Intro
Discover a comprehensive Low Fibre Foods List, featuring low-fiber diet options, gentle digestive foods, and minimal residue foods for sensitive stomachs and digestive health management.
The importance of fibre in our diet cannot be overstated. Fibre plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system, promoting satiety, and supporting healthy blood sugar levels. However, with the increasing prevalence of processed and refined foods, many of us are not getting enough fibre in our diets. In fact, the average person consumes less than half of the daily recommended intake of fibre. To make matters worse, some foods are notoriously low in fibre, making it even more challenging to meet our daily needs. In this article, we will delve into the world of low fibre foods, exploring what they are, why they are problematic, and how we can make informed choices to boost our fibre intake.
A low fibre diet can have serious consequences for our health, including constipation, diverticulitis, and even an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, a diet lacking in fibre can lead to a range of digestive issues, from bloating and abdominal pain to irritable bowel syndrome. It is essential, therefore, to be aware of the foods that are low in fibre and to make a conscious effort to incorporate more fibre-rich foods into our diets. By doing so, we can take a significant step towards maintaining a healthy digestive system and reducing our risk of chronic disease.
The benefits of a high fibre diet are numerous, and it is clear that fibre plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and wellbeing. From promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation to supporting healthy blood sugar levels and even aiding in weight management, the importance of fibre cannot be overstated. With this in mind, it is essential to be aware of the foods that are low in fibre and to make informed choices about the foods we eat. By understanding which foods are low in fibre, we can take the first step towards creating a balanced and nutritious diet that supports our overall health and wellbeing.
What are Low Fibre Foods?
Low fibre foods are those that contain less than 2 grams of fibre per serving. These foods are often highly processed and refined, making them lacking in essential nutrients, including fibre. Examples of low fibre foods include white bread, sugary snacks, and processed meats. These foods are not only low in fibre but also tend to be high in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats, making them a detrimental part of a healthy diet.
Types of Low Fibre Foods
Low fibre foods can be categorized into several groups, including grains, proteins, and snacks. Refined grains, such as white bread and pasta, are examples of low fibre foods, as they have been stripped of their fibre and nutrient-rich bran and germ during processing. Processed meats, such as hot dogs and sausages, are also low in fibre, as they are made from meat that has been ground and processed, removing any fibre that may have been present.Grains that are Low in Fibre
Grains that are low in fibre include:
- White bread
- White rice
- Pasta
- Cereals
- Crackers These grains have been refined and processed, removing the fibre and nutrient-rich bran and germ. As a result, they are low in fibre and other essential nutrients, making them a less than ideal choice for a healthy diet.
Proteins that are Low in Fibre
Proteins that are low in fibre include: * Processed meats, such as hot dogs and sausages * Bacon * Sausages * Ham * Chicken nuggets These proteins are often highly processed and contain added preservatives and ingredients that are low in fibre. While they may be convenient and tasty, they are not the best choice for a healthy diet.Snacks that are Low in Fibre
Snacks that are low in fibre include:
- Chips
- Cookies
- Cakes
- Pastries
- Sugary snacks, such as candy and chocolate These snacks are often highly processed and contain added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats. They are low in fibre and other essential nutrients, making them a less than ideal choice for a healthy diet.
