Intro
Discover low fiber vegetable options, including low-fiber veggies, gentle greens, and easily digestible roots, perfect for sensitive stomachs and digestive health, with tips on managing fiber intake.
The importance of a balanced diet cannot be overstated, and one crucial aspect of this balance is the intake of fiber. While fiber is essential for healthy digestion and bowel function, there are instances where individuals may need to limit their fiber intake. This could be due to certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or preparation for specific medical procedures that require a low-fiber diet. Understanding which vegetables are low in fiber is vital for managing these requirements effectively.
For individuals who are looking to reduce their fiber intake, it's essential to know that not all vegetables are created equal when it comes to fiber content. Some vegetables are naturally lower in fiber compared to others, making them suitable options for a low-fiber diet. It's also important to note that while reducing fiber intake, it's crucial to ensure that the diet remains balanced and nutrient-rich to avoid any nutritional deficiencies. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a dietitian can provide personalized advice tailored to individual needs.
The world of vegetables is vast and varied, offering numerous options that can fit into a low-fiber dietary plan. From leafy greens to root vegetables, there's a wide range of choices available. By understanding the fiber content of different vegetables, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, ensuring they meet their nutritional needs while adhering to any necessary dietary restrictions. This knowledge empowers individuals to take control of their health, making it easier to navigate the complexities of dietary management.
Introduction to Low Fiber Vegetables
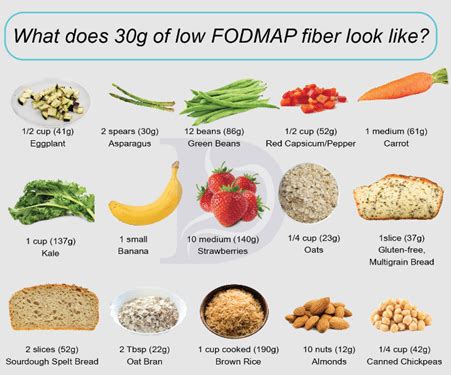
When considering a low-fiber diet, it's crucial to focus on vegetables that are inherently low in fiber. These typically include certain types of cucumbers, bell peppers, and tomatoes, among others. The key is to understand the nutritional content of the vegetables you're consuming to make informed choices. This section will delve into the specifics of low-fiber vegetable options, providing a comprehensive overview of the choices available.
Benefits of Low Fiber Vegetables
The benefits of incorporating low-fiber vegetables into your diet are multifaceted. Not only do they provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, but they also offer a way to manage certain health conditions that require a reduction in fiber intake. For individuals with digestive issues, low-fiber vegetables can be easier to digest, reducing discomfort and promoting overall gastrointestinal health. Furthermore, these vegetables can be a valuable component of a balanced diet, ensuring that nutritional needs are met without exacerbating health issues.Types of Low Fiber Vegetables
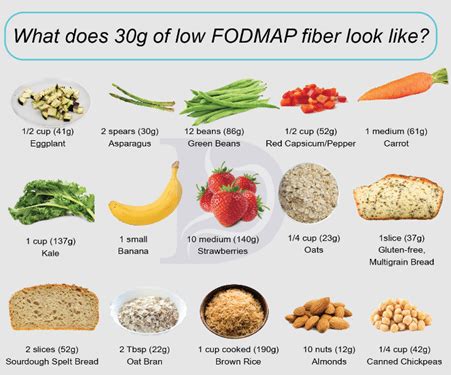
There are several types of vegetables that are considered low in fiber, making them ideal for individuals who need to limit their fiber intake. These include:
- Cucumbers: With a fiber content of about 0.5 grams per 100 grams, cucumbers are one of the lowest fiber vegetables.
- Bell Peppers: Green, red, or yellow, bell peppers contain approximately 1.7 grams of fiber per 100 grams, making them a low to moderate fiber option.
- Tomatoes: Fresh tomatoes have about 1 gram of fiber per 100 grams, although this can vary slightly depending on the variety and preparation.
- Zucchini: This summer squash has a fiber content of around 1 gram per 100 grams, making it a good choice for low-fiber diets.
- Yellow Squash: Similar to zucchini, yellow squash is low in fiber, with approximately 1 gram per 100 grams.
