Intro
Discover Metronidazoles side effects, interactions, and warnings. Learn about antibiotic resistance, dosage, and treatment for infections, including GI and vaginal issues, to minimize adverse reactions and ensure safe usage.
Metronidazole is a widely used antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that has been prescribed to millions of people around the world. It is effective against a variety of infections, including bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infections caused by susceptible organisms such as Giardia and Trichomonas. However, like all medications, metronidazole can cause side effects, some of which can be severe. In this article, we will explore the importance of understanding metronidazole and its side effects, and why it is crucial for patients to be aware of the potential risks associated with this medication.
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic that works by killing bacteria and other microorganisms that are sensitive to it. It is commonly prescribed for infections such as bacterial vaginosis, which is a common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. Bacterial vaginosis is caused by an imbalance of the natural bacteria in the vagina, and metronidazole is often used to treat this condition. However, metronidazole can also be used to treat other infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, which is a serious condition that can cause infertility and other complications if left untreated.
The use of metronidazole has been associated with a range of side effects, some of which can be mild and temporary, while others can be severe and long-lasting. Common side effects of metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days of stopping the medication. However, some patients may experience more severe side effects, such as seizures, allergic reactions, and blood disorders. It is essential for patients to be aware of the potential risks associated with metronidazole and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any severe side effects.
How Metronidazole Works
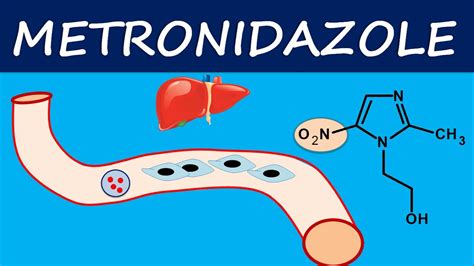
Benefits of Metronidazole
The benefits of metronidazole include its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms, its ability to penetrate deep into tissues and cells, and its relatively low cost compared to other antibiotics. Metronidazole is also available in a variety of formulations, including tablets, capsules, and creams, which makes it easy to use and administer. Additionally, metronidazole has been shown to be effective in treating infections that are resistant to other antibiotics, making it a valuable option for patients who have failed other treatments.Common Side Effects of Metronidazole
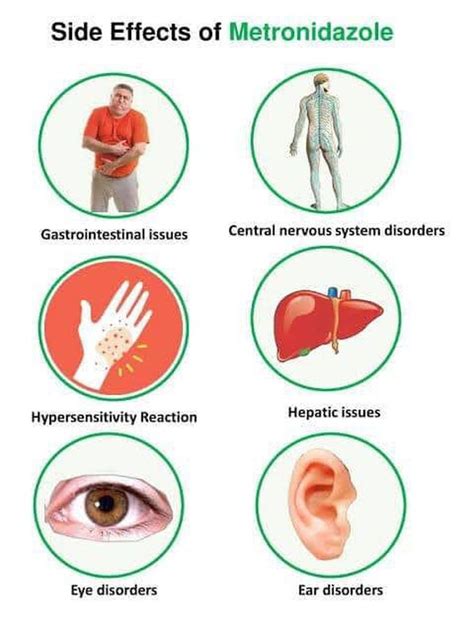
Severe Side Effects of Metronidazole
The severe side effects of metronidazole include: * Seizures and convulsions * Allergic reactions, such as hives and itching * Blood disorders, such as anemia and thrombocytopenia * Liver damage and elevated liver enzymes * Peripheral neuropathy and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet These side effects are rare but can be life-threatening. Patients who experience any of these side effects should seek medical attention immediately.Precautions and Warnings
Interactions with Other Medications
Metronidazole can interact with other medications, including: * Warfarin: Metronidazole can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin. * Phenytoin: Metronidazole can reduce the effectiveness of phenytoin and increase the risk of seizures. * Alcohol: Metronidazole can cause a disulfiram-like reaction when taken with alcohol, which can lead to nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Patients should inform their doctor of all medications they are taking before starting metronidazole.Dosage and Administration

Overdose and Toxicity
Metronidazole overdose can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, metronidazole overdose can cause seizures, coma, and death. Patients who suspect they have taken an overdose of metronidazole should seek medical attention immediately.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metronidazole in the comments section below. Have you taken metronidazole before? What were your experiences with this medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about metronidazole? We would be happy to hear from you and provide any additional information or support you may need.
What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat a range of infections, including bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infections caused by susceptible organisms such as Giardia and Trichomonas.
What are the common side effects of metronidazole?
+The common side effects of metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days of stopping the medication.
Can metronidazole interact with other medications?
+Yes, metronidazole can interact with other medications, including warfarin and phenytoin, and reduce their effectiveness. Patients should inform their doctor of all medications they are taking before starting metronidazole.
Can metronidazole cause birth defects?
+Yes, metronidazole can cause birth defects and should not be taken during pregnancy. Patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding should inform their doctor before taking metronidazole.
How long does metronidazole take to work?
+Metronidazole can start to work within a few days of treatment, but it may take several weeks to fully clear up an infection. Patients should complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
