperamide can increase the risk of constipation in nursing infants, and its long-term effects on infant development are not well understood. As with any medication, it is crucial to weigh the benefits and risks of using loperamide during breastfeeding and to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines.Loperamide Overdose and Toxicity
Loperamide Interactions with Other Medications
Loperamide can interact with other medications, including: * Opioid medications * Antihistamines * Antibiotics * Antacids * Anti-diarrheal medications It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication, especially if you are taking other medications or have underlying medical conditions.Loperamide Warnings and Precautions

Loperamide Storage and Disposal
Loperamide should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Loperamide should be disposed of properly, and any unused medication should be returned to a pharmacy or other authorized facility.Loperamide Conclusion and Future Directions

As we conclude our discussion on loperamide for diarrhea relief, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with this medication. Have you used loperamide to treat diarrhea, and if so, what were your results? Do you have any questions or concerns about using loperamide, and if so, how can we address them? By engaging in a dialogue about loperamide and its uses, we can work together to promote better health outcomes and improve the lives of individuals affected by diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disorders.
What is loperamide, and how does it work?
+Loperamide is a medication that works by slowing down the movement of the gut, allowing the body to absorb more water and electrolytes from the fecal material, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of diarrhea episodes.
What are the benefits of using loperamide for diarrhea relief?
+The benefits of using loperamide for diarrhea relief include rapid relief from symptoms, effective reduction of stool frequency and improvement of stool consistency, and a relatively low risk of side effects.
Can loperamide be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, loperamide can be used in combination with other medications, such as antibiotics, to treat underlying infections. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication, especially if you are taking other medications or have underlying medical conditions.
Is loperamide safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Loperamide is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications.
What are the potential side effects of loperamide, and how can they be managed?
+The potential side effects of loperamide include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and constipation. These side effects can be managed by following the recommended dosage and administration guidelines, staying hydrated, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
