Intro
The world of pharmaceuticals is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of conditions. One such medication is Lovenox, which belongs to a specific class of drugs known as low molecular weight heparins. Understanding the classification of Lovenox and its mechanism of action is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. In this article, we will delve into the details of Lovenox, its uses, benefits, and potential side effects, as well as explore the broader context of low molecular weight heparins.
Lovenox, also known by its generic name enoxaparin, is a prescription medication used to prevent and treat blood clots. Blood clots can be life-threatening if they occur in critical areas such as the lungs or brain, leading to conditions like pulmonary embolism or stroke. The importance of medications like Lovenox cannot be overstated, as they play a vital role in the management and prevention of these potentially fatal conditions. The drug works by inhibiting the formation of new clots and preventing existing ones from growing.
The classification of Lovenox as a low molecular weight heparin is significant. Low molecular weight heparins are a subclass of heparin, a naturally occurring anticoagulant found in the body. Unlike unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparins like Lovenox have a more predictable dose-response relationship, which makes them easier to administer and monitor. This predictability reduces the risk of over-anticoagulation, a condition where the blood becomes too thin, leading to an increased risk of bleeding.
Lovenox Drug Class and Mechanism of Action
Lovenox exerts its anticoagulant effect through the inhibition of factor Xa and, to a lesser extent, thrombin. Factor Xa is a crucial enzyme in the coagulation cascade, the series of reactions that lead to the formation of a blood clot. By inhibiting factor Xa, Lovenox effectively reduces the formation of new clots and prevents the growth of existing ones. This mechanism of action is specific and targeted, reducing the risk of bleeding compared to older anticoagulants.
The benefits of Lovenox are numerous. It is effective in preventing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism, especially in patients undergoing major surgery or who are at high risk due to prolonged immobilization. Lovenox is also used to treat acute DVT and pulmonary embolism, showcasing its versatility in both prevention and treatment. Furthermore, its once or twice daily subcutaneous administration makes it a convenient option for patients, enhancing compliance and reducing the need for close monitoring compared to other anticoagulants.
Benefits and Uses of Lovenox

The uses of Lovenox are diverse and include the prevention of blood clots in patients with a history of DVT or pulmonary embolism, as well as in those at high risk due to recent surgery, trauma, or immobilization. It is also used in the management of acute coronary syndrome, where the risk of clot formation is high. The effectiveness of Lovenox in these scenarios has been demonstrated through numerous clinical trials, which have shown a significant reduction in the incidence of clot-related events.
Despite its benefits, Lovenox can cause side effects. The most common side effect is bleeding, which can range from minor bruising at the injection site to more severe bleeding events. Other potential side effects include thrombocytopenia (a decrease in platelet count), allergic reactions, and elevations in liver enzymes. Monitoring for these side effects is crucial, especially in patients with a history of bleeding disorders or those taking other medications that may increase the risk of bleeding.
Potential Side Effects of Lovenox

The administration of Lovenox requires careful consideration of the patient's renal function, as the drug is primarily excreted by the kidneys. Dose adjustments may be necessary in patients with renal impairment to avoid accumulation of the drug and increase the risk of bleeding. Additionally, patients should be educated on the proper technique for self-administration, as well as the importance of adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen.
In comparison to other anticoagulants, Lovenox offers several advantages. Its predictable pharmacokinetic profile and once or twice daily dosing make it more convenient than unfractionated heparin, which requires continuous intravenous infusion and close monitoring. Lovenox also has a lower risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia compared to unfractionated heparin, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Comparison with Other Anticoagulants
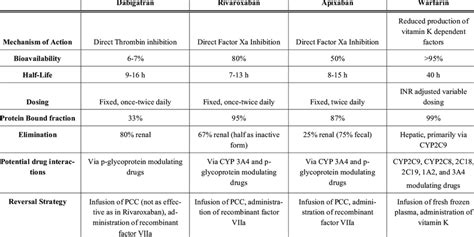
The future of anticoagulation therapy is evolving, with new oral anticoagulants (NOACs) offering an alternative to traditional heparins and vitamin K antagonists like warfarin. NOACs, such as rivaroxaban and apixaban, have the advantage of oral administration and do not require regular blood monitoring. However, they also come with their own set of risks and benefits, and the choice between Lovenox and a NOAC depends on various factors, including the patient's specific condition, renal function, and the presence of other medications that may interact with the anticoagulant.
Future Directions in Anticoagulation Therapy
In conclusion, Lovenox is a valuable medication in the management and prevention of blood clots. Its classification as a low molecular weight heparin, its mechanism of action, and its benefits make it a preferred choice for many patients. While it is not without side effects, careful patient selection, monitoring, and education can minimize risks. As the field of anticoagulation continues to evolve, medications like Lovenox will remain crucial in the prevention and treatment of thrombotic disorders.
Final Thoughts on Lovenox and Anticoagulation Therapy

We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about Lovenox and anticoagulation therapy. Your feedback is invaluable in helping us understand the complexities of these medications and how they impact patients' lives. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What is Lovenox used for?
+Lovenox is used to prevent and treat blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
How does Lovenox work?
+Lovenox works by inhibiting the formation of new clots and preventing existing ones from growing through the inhibition of factor Xa.
What are the potential side effects of Lovenox?
+Potential side effects include bleeding, thrombocytopenia, allergic reactions, and elevations in liver enzymes.
