Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Metformin Hydrochloride, a diabetes medication, including its benefits, side effects, and interactions, to better manage type 2 diabetes and improve overall health outcomes with this oral antidiabetic drug.
Metformin hydrochloride is a widely prescribed oral antidiabetic drug in the biguanide class that is primarily used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. One of the key aspects of metformin hydrochloride is its ability to decrease glucose production by the liver, increase insulin sensitivity, and thereby lower blood sugar levels. The importance of understanding metformin hydrochloride lies in its efficacy, safety profile, and the significant role it plays in managing a disease that affects millions of people worldwide. As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to rise, the significance of metformin hydrochloride as a first-line treatment option becomes increasingly evident. Moreover, its potential benefits extend beyond glycemic control, with research indicating possible effects on cardiovascular outcomes and weight management.
The mechanism of action of metformin hydrochloride involves the inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory-chain complex 1, which results in a decrease in hepatic glucose production. This action, combined with its effects on improving insulin sensitivity, makes metformin hydrochloride an effective agent in lowering blood glucose levels without causing significant hypoglycemia, a common side effect of other diabetes treatments. Furthermore, metformin hydrochloride has been observed to have a favorable effect on lipid metabolism, which contributes to its potential in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in diabetic patients. As research continues to uncover the full spectrum of metformin hydrochloride's effects, its position as a cornerstone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes is reinforced.
Given the extensive use and the critical role of metformin hydrochloride in diabetes management, it is essential to delve into the specifics of its pharmacology, clinical applications, and patient considerations. This includes understanding its pharmacokinetics, potential side effects, and drug interactions, as well as its use in special populations such as pregnant women and individuals with renal impairment. The drug's efficacy and safety profile make it not only an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes but also a subject of interest for researchers exploring its potential in other therapeutic areas. As the medical community continues to seek innovative and effective treatments for metabolic disorders, the study of metformin hydrochloride and its applications remains a vital area of research.
Introduction to Metformin Hydrochloride

Pharmacological Mechanism
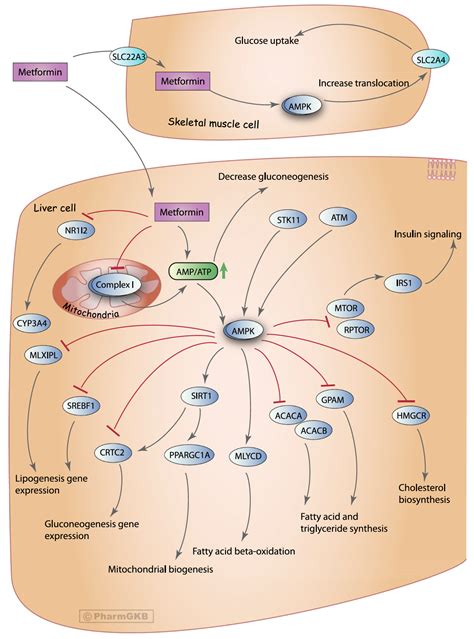
The pharmacological mechanism of metformin hydrochloride is multifaceted, involving several key pathways that ultimately lead to reduced hepatic glucose production and enhanced insulin action. At the molecular level, metformin hydrochloride inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory-chain complex 1, an action that decreases ATP production and increases AMP levels, leading to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). The activation of AMPK plays a central role in metformin's effects, influencing various downstream targets that are involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. This intricate mechanism of action underscores the drug's ability to improve glycemic control without promoting significant weight gain or hypoglycemia, characteristics that are highly desirable in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Benefits of Metformin Hydrochloride
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While metformin hydrochloride is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal bloating. More severe but rare side effects include lactic acidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of lactate in the body, which can be life-threatening if not promptly treated. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Additionally, metformin hydrochloride is contraindicated in certain conditions, such as renal impairment, where the risk of lactic acidosis is increased.Clinical Applications and Guidelines

Dosage and Administration
The dosage of metformin hydrochloride should be individualized based on the patient's response and tolerance. Typically, treatment is initiated with a low dose, which is gradually increased until adequate glycemic control is achieved or the maximum dose is reached. The drug is available in immediate-release and extended-release formulations, allowing for flexibility in dosing regimens. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.Future Perspectives and Research Directions
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, metformin hydrochloride remains a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes, offering a safe and effective means of achieving glycemic control. Its benefits extend beyond blood glucose management, with potential impacts on weight, lipid profiles, and cardiovascular risk. As the medical community continues to explore the full potential of metformin hydrochloride, it is clear that this drug will remain a vital component of diabetes treatment for the foreseeable future. Patients and healthcare providers alike should be aware of its indications, benefits, and potential side effects to ensure its optimal use.What is metformin hydrochloride used for?
+Metformin hydrochloride is primarily used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, helping to lower blood glucose levels and mitigate the risk of diabetes-related complications.
How does metformin hydrochloride work?
+Metformin hydrochloride works by inhibiting hepatic glucose production, increasing insulin sensitivity, and thereby lowering blood sugar levels without causing significant hypoglycemia.
What are the common side effects of metformin hydrochloride?
+Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal bloating. Rare but serious side effects include lactic acidosis.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about metformin hydrochloride in the comments below. Your insights and inquiries can help foster a more comprehensive understanding of this critical medication and its role in managing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information provided, contributing to a broader awareness of the importance of metformin hydrochloride in modern diabetes care.