Dairy Products that are Low in Fibre
Dairy products that are low in fibre include: * Milk * Cheese * Yogurt * Ice cream These dairy products are naturally low in fibre, as they are derived from animal milk. However, they can still be part of a healthy diet, as they provide essential nutrients, such as calcium and protein.How to Increase Fibre Intake

Increasing fibre intake can be achieved by making a few simple changes to our diet. Here are some tips to help boost fibre intake:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables, such as apples, bananas, and broccoli
- Incorporate whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, into our diet
- Add legumes, such as beans, lentils, and peas, to our meals
- Snack on nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds
- Drink plenty of water to help fibre move through our digestive system
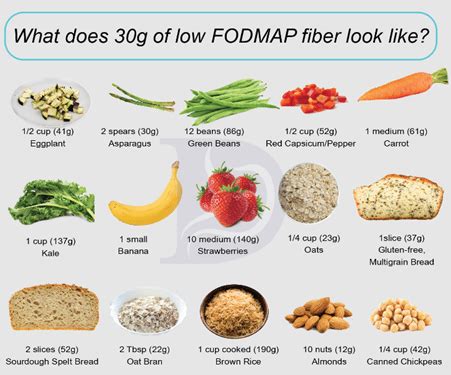
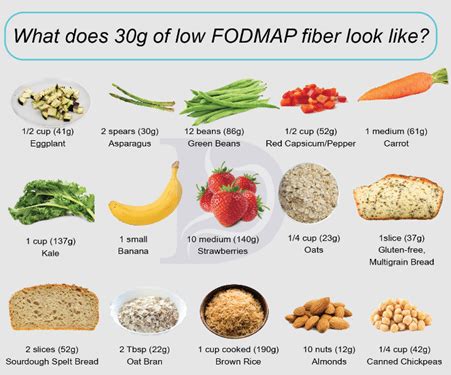
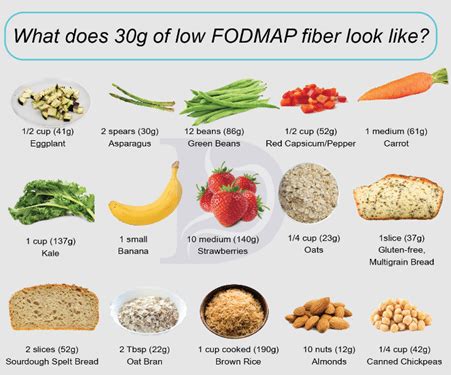
Fibre-Rich Foods
Fibre-rich foods include: * Fruits, such as apples, bananas, and berries * Vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and sweet potatoes * Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread * Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and peas * Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds These foods are not only high in fibre but also provide essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.Benefits of a High Fibre Diet

A high fibre diet has numerous benefits, including:
- Promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation
- Supporting healthy blood sugar levels
- Aiding in weight management
- Reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes
- Supporting healthy gut bacteria
How Much Fibre Do We Need?
The daily recommended intake of fibre varies based on age and sex. Generally, adults need 25-30 grams of fibre per day. However, most of us are not getting enough fibre in our diets, with the average person consuming less than 15 grams per day.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, a low fibre diet can have serious consequences for our health, from constipation and digestive issues to an increased risk of chronic diseases. By understanding which foods are low in fibre and making informed choices about the foods we eat, we can take a significant step towards maintaining a healthy digestive system and reducing our risk of chronic disease. To increase fibre intake, we can eat more fruits and vegetables, incorporate whole grains into our diet, and add legumes and nuts and seeds to our meals. By making these simple changes, we can boost our fibre intake and support our overall health and wellbeing.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with low fibre foods and how you have incorporated more fibre-rich foods into your diet. Please comment below and share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can create a community that prioritizes healthy eating and supports overall wellbeing.
What are the benefits of a high fibre diet?
+A high fibre diet has numerous benefits, including promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation, supporting healthy blood sugar levels, aiding in weight management, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and supporting healthy gut bacteria.
How much fibre do we need per day?
+The daily recommended intake of fibre varies based on age and sex, but generally, adults need 25-30 grams of fibre per day.
What are some examples of low fibre foods?
+Examples of low fibre foods include white bread, sugary snacks, processed meats, and refined grains, such as white rice and pasta.
How can I increase my fibre intake?
+To increase fibre intake, eat more fruits and vegetables, incorporate whole grains into your diet, add legumes and nuts and seeds to your meals, and drink plenty of water to help fibre move through your digestive system.
What are some high fibre foods that I can add to my diet?
+High fibre foods include fruits, such as apples and bananas, vegetables, such as broccoli and carrots, whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, legumes, such as beans and lentils, and nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds.
