Intro
Discover 5 ways melanoma spots form, including skin cancer signs, mole changes, and UV damage, to catch early warning signs of melanoma symptoms and prevent skin malignancies.
Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the most common ways to detect melanoma is by identifying unusual spots or moles on the skin. But have you ever wondered how these melanoma spots form in the first place? Understanding the formation of melanoma spots is crucial for early detection and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of melanoma, exploring the different ways these spots can form and what you can do to protect yourself.
The formation of melanoma spots is a complex process that involves the uncontrolled growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled manner. However, when the skin is exposed to too much ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it can cause the skin cells to become damaged. This damage can lead to mutations in the skin cells' DNA, which can cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably. Over time, these abnormal cells can accumulate and form a tumor, which can eventually become a melanoma spot.
The importance of understanding how melanoma spots form cannot be overstated. By recognizing the risk factors and taking steps to prevent skin damage, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing melanoma. Additionally, being able to identify the early signs of melanoma can help you seek medical attention promptly, which is critical for effective treatment. In the following sections, we will explore the different ways melanoma spots can form, including the role of UV radiation, genetic mutations, and other factors.
Introduction to Melanoma
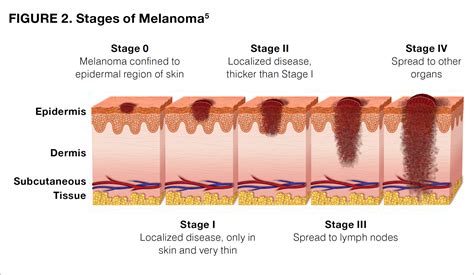
UV Radiation and Melanoma
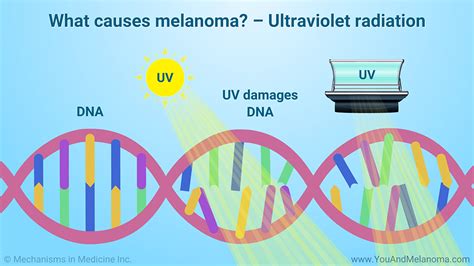
Types of UV Radiation
There are two types of UV radiation: UVA and UVB. UVA radiation penetrates deep into the skin, causing damage to the skin cells' DNA and contributing to the formation of melanoma. UVB radiation, on the other hand, is primarily responsible for causing sunburn. Both types of UV radiation can increase the risk of developing melanoma, and it is essential to protect yourself from both.Genetic Mutations and Melanoma
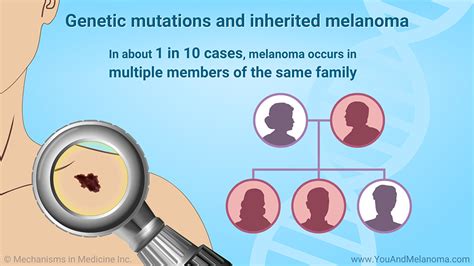
BRCA2 Gene Mutation
The BRCA2 gene mutation is a genetic mutation that can increase the risk of developing melanoma. This mutation is typically associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, but it can also increase the risk of developing melanoma. Individuals with a BRCA2 gene mutation should take extra precautions to protect their skin from UV radiation and undergo regular skin checks to detect any unusual moles or spots.Other Risk Factors for Melanoma

Reducing the Risk of Melanoma
While some risk factors, such as genetic mutations, cannot be changed, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing melanoma. These include: * Protecting your skin from UV radiation by wearing sunscreen, clothing, and seeking shade * Avoiding tanning beds and artificial sources of UV radiation * Getting regular skin checks to detect any unusual moles or spots * Avoiding smoking and other substances that can weaken the immune systemEarly Detection and Treatment of Melanoma
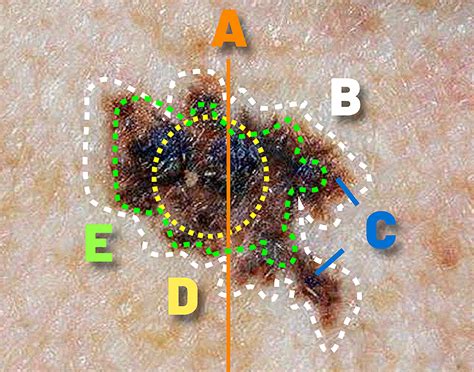
ABCDE Rule
The ABCDE rule is a helpful guide for identifying potential melanoma spots. The rule stands for: * A: Asymmetry - If the mole or spot is not symmetrical, it could be a sign of melanoma. * B: Border - If the mole or spot has an irregular border, it could be a sign of melanoma. * C: Color - If the mole or spot has multiple colors or an unusual color, it could be a sign of melanoma. * D: Diameter - If the mole or spot is larger than 6mm in diameter, it could be a sign of melanoma. * E: Evolving - If the mole or spot is changing in size, shape, or color, it could be a sign of melanoma.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with melanoma in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been affected by melanoma? What steps have you taken to reduce your risk of developing the disease? By sharing your story, you can help raise awareness and support for melanoma research and treatment.
What are the symptoms of melanoma?
+The symptoms of melanoma can vary, but common signs include unusual moles or spots on the skin, changes in the size or shape of a mole, and bleeding or itching of a mole.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
+Melanoma is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, biopsy, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans.
What are the treatment options for melanoma?
+The treatment options for melanoma depend on the stage and severity of the disease, but common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.
Can melanoma be prevented?
+While some risk factors for melanoma cannot be changed, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as protecting your skin from UV radiation, avoiding tanning beds, and getting regular skin checks.
What is the prognosis for melanoma?
+The prognosis for melanoma depends on the stage and severity of the disease, but early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and survival.
