Intro
Discover 7 low sodium symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and muscle cramps, and learn about hyponatremia causes, effects, and treatment options to manage sodium deficiency and related electrolyte imbalances.
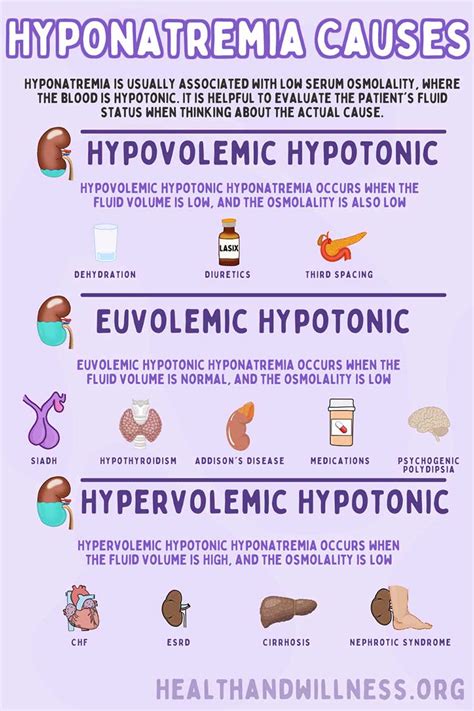
Low sodium levels in the blood, also known as hyponatremia, can cause a range of symptoms that vary in severity. It is essential to recognize these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. Sodium is a crucial electrolyte that helps regulate the amount of water in and around cells, and its imbalance can lead to serious health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of low sodium symptoms, exploring their causes, effects, and importance.
Sodium plays a vital role in maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. When sodium levels fall below 135 mmol/L, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may exhibit noticeable signs of hyponatremia. It is crucial to understand that low sodium symptoms can be subtle, making it challenging to diagnose the condition.
Low sodium levels can be caused by various factors, including excessive water intake, certain medications, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and kidney disease. In some cases, hyponatremia can be a side effect of a underlying medical condition, such as adrenal insufficiency or hypothyroidism. The symptoms of low sodium levels can be divided into two categories: mild and severe. Mild symptoms may include headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps, while severe symptoms can range from seizures and coma to respiratory arrest.
Introduction to Low Sodium Symptoms

Causes of Low Sodium Symptoms

Excessive Water Intake
Excessive water intake is a common cause of low sodium symptoms. When an individual drinks large amounts of water, it can dilute the sodium levels in the blood, leading to hyponatremia. This can occur in athletes, endurance runners, or people participating in activities that involve excessive sweating. In some cases, excessive water intake can be a result of a underlying medical condition, such as diabetes insipidus or primary polydipsia.Excessive Sodium Loss
Excessive sodium loss can also lead to low sodium levels. This can occur in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, or liver cirrhosis. In these conditions, the body loses excessive amounts of sodium, leading to hyponatremia. Other causes of excessive sodium loss include certain medications, such as diuretics, and hormonal imbalances, such as adrenal insufficiency.Symptoms of Low Sodium Levels
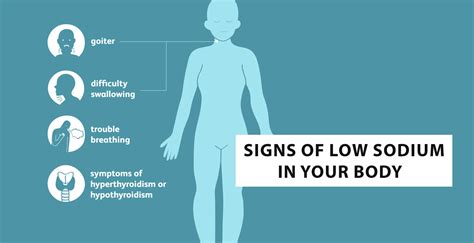
Severe symptoms can include:
- Seizures
- Coma
- Respiratory arrest
- Brain swelling
- Death
Mild Symptoms
Mild symptoms of low sodium levels can be subtle and may resemble those of other medical conditions. Headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps are common symptoms of hyponatremia. In some cases, individuals may experience nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration and further exacerbate the condition.Severe Symptoms
Severe symptoms of low sodium levels can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Seizures, coma, and respiratory arrest are potential complications of hyponatremia. In some cases, brain swelling can occur, leading to permanent brain damage or death.Treatment and Management of Low Sodium Symptoms
Fluid Restriction
Fluid restriction is a common treatment for mild low sodium symptoms. By limiting fluid intake, individuals can help reduce the amount of water in the body and increase sodium levels. In some cases, sodium supplements may be prescribed to help replenish sodium stores.Sodium Supplements
Sodium supplements can be prescribed to help replenish sodium stores. These supplements can be given orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage the underlying condition and prevent further complications.Prevention of Low Sodium Symptoms
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential to maintaining proper sodium levels. By consuming foods rich in sodium, such as table salt, soy sauce, and processed foods, individuals can help replenish sodium stores. However, it is crucial to consume these foods in moderation, as excessive sodium intake can lead to other health issues.Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated is essential to maintaining proper sodium levels. By drinking plenty of water, individuals can help regulate fluid balance and prevent dehydration. However, it is crucial to drink water in moderation, as excessive water intake can lead to hyponatremia.What are the common causes of low sodium symptoms?
+Low sodium symptoms can be caused by excessive water intake, excessive sodium loss, and inadequate sodium intake. Other causes include certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, and liver cirrhosis.
What are the symptoms of low sodium levels?
+The symptoms of low sodium levels can range from mild to severe and include headaches, fatigue, muscle cramps, nausea and vomiting, seizures, coma, and respiratory arrest.
How can low sodium symptoms be treated and managed?
+The treatment and management of low sodium symptoms depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild symptoms can be treated with fluid restriction and sodium supplements, while severe symptoms require hospitalization and aggressive treatment.
As we conclude our discussion on low sodium symptoms, it is essential to remember that prevention and timely treatment are crucial to managing this condition. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain proper sodium levels and reduce their risk of developing hyponatremia. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on low sodium symptoms and encourage you to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your sodium levels.
