Intro
Discover the proper Lorazepam 1mg dosage guide, including usage, side effects, and interactions, to ensure safe and effective treatment for anxiety and insomnia, with expert advice on dosing, warnings, and precautions.
Lorazepam, commonly known by its brand name Ativan, is a medication that belongs to the class of benzodiazepines. It is widely used for its anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. Lorazepam 1mg is a common dosage for various conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. Understanding the proper use, benefits, and potential risks of lorazepam 1mg is crucial for individuals who are prescribed this medication.
The importance of following a lorazepam 1mg dosage guide cannot be overstated. Incorrect dosages can lead to adverse effects, reduced efficacy, or even dependence on the drug. Furthermore, lorazepam interacts with various other medications and substances, which can significantly alter its effects. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting lorazepam treatment and to adhere strictly to their prescribed dosage and administration instructions.
Lorazepam's mechanism of action involves enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter in the brain that promotes calmness and reduces anxiety. By increasing GABA's activity, lorazepam helps to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, induce relaxation, and improve sleep quality. However, due to its potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms, lorazepam is typically recommended for short-term use.
Lorazepam 1mg Uses and Benefits

Lorazepam 1mg is prescribed for a variety of medical conditions. Its primary uses include the treatment of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorders. It is also effective in managing insomnia, particularly in cases where difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep is a significant issue. Additionally, lorazepam can be used as a premedication before surgical procedures to reduce anxiety and induce sedation.
The benefits of lorazepam 1mg include its rapid onset of action, which provides quick relief from anxiety symptoms. It is also available in various formulations, including tablets and injectables, making it versatile for different clinical settings. Furthermore, lorazepam has a relatively short half-life, which reduces the risk of accumulation and potential for abuse compared to some other benzodiazepines.
Administration and Dosage
The administration and dosage of lorazepam 1mg depend on the patient's medical condition, age, and response to treatment. For anxiety, the typical starting dose is 1mg to 2mg orally two to three times a day. For insomnia, a dose of 1mg to 2mg taken at bedtime is common. It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions and not to exceed the recommended dose without consulting them first.Side Effects and Interactions
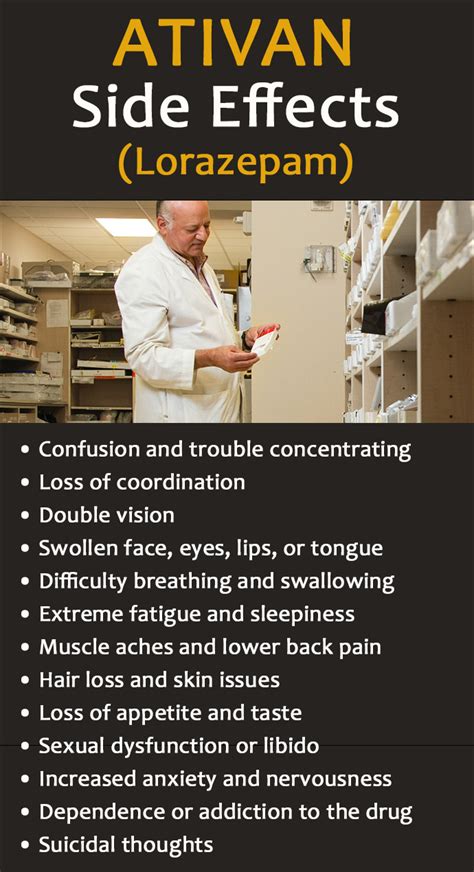
Like all medications, lorazepam 1mg can cause side effects, some of which are more common than others. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, and headache. Less common but more serious side effects can include memory problems, confusion, depression, and paradoxical reactions such as agitation or aggression.
Lorazepam can interact with a wide range of substances, including alcohol, opioids, and other central nervous system depressants, which can enhance its sedative effects and increase the risk of respiratory depression. It is also important to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions.
Risks and Precautions
Given its potential for dependence and abuse, lorazepam is a controlled substance in many countries. Patients with a history of substance abuse or those taking lorazepam for extended periods are at higher risk of developing dependence. Withdrawal symptoms can occur when the medication is stopped abruptly, and these can range from mild (anxiety, insomnia) to severe (seizures, psychosis).Pregnant women should use lorazepam with caution, as benzodiazepines can pass through the placenta and may cause harm to the fetus. Similarly, breastfeeding mothers should consult their healthcare provider before taking lorazepam, as it can be excreted in breast milk.
Lorazepam 1mg for Anxiety and Insomnia
For individuals suffering from anxiety disorders or insomnia, lorazepam 1mg can provide significant relief. Its anxiolytic effects can help reduce anxiety symptoms, making it easier to manage daily activities. For insomnia, lorazepam's ability to induce relaxation and reduce sleep latency can improve sleep quality and duration.
However, it is crucial to address the underlying causes of anxiety and insomnia rather than solely relying on medication. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, can complement lorazepam treatment and potentially reduce the need for medication over time.
Alternatives and Lifestyle Changes
There are several alternatives to lorazepam for managing anxiety and insomnia, including other medications and non-pharmacological interventions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness, and relaxation techniques can be effective in reducing anxiety symptoms without the risk of dependence associated with benzodiazepines.Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can also improve sleep quality. For some individuals, alternative herbal supplements like melatonin or valerian root may offer a safer, non-habit-forming option for managing insomnia.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, lorazepam 1mg is a valuable medication for the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia. However, its use must be carefully managed to minimize the risk of dependence and adverse effects. By understanding the benefits, risks, and proper use of lorazepam, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Future research should continue to explore safer, more effective treatments for anxiety and insomnia, including non-pharmacological interventions and novel medications with lower potential for abuse. Additionally, efforts to improve public awareness about the proper use of benzodiazepines like lorazepam can help mitigate the risks associated with these medications.
Final Thoughts
As with any medication, the decision to use lorazepam 1mg should be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider. By working together with healthcare professionals and adopting a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety and insomnia, individuals can find relief from their symptoms while minimizing the risks associated with lorazepam treatment.What is the typical dosage of lorazepam for anxiety?
+The typical starting dose of lorazepam for anxiety is 1mg to 2mg orally two to three times a day.
Can lorazepam be used for long-term treatment of insomnia?
+Lorazepam is generally recommended for short-term use due to its potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Long-term use should be avoided unless under the close supervision of a healthcare provider.
Are there any alternatives to lorazepam for managing anxiety and insomnia?
+We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about lorazepam 1mg in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
