Intro
Discover the ultimate Low Glucose Blood Test Guide, covering hypoglycemia symptoms, diagnosis, and management, with expert tips on glucose monitoring, blood sugar levels, and healthy lifestyle changes to prevent low blood glucose episodes.
Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is crucial for overall well-being, and a low glucose blood test is an essential tool for diagnosing and managing conditions related to blood sugar. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When glucose levels in the blood drop below normal, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Understanding the importance of glucose in the body and the implications of low blood glucose levels can empower individuals to take control of their health.
The human body is designed to maintain blood glucose levels within a narrow range, typically between 70 and 110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting. This balance is achieved through the coordinated effort of the pancreas, liver, and other organs. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, and glucagon, which stimulates the release of glucose stored in the liver. When this delicate balance is disrupted, either due to medical conditions, dietary factors, or other reasons, blood glucose levels can become too low, a condition known as hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia can manifest in various ways, depending on its severity and the individual's overall health. Mild cases might cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, and irritability. If left untreated, hypoglycemia can progress to more severe stages, leading to confusion, difficulty speaking, loss of consciousness, and even seizures or death in extreme cases. Given the potential risks, recognizing the signs of low blood glucose and understanding how to manage them is vital for individuals at risk, including those with diabetes, certain metabolic disorders, or those taking medications that can affect blood sugar levels.
Understanding Low Glucose Blood Tests
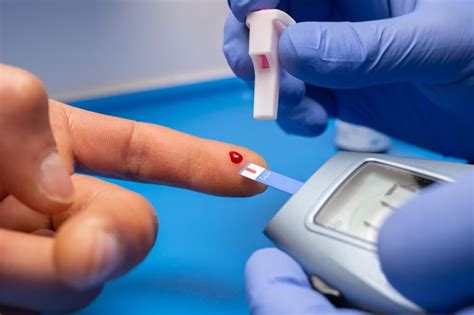
Low glucose blood tests are designed to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood. These tests can be performed at various times, including after an overnight fast, after meals, or at random. The fasting plasma glucose test, which measures glucose levels after at least 8 hours of fasting, is commonly used to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes. For individuals experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia, a blood glucose test can confirm whether their symptoms are due to low blood sugar. Understanding the results of these tests is crucial; a level below 70 mg/dL is generally considered low, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and specific testing methods.
Preparation for Low Glucose Blood Tests
Preparing for a blood glucose test typically involves fasting for a specified period, usually overnight, to ensure that the test results reflect the body's baseline glucose level. It's also important to follow any specific instructions provided by a healthcare provider, which might include avoiding certain foods or drinks that could affect glucose levels. For random or postprandial (after meal) glucose tests, individuals may be asked to consume a standardized meal or glucose solution to assess how their body responds to glucose ingestion.Causes of Low Blood Glucose

Low blood glucose can result from various factors, including medical treatments, certain medications, skipped meals, excessive alcohol consumption, and critical illnesses. Individuals with diabetes are particularly at risk due to the medications they take, such as insulin and sulfonylureas, which can cause the body to produce more insulin than it needs, leading to hypoglycemia. Other health conditions, like hypopituitarism, hypothyroidism, and certain tumors, can also increase the risk of developing hypoglycemia.
Treating and Managing Low Blood Glucose
Treating low blood glucose involves promptly raising blood glucose levels to normal. The American Diabetes Association recommends the "15-15 rule" as a guideline for treatment: consuming 15 grams of glucose or glucose-containing foods and drinks (such as glucose tablets, juice, or candy) and checking blood glucose levels after 15 minutes. If levels are still low, the process should be repeated. For more severe cases where the individual is unconscious or unable to consume glucose by mouth, glucagon injections or intravenous glucose administered by medical professionals may be necessary.Preventing Low Blood Glucose
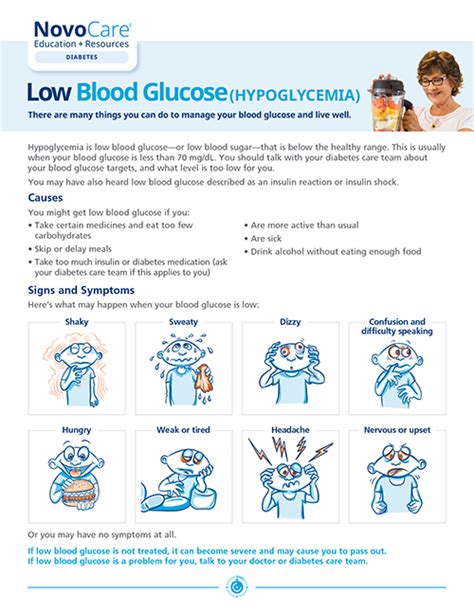
Preventing hypoglycemia is crucial for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adjusting medication doses as prescribed by a healthcare provider, eating regular meals, and being mindful of the carbohydrate content in meals can help prevent episodes of low blood glucose. Additionally, being aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and knowing how to treat it promptly can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Low Blood Glucose
Making informed lifestyle choices can play a significant role in managing and preventing low blood glucose. This includes maintaining a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Regular physical activity, such as walking or other forms of exercise, can also help improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. Furthermore, managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help regulate blood glucose levels.Technological Advances in Managing Low Blood Glucose

Recent technological advancements have transformed the management of low blood glucose, offering individuals more convenience, accuracy, and peace of mind. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, for example, provide real-time glucose level readings throughout the day and night, allowing for prompt identification of trends and patterns that could lead to hypoglycemia. Smart insulin pens and pumps can also help track insulin doses and calculate future doses based on current glucose levels, reducing the risk of over-insulinization.
Future Directions in Low Glucose Management
The future of managing low blood glucose looks promising, with ongoing research into new technologies and treatments. Closed-loop systems, also known as artificial pancreas systems, which automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, are being developed and tested. Additionally, non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies, such as wearable devices that use optical or electrical signals to estimate glucose levels, are under development, aiming to make glucose monitoring easier and less painful.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, managing low blood glucose is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly for those with diabetes or at risk of hypoglycemia. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for low blood glucose, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent episodes and manage their condition effectively. Staying informed about the latest advancements in glucose monitoring and management technologies can also empower individuals to make better decisions about their health.
What are the symptoms of low blood glucose?
+Symptoms of low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) can include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, difficulty speaking, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness or seizures.
How is low blood glucose treated?
+Treatment for low blood glucose involves consuming glucose or glucose-containing foods and drinks to raise blood glucose levels. For severe cases, glucagon injections or intravenous glucose may be necessary.
Can low blood glucose be prevented?
+Yes, low blood glucose can often be prevented by monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, adjusting medication as needed, eating regular meals, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about managing low blood glucose in the comments below. Your insights can help others navigate their journey with hypoglycemia and contribute to a supportive community focused on health and wellness. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can promote awareness and understanding of low blood glucose and work towards better health outcomes for all.
