Intro
Hypothermia, or low human body temperature, is a serious medical condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Normal body temperature ranges from 97.7°F to 99.5°F (36.5°C to 37.5°C), and any temperature below 95°F (35°C) is considered hypothermic. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effects of low body temperature, as well as discuss ways to prevent and treat hypothermia.
The human body is designed to maintain a stable internal temperature, despite changes in external temperatures. However, certain conditions can disrupt this balance, leading to hypothermia. Some common causes of low body temperature include exposure to cold environments, such as cold water or air, inadequate clothing or shelter, and certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes. Additionally, certain medications, such as sedatives or antidepressants, can also increase the risk of hypothermia.
Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can cause the body to lose heat faster than it can produce it, leading to a drop in body temperature. This can occur in various situations, such as outdoor activities like hiking or skiing, or in cases of homelessness or inadequate housing. Furthermore, certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency, can affect the body's ability to regulate its temperature, making it more susceptible to hypothermia.
Causes of Low Body Temperature
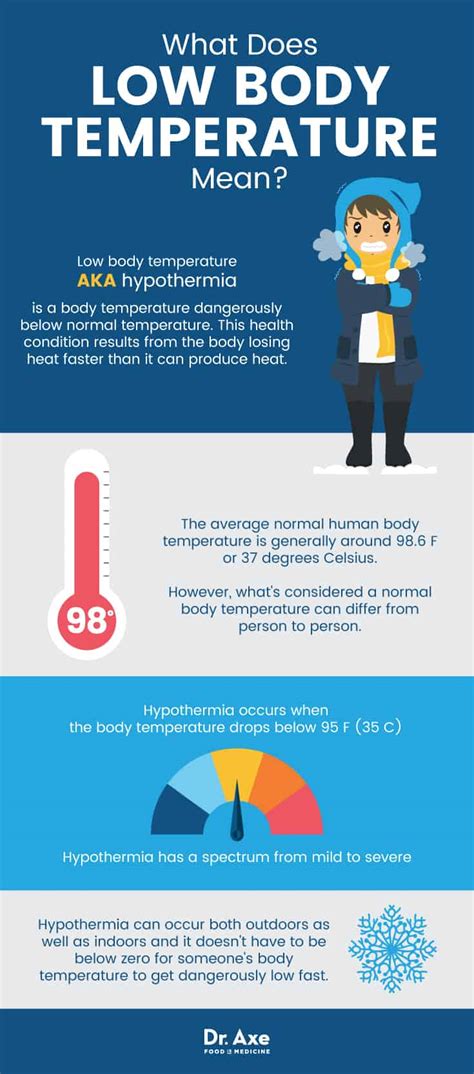
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are a significant contributor to hypothermia. Exposure to cold temperatures, either through outdoor activities or inadequate housing, can cause the body to lose heat rapidly. Additionally, high altitudes can also increase the risk of hypothermia, as the air pressure is lower, and the body may have difficulty adapting. Inadequate clothing or shelter can also contribute to hypothermia, as the body may not be able to maintain its internal temperature.Medical Factors
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of hypothermia. Hypothyroidism, for example, can affect the body's ability to regulate its temperature, making it more susceptible to hypothermia. Diabetes, particularly if left untreated, can also increase the risk of hypothermia, as high blood sugar levels can affect the body's ability to regulate its temperature. Adrenal insufficiency, a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones, can also increase the risk of hypothermia.Symptoms of Low Body Temperature

Mild Hypothermia
Mild hypothermia is characterized by a body temperature between 90°F and 95°F (32°C and 35°C). Symptoms of mild hypothermia include shivering, confusion, and drowsiness. Additionally, individuals with mild hypothermia may experience numbness or tingling in their extremities, as well as a lack of coordination.Severe Hypothermia
Severe hypothermia is characterized by a body temperature below 90°F (32°C). Symptoms of severe hypothermia include slurred speech, slow breathing, and unconsciousness. In severe cases, hypothermia can also cause cardiac arrest, which can be fatal if left untreated. Additionally, severe hypothermia can also cause frostbite, which can lead to permanent damage to the affected area.Effects of Low Body Temperature

Short-Term Effects
The short-term effects of low body temperature include confusion, drowsiness, and numbness or tingling in the extremities. In severe cases, hypothermia can also cause cardiac arrest, which can be fatal if left untreated. Additionally, hypothermia can also cause frostbite, which can lead to permanent damage to the affected area.Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of low body temperature can be severe and long-lasting. Hypothermia can cause damage to the brain, heart, and other organs, which can lead to permanent disability or even death. Additionally, hypothermia can also increase the risk of infections, such as pneumonia, which can be fatal if left untreated.Prevention and Treatment of Low Body Temperature

Prevention
Prevention is the best way to avoid hypothermia. Individuals can prevent hypothermia by dressing warmly in cold weather, staying dry, and avoiding prolonged exposure to cold temperatures. Additionally, individuals can also prevent hypothermia by staying hydrated, eating nutritious food, and getting regular exercise.Treatment
Treatment for hypothermia depends on the severity of the condition. Mild hypothermia can be treated with warm clothing, hot drinks, and warm baths. Severe hypothermia, on the other hand, requires immediate medical attention. Treatment for severe hypothermia includes cardiac monitoring, oxygen therapy, and rewarming techniques, such as warm baths or heating pads.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with hypothermia in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know ever experienced hypothermia? What were the symptoms, and how was it treated? Your input can help others understand the importance of preventing and treating low body temperature.
What is hypothermia?
+Hypothermia is a medical condition that occurs when the body's internal temperature drops below 95°F (35°C).
What are the symptoms of hypothermia?
+The symptoms of hypothermia include shivering, confusion, drowsiness, numbness or tingling in the extremities, and in severe cases, cardiac arrest.
How can I prevent hypothermia?
+You can prevent hypothermia by dressing warmly in cold weather, staying dry, avoiding prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, staying hydrated, eating nutritious food, and getting regular exercise.
