Intro
Discover 7 low purine foods to manage gout and kidney stones, including purine-free and low-purine diet options like lean meats, fish, and vegetables, to reduce uric acid levels and alleviate symptoms.
Eating a healthy and balanced diet is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. For individuals who suffer from gout or are at risk of developing kidney stones, it is crucial to pay attention to the amount of purines in their diet. Purines are naturally occurring substances found in many foods, and when they break down in the body, they can lead to the formation of uric acid. High levels of uric acid can cause a range of health problems, including gout, kidney stones, and kidney disease. Fortunately, there are many low-purine foods that can help individuals manage their purine intake and reduce their risk of developing these health issues.
A low-purine diet is not just beneficial for individuals with gout or kidney disease, but it can also be beneficial for anyone looking to improve their overall health and well-being. By incorporating low-purine foods into their diet, individuals can help reduce their risk of developing a range of health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. In addition, a low-purine diet can also help individuals maintain a healthy weight, improve their energy levels, and enhance their mental clarity and focus.
Incorporating low-purine foods into your diet can be easy and delicious. There are many tasty and nutritious foods that are naturally low in purines, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. By focusing on these foods and limiting your intake of high-purine foods, you can help manage your purine intake and reduce your risk of developing health problems. In this article, we will explore 7 low-purine foods that you can incorporate into your diet to improve your health and well-being.
Introduction to Low-Purine Foods
Benefits of a Low-Purine Diet
A low-purine diet can have numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of gout, kidney stones, and kidney disease. By limiting your intake of high-purine foods, you can help reduce the amount of uric acid in your body and lower your risk of developing these health problems. Additionally, a low-purine diet can also help you maintain a healthy weight, improve your energy levels, and enhance your mental clarity and focus.7 Low-Purine Foods to Include in Your Diet
Low-Purine Food Options
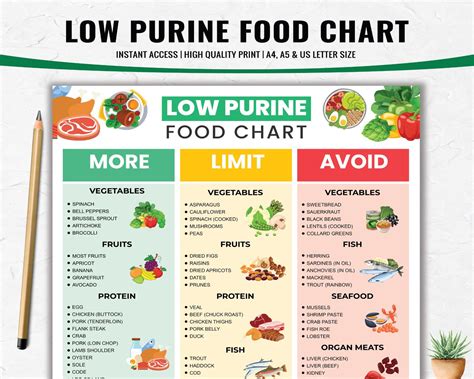
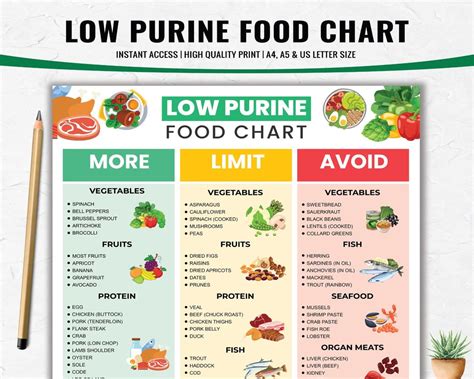
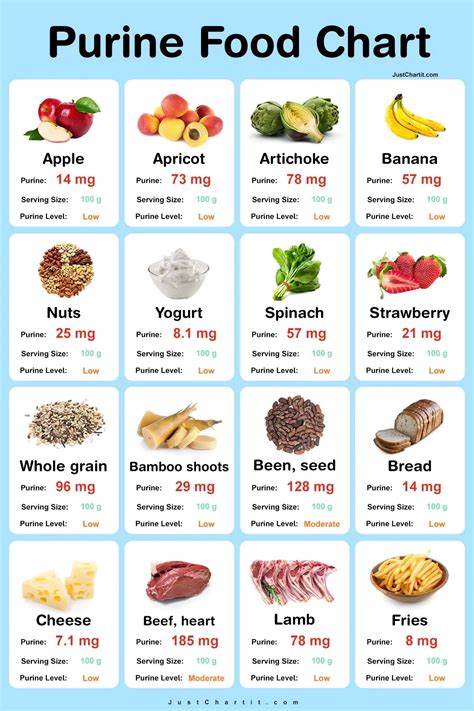
Here are some specific low-purine food options that you can include in your diet: * Fresh fruit: apples, bananas, berries, citrus fruits, and stone fruits * Vegetables: leafy greens, broccoli, bell peppers, carrots, and cucumbers * Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, whole-grain pasta, and oats * Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes * Low-fat dairy products: milk, cheese, yogurt, and cottage cheese * Healthy fats: olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds * Herbs and spices: turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and basilHigh-Purine Foods to Avoid
Avoiding High-Purine Foods
To manage your purine intake and reduce your risk of developing health problems, it is essential to avoid high-purine foods as much as possible. Here are some tips for avoiding high-purine foods: * Read food labels carefully and choose products that are low in purines * Limit your intake of red meat and organ meats * Avoid processed meats and foods high in sugar and salt * Choose low-purine alternatives to high-purine foods, such as chicken or fish instead of beef or porkManaging Purine Intake

Purine Intake and Health
Purine intake can have a significant impact on your health, particularly if you are at risk of developing gout, kidney stones, or kidney disease. By managing your purine intake and limiting your consumption of high-purine foods, you can help reduce your risk of developing these health problems. Additionally, a low-purine diet can also help you maintain a healthy weight, improve your energy levels, and enhance your mental clarity and focus.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are purines and why are they important?
+Purines are naturally occurring substances found in many foods. They can increase uric acid levels in the body, which can lead to health problems such as gout, kidney stones, and kidney disease.
What are some examples of low-purine foods?
+Some examples of low-purine foods include fresh fruits, leafy green vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
How can I manage my purine intake?
+To manage your purine intake, keep a food diary, limit your intake of high-purine foods, choose low-purine alternatives, stay hydrated, and consider taking supplements.
We hope this article has provided you with helpful information on low-purine foods and how to manage your purine intake. Remember to always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet. By incorporating low-purine foods into your diet and managing your purine intake, you can help reduce your risk of developing health problems and improve your overall health and well-being. If you have any further questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help them learn more about the importance of low-purine foods and how to incorporate them into their diet.
