Intro
Discover how a low reticulocyte count impacts your health, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, affecting red blood cell production, and increasing anemia risk, requiring medical attention and treatment to restore normal blood cell counts.
A low reticulocyte count can have significant effects on the body, impacting overall health and well-being. Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow and released into the bloodstream, where they mature into adult red blood cells. These cells play a crucial role in carrying oxygen throughout the body. When the reticulocyte count is low, it can indicate a problem with the production of red blood cells, which can lead to a range of health issues.
The importance of understanding the impact of a low reticulocyte count cannot be overstated. It is a critical component of diagnosing and treating various blood disorders, such as anemia. A low reticulocyte count can be a sign of a underlying condition that needs to be addressed, and ignoring it can lead to more severe health problems. In this article, we will delve into the ways a low reticulocyte count can affect the body and discuss the potential causes and treatments.
A low reticulocyte count can be caused by a variety of factors, including bone marrow disorders, vitamin deficiencies, and chronic diseases. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of the low reticulocyte count to develop an effective treatment plan. With the right diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to manage the condition and prevent further complications. In the following sections, we will explore the effects of a low reticulocyte count in more detail and discuss the ways to address this issue.
Introduction to Reticulocyte Count
Causes of Low Reticulocyte Count
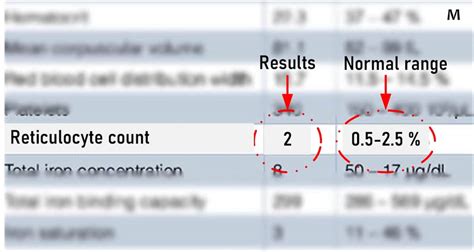
Effects of Low Reticulocyte Count on the Body

Treatment Options for Low Reticulocyte Count

Prevention and Management of Low Reticulocyte Count
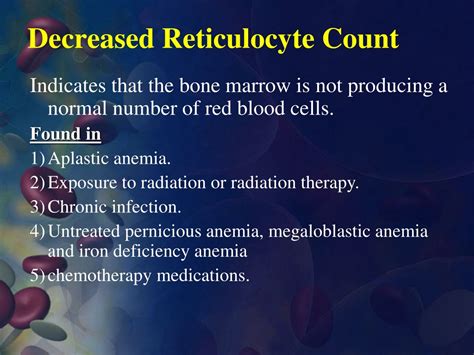
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of a low reticulocyte count is crucial for preventing further complications. Regular blood tests can help to detect this condition early, allowing for prompt treatment and management. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan and to manage the condition effectively.Risk Factors for Low Reticulocyte Count
There are several risk factors for a low reticulocyte count, including: * Age: Older adults are more likely to develop a low reticulocyte count. * Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or HIV/AIDS, can increase the risk of developing a low reticulocyte count. * Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy and certain antibiotics, can increase the risk of developing a low reticulocyte count. * Nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients, such as iron and vitamin B12, can increase the risk of developing a low reticulocyte count.What is a normal reticulocyte count?
+A normal reticulocyte count varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but it is typically between 0.5% and 1.5% of the total red blood cell count.
What are the symptoms of a low reticulocyte count?
+The symptoms of a low reticulocyte count include anemia, fatigue, pale skin, headaches, and poor wound healing.
How is a low reticulocyte count treated?
+The treatment for a low reticulocyte count depends on the underlying cause, but may include vitamin supplements, medications, blood transfusions, and bone marrow transplantation.
Can a low reticulocyte count be prevented?
+Yes, a low reticulocyte count can be prevented by eating a healthy diet, avoiding certain medications, managing underlying conditions, and getting regular blood tests.
What are the risk factors for a low reticulocyte count?
+The risk factors for a low reticulocyte count include age, underlying medical conditions, medications, and nutrition.
In conclusion, a low reticulocyte count can have significant effects on the body, and it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition. By working with a healthcare professional and following a treatment plan, it is possible to manage a low reticulocyte count and prevent further complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about low reticulocyte count and its effects on the body.
