Intro
Discover 5 accurate ways to test for Lyme disease, including ELISA, Western blot, and PCR tests, to diagnose and treat this tick-borne illness effectively, reducing misdiagnosis and promoting timely recovery from Lyme disease symptoms.
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. The disease can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash. If left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to more serious health problems, such as arthritis, neurological disorders, and heart problems. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, and there are several ways to test for Lyme disease.
The importance of testing for Lyme disease cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Moreover, Lyme disease can be challenging to diagnose, as its symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. Therefore, it is essential to understand the different testing methods available and their limitations. In this article, we will explore the various ways to test for Lyme disease, including their benefits and drawbacks.
Lyme disease testing is a complex process that involves several steps. The first step is to determine whether the patient has been exposed to the bacteria that cause the disease. This is typically done through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. If the patient has a history of tick bites or has spent time outdoors in areas where Lyme disease is common, the doctor may order a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests can include blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies.
Introduction to Lyme Disease Testing
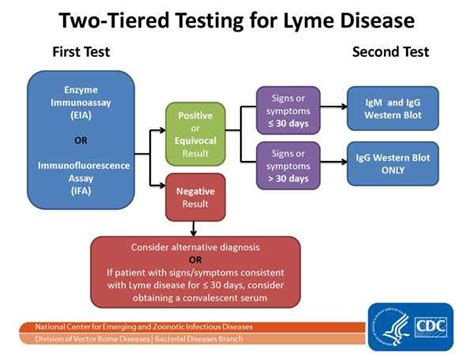
Types of Lyme Disease Tests

ELISA Test
The ELISA test is a commonly used screening test for Lyme disease. It detects the presence of antibodies against the bacteria that cause the disease. The test is relatively simple and inexpensive, but it can produce false-positive results. Therefore, a confirmatory test is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.Western Blot Test
The Western blot test is a confirmatory test used to diagnose Lyme disease. It detects the presence of specific antibodies against the bacteria that cause the disease. The test is more specific than the ELISA test and can confirm the diagnosis.Lyme Disease Testing Methods
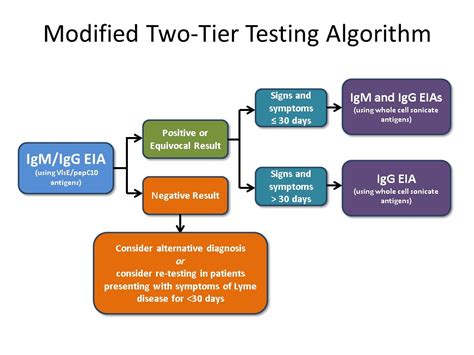
Blood Tests
Blood tests are the most common method used to diagnose Lyme disease. They detect the presence of antibodies against the bacteria that cause the disease. The tests can be performed at any stage of the disease, but they are most accurate during the later stages.Urine Tests
Urine tests are used to detect the presence of antibodies against the bacteria that cause the disease. The tests are less common than blood tests but can be used to diagnose the disease in people who have not responded to treatment.Benefits and Drawbacks of Lyme Disease Testing
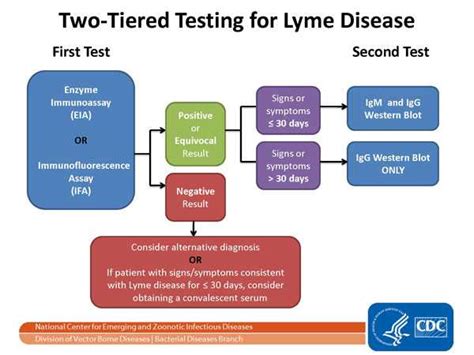
The drawbacks of Lyme disease testing include:
- False-positive results: False-positive results can occur, especially with the ELISA test.
- False-negative results: False-negative results can occur, especially during the early stages of the disease.
- Cost: Lyme disease testing can be expensive, especially if multiple tests are required.
Interpreting Lyme Disease Test Results
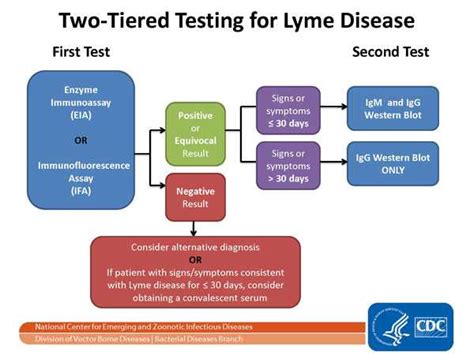
Positive Test Results
A positive test result indicates that the patient has been exposed to the bacteria that cause the disease. The patient may require treatment, even if they do not have any symptoms.Negative Test Results
A negative test result indicates that the patient has not been exposed to the bacteria that cause the disease. However, it is essential to note that false-negative results can occur, especially during the early stages of the disease.Conclusion and Future Directions

Lyme disease testing is a complex process that requires a comprehensive approach. By understanding the different testing methods available and their limitations, healthcare professionals can provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment. Patients who have been diagnosed with Lyme disease should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their condition and adjust their treatment plan as necessary.
What is the most common method used to diagnose Lyme disease?
+The most common method used to diagnose Lyme disease is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test, followed by a Western blot test to confirm the diagnosis.
Can Lyme disease be diagnosed through a urine test?
+Yes, Lyme disease can be diagnosed through a urine test, although this method is less common than blood tests.
How long does it take to get the results of a Lyme disease test?
+The time it takes to get the results of a Lyme disease test can vary depending on the type of test and the laboratory. Typically, results are available within a few days to a week.
Can Lyme disease be diagnosed through imaging studies?
+Yes, imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRI scans, can be used to detect any damage to the joints or other organs caused by Lyme disease.
How accurate are Lyme disease tests?
+Lyme disease tests can be accurate, but they are not 100% reliable. False-positive and false-negative results can occur, especially during the early stages of the disease.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Lyme disease testing. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about Lyme disease testing. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote early detection and treatment of this complex disease.
