Intro
Discover how low CO2 levels impact blood health, causing respiratory issues, numbness, and dizziness, and learn about carbon dioxides crucial role in blood pH balance, oxygen delivery, and overall well-being.
The human body is a complex system that relies on a delicate balance of various elements to function properly. One of these essential elements is carbon dioxide (CO2), a colorless, odorless gas that plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's acid-base balance. While high levels of CO2 can be detrimental to health, low CO2 levels can also have significant effects on the body, particularly on the blood. In this article, we will explore the importance of CO2 in the body, the causes and symptoms of low CO2 levels, and the ways in which low CO2 levels can affect blood.
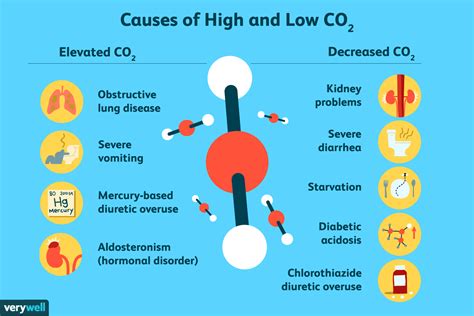
The body's CO2 levels are regulated by the respiratory system, which removes excess CO2 from the body through exhalation. However, when CO2 levels drop too low, it can disrupt the body's delicate balance and lead to various health problems. Low CO2 levels, also known as hypocapnia, can be caused by a range of factors, including hyperventilation, high-altitude environments, and certain medical conditions. Symptoms of low CO2 levels can include dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
Low CO2 levels can have significant effects on the blood, including changes in blood pH, reduced oxygen delivery to tissues, and increased blood viscosity. These effects can have serious consequences, including respiratory alkalosis, decreased athletic performance, and increased risk of blood clots. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the ways in which low CO2 levels can affect blood and explore the potential consequences of these effects.
Introduction to Low Co2 Levels and Blood
Causes and Symptoms of Low Co2 Levels
Low CO2 levels can be caused by a range of factors, including hyperventilation, high-altitude environments, and certain medical conditions. Hyperventilation, which is characterized by rapid and deep breathing, can quickly reduce CO2 levels in the blood. High-altitude environments, where the air pressure is lower, can also lead to low CO2 levels due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Certain medical conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can also increase the risk of low CO2 levels.Effects of Low Co2 Levels on Blood pH
Reduced Oxygen Delivery to Tissues
Low CO2 levels can also reduce oxygen delivery to tissues, which can have significant effects on the body. When CO2 levels drop, the blood's ability to release oxygen to tissues is impaired, leading to a decrease in oxygen delivery. This can have serious consequences, including decreased athletic performance, as the body's tissues are not receiving the oxygen they need to function properly.Increased Blood Viscosity
Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition characterized by an increase in blood pH due to hyperventilation. When CO2 levels drop, the body's acid-base balance is disrupted, leading to an increase in blood pH. This can have significant consequences, including dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.Treatment and Prevention of Low Co2 Levels

Practical Tips for Maintaining Healthy Co2 Levels
Here are some practical tips for maintaining healthy CO2 levels: * Practice proper breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing, to avoid hyperventilation. * Avoid high-altitude environments, or take steps to acclimatize to high altitudes. * Manage underlying medical conditions, such as asthma and COPD, to reduce the risk of low CO2 levels. * Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support proper blood function.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Final Thoughts and Recommendations
In final thoughts, it is crucial to prioritize maintaining healthy CO2 levels to support proper blood function and overall health. By practicing proper breathing techniques, avoiding high-altitude environments, and managing underlying medical conditions, individuals can reduce the risk of low CO2 levels. Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet can support proper blood function and overall health.What are the causes of low CO2 levels?
+Low CO2 levels can be caused by a range of factors, including hyperventilation, high-altitude environments, and certain medical conditions.
What are the symptoms of low CO2 levels?
+Symptoms of low CO2 levels can include dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
How can low CO2 levels affect blood?
+Low CO2 levels can affect blood by changing blood pH, reducing oxygen delivery to tissues, and increasing blood viscosity.
What are the treatment options for low CO2 levels?
+Treatment options for low CO2 levels include addressing the underlying cause, such as hyperventilation or high-altitude environments, and practicing proper breathing techniques.
How can I maintain healthy CO2 levels?
+Individuals can maintain healthy CO2 levels by practicing proper breathing techniques, avoiding high-altitude environments, and managing underlying medical conditions.
