Intro
Discover Metoprolol uses and benefits, a beta-blocker for hypertension, angina, and heart failure, offering cardiovascular protection and symptom relief.
Metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication that belongs to the class of beta-blockers. It has been used for decades to manage various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. The importance of metoprolol lies in its ability to reduce the workload on the heart, thereby decreasing the risk of heart-related complications. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of metoprolol, exploring its mechanisms, advantages, and potential side effects.
Metoprolol is a selective beta-1 blocker, which means it primarily targets the beta-1 receptors in the heart. By blocking these receptors, metoprolol reduces the effects of epinephrine, a hormone that increases heart rate and blood pressure. This results in a decrease in heart rate, blood pressure, and the heart's oxygen demand. The medication is available in various forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, as well as injectable solutions.
The uses of metoprolol are diverse and well-established. It is commonly prescribed to manage high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. By reducing blood pressure, metoprolol decreases the strain on the heart, arteries, and kidneys, thereby lowering the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage. Additionally, metoprolol is used to treat angina, a condition characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart. The medication helps to increase blood flow to the heart, reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks.
How Metoprolol Works

Benefits of Metoprolol
The benefits of metoprolol are numerous and well-documented. Some of the advantages of using metoprolol include: * Reduced blood pressure: Metoprolol is effective in lowering blood pressure, which reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease. * Decreased heart rate: The medication slows down the heart rate, reducing the heart's oxygen demand and decreasing the risk of heart-related complications. * Increased blood flow: Metoprolol increases blood flow to the heart, reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks. * Improved survival: The medication has been shown to improve survival rates in patients with heart failure and after a heart attack.Uses of Metoprolol

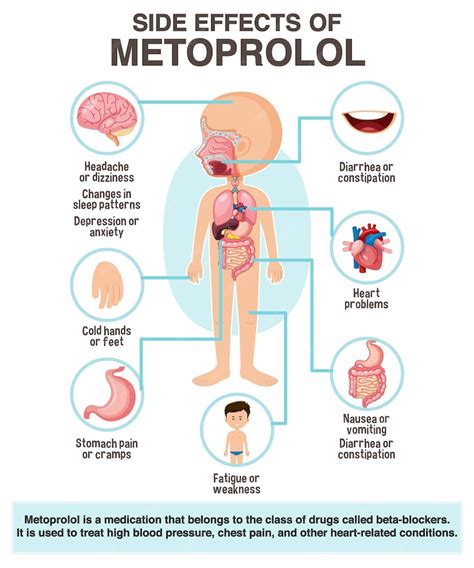
Side Effects of Metoprolol
While metoprolol is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Some of the common side effects of metoprolol include: * Fatigue: Metoprolol can cause fatigue, which can be a problem for individuals who need to be active. * Dizziness: The medication can cause dizziness, which can increase the risk of falls. * Shortness of breath: Metoprolol can cause shortness of breath, which can be a problem for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. * Nausea: The medication can cause nausea, which can be a problem for individuals who are prone to vomiting.Precautions and Interactions
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of metoprolol vary depending on the individual and the condition being treated. Some of the common dosages and administration routes of metoprolol include: * Immediate-release tablets: The usual dosage of metoprolol is 50-100 mg twice daily. * Extended-release tablets: The usual dosage of metoprolol is 50-200 mg once daily. * Injectable solutions: The usual dosage of metoprolol is 1-5 mg per minute, administered intravenously.Conclusion and Recommendations
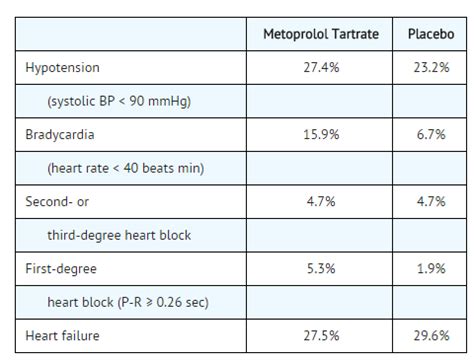
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metoprolol in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to manage various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
What are the benefits of metoprolol?
+The benefits of metoprolol include reduced blood pressure, decreased heart rate, increased blood flow, and improved survival rates.
What are the side effects of metoprolol?
+The common side effects of metoprolol include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and nausea.
Can I take metoprolol with other medications?
+Metoprolol can interact with other medications, such as calcium channel blockers, digoxin, and clonidine. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking metoprolol with other medications.
Can I take metoprolol during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Metoprolol should be used with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, as it can pass into the fetus or baby. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking metoprolol during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