Preparing Low Fiber Vegetables
Preparing low-fiber vegetables can be straightforward and versatile. These vegetables can be cooked in a variety of ways, including steaming, roasting, grilling, or sautéing, which helps retain their nutritional value. For individuals on a low-fiber diet, it's also important to avoid adding high-fiber ingredients during preparation. For example, using herbs and spices for flavor instead of high-fiber sauces or seasonings can help keep the fiber content low.Nutritional Value of Low Fiber Vegetables
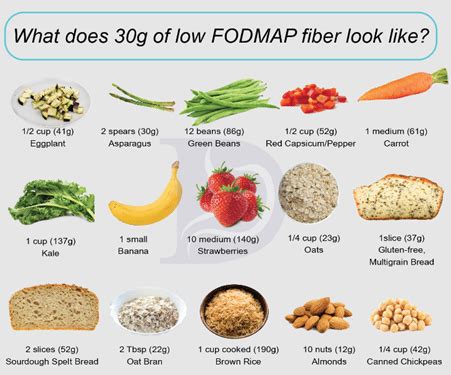
Despite being low in fiber, these vegetables are rich in other essential nutrients. They are good sources of vitamins A and C, potassium, and antioxidants. For instance, bell peppers are high in vitamin C, while tomatoes are rich in lycopene, an antioxidant that has been linked to several health benefits. Understanding the nutritional value of these vegetables can help individuals make the most of their dietary choices, ensuring they get the nutrients they need.
Health Benefits of Low Fiber Vegetables
The health benefits of low-fiber vegetables are significant. They can help support healthy digestion in individuals who need to limit their fiber intake, reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders, and provide essential vitamins and minerals. Additionally, the antioxidants and other nutrients in these vegetables can contribute to overall health, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain cancers.Managing a Low Fiber Diet
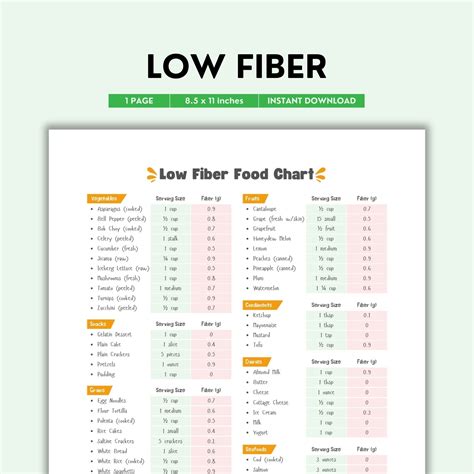
Managing a low-fiber diet requires careful planning and attention to the nutritional content of the foods consumed. It's essential to read food labels, understand portion sizes, and be aware of hidden sources of fiber in foods. Additionally, consulting with a healthcare provider or a dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support, helping individuals navigate the challenges of a low-fiber diet effectively.
Tips for a Balanced Low Fiber Diet
To maintain a balanced diet while limiting fiber intake, consider the following tips: - Focus on lean protein sources and healthy fats in addition to low-fiber vegetables. - Choose whole foods over processed ones whenever possible to minimize unwanted additives and fiber. - Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, as this can help with digestion and overall health. - Consider supplements if necessary, under the guidance of a healthcare provider, to ensure all nutritional needs are met.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, managing a low-fiber diet requires a deep understanding of the fiber content of various foods, particularly vegetables. By focusing on low-fiber vegetable options and understanding their nutritional value, individuals can make informed dietary choices that support their health needs. As research continues to evolve, it's likely that new insights into the benefits and management of low-fiber diets will emerge, offering even more tailored advice for individuals with specific dietary requirements.
Final Thoughts on Low Fiber Diets
The journey to a healthier lifestyle through dietary management is highly personal and can be influenced by numerous factors, including health conditions, lifestyle, and personal preferences. For those who require a low-fiber diet, the path forward involves not just limiting fiber intake but also ensuring that the diet remains balanced and nutrient-rich. By embracing the variety of low-fiber vegetables available and staying informed about nutritional content, individuals can navigate their dietary needs with confidence.What are the primary benefits of a low-fiber diet?
+A low-fiber diet can be beneficial for individuals with certain digestive issues, as it may help reduce discomfort and manage conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It's also sometimes recommended before certain medical procedures to minimize the risk of complications.
How can I ensure I'm getting enough nutrients on a low-fiber diet?
+To ensure you're getting enough nutrients, focus on consuming a variety of low-fiber foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Also, consider consulting with a dietitian or healthcare provider who can offer personalized advice and recommend supplements if necessary.
Are there any potential risks associated with long-term low-fiber diets?
+Yes, long-term low-fiber diets can lead to nutrient deficiencies and may increase the risk of constipation and other digestive issues. It's crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor health and adjust the diet as needed to prevent potential complications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with low-fiber diets in the comments below. Your insights can help others who are navigating similar dietary requirements. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can create a supportive community that prioritizes health and wellness.
